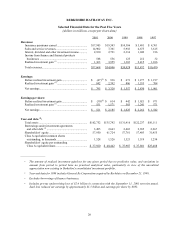
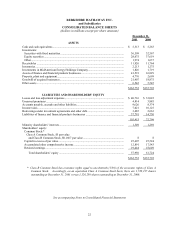
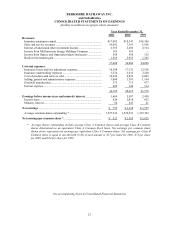
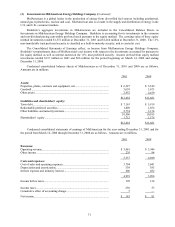
Berkshire Hathaway 2001 Annual Report Download - page 27
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 27 of the 2001 Berkshire Hathaway annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.26
BERKSHIRE HATHAWAY INC.
and Subsidiaries
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
December 31, 2001
(1) Significant accounting policies and practices
(a) Nature of operations and basis of consolidation
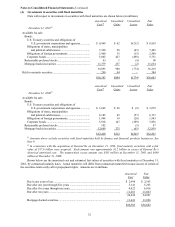
Berkshire Hathaway Inc. ("Berkshire" or "Company") is a holding company owning subsidiaries engaged in
a number of diverse business activities. The most important of these are property and casualty insurance
businesses conducted on both a direct and reinsurance basis. Further information regarding these
businesses and Berkshire's other reportable business segments is contained in Note 19. Berkshire
initiated and/or consummated several business acquisitions over the past three years. The significant
business acquisitions are described more fully in Note 2. The accompanying Consolidated Financial
Statements include the accounts of Berkshire consolidated with accounts of all its subsidiaries.
Intercompany accounts and transactions have been eliminated. Certain amounts in 2000 and 1999 have
been reclassified to conform with current year presentation.
Since acquired in December 1998 and through the third quarter of 2000, the international property/casualty
and global life/health reinsurance activities of General Re were reported in Berkshire’ s financial
statements based on a one-quarter lag to facilitate the timely completion of the Consolidated Financial
Statements. During the fourth quarter of 2000, General Re implemented a number of procedural changes
and improvements to allow reporting of these businesses without the one-quarter lag. Accordingly,
Berkshire’ s Consolidated Statements of Earnings and Cash Flows for the year ended December 31, 2000
include five quarters of results of operations and cash flows of these operations. The effect of eliminating
the one-quarter lag in reporting was not significant to Berkshire’ s Consolidated Statement of Earnings for
the year ending December 31, 2000.
(b) Use of estimates in preparation of financial statements
The preparation of the Consolidated Financial Statements in conformity with generally accepted accounting
principles ("GAAP") requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported
amount of assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements and the reported amount of
revenues and expenses during the period. In particular, estimates of unpaid losses and loss adjustment
expenses for property and casualty insurance are subject to considerable estimation error due to the
inherent uncertainty in projecting ultimate claim amounts that will be reported and settled over a period
of many years. Actual results may differ from the estimates and assumptions used in preparing the
Consolidated Financial Statements.
(c) Cash equivalents
Cash equivalents consist of funds invested in money market accounts and in investments with a maturity of
three months or less when purchased.
(d) Investments
Berkshire’ s management determines the appropriate classifications of investments at the time of acquisition
and re-evaluates the classifications at each balance sheet date. Investments may be classified as held-for-
trading, held-to-maturity, or, when neither of those classifications is appropriate, as available-for-sale.
Berkshire’ s investments in fixed maturity and equity securities are primarily classified as available-for-
sale, except for certain investments, which are classified as held-to-maturity. Held-to-maturity
investments are carried at amortized cost, reflecting Berkshire’ s intent and ability to hold the securities to
maturity. Available-for-sale securities are stated at fair value with net unrealized gains or losses reported
as a separate component in shareholders’ equity. Realized gains and losses, which arise when available-
for-sale investments are sold (as determined on a specific identification basis) or other-than-temporarily
impaired are included in the Consolidated Statements of Earnings.
Other investments include investments in commodities, limited partnerships and warrants, which are carried
at fair value in the accompanying Consolidated Balance Sheets. Realized and unrealized gains and
losses associated with these investments are included in the Consolidated Statements of Earnings as a
component of realized investment gain.
Accounting policies and practices for investments held by finance and financial products businesses are
described in Note 9.