Avon 2011 Annual Report Download - page 80
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 80 of the 2011 Avon annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
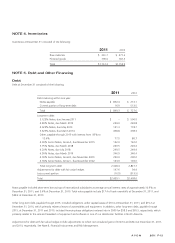
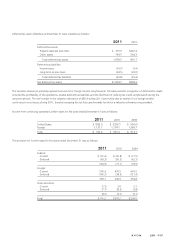
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
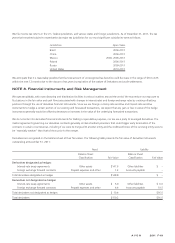
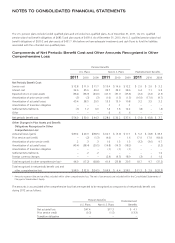
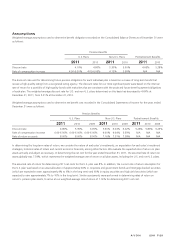
The following table presents the fair value of derivative instruments outstanding at December 31, 2010:
Asset Liability
Balance Sheet
Classification Fair Value
Balance Sheet
Classification Fair Value
Derivatives designated as hedges:
Interest-rate swap agreements Other assets $ 94.4 Other liabilities $ –
Derivatives not designated as hedges:
Interest-rate swap agreements Other assets $ 9.5 Other liabilities $ 9.5
Foreign exchange forward contracts Prepaid expenses and other 11.1 Accounts payable 4.3
Total derivatives not designated as hedges $ 20.6 $13.8
Total derivatives $115.0 $13.8
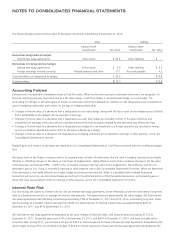
Accounting Policies
Derivatives are recognized on the balance sheet at their fair values. When we become a party to a derivative instrument, we designate, for
financial reporting purposes, the instrument as a fair value hedge, a cash flow hedge, a net investment hedge, or a non-hedge. The
accounting for changes in fair value (gains or losses) of a derivative instrument depends on whether we had designated it and it qualified as
part of a hedging relationship and further, on the type of hedging relationship.
• Changes in the fair value of a derivative that is designated as a fair value hedge, along with the loss or gain on the hedged asset or liability
that is attributable to the hedged risk are recorded in earnings.
• Changes in the fair value of a derivative that is designated as a cash flow hedge are recorded in AOCI to the extent effective and
reclassified into earnings in the same period or periods during which the transaction hedged by that derivative also affects earnings.
• Changes in the fair value of a derivative that is designated as a hedge of a net investment in a foreign operation are recorded in foreign
currency translation adjustments within AOCI to the extent effective as a hedge.
• Changes in the fair value of a derivative not designated as a hedging instrument are recognized in earnings in other expense, net on the
Consolidated Statements of Income.
Realized gains and losses on a derivative are reported on the Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows consistent with the underlying hedged
item.
We assess, both at the hedge’s inception and on an ongoing basis, whether the derivatives that are used in hedging transactions are highly
effective in offsetting changes in fair values or cash flows of hedged items. Highly effective means that cumulative changes in the fair value
of the derivative are between 85% – 125% of the cumulative changes in the fair value of the hedged item. The ineffective portion of a
derivative’s gain or loss, if any, is recorded in earnings in other expense, net on the Consolidated Statements of Income. When we determine
that a derivative is not highly effective as a hedge, hedge accounting is discontinued. When it is probable that a hedged forecasted
transaction will not occur, we discontinue hedge accounting for the affected portion of the forecasted transaction, and reclassify gains or
losses that were accumulated in AOCI to earnings in other expense, net on the Consolidated Statements of Income.
Interest Rate Risk
Our borrowings are subject to interest rate risk. We use interest-rate swap agreements, which effectively convert the fixed rate on long-term
debt to a floating interest rate, to manage our interest rate exposure. The agreements are designated as fair value hedges. We held interest-
rate swap agreements that effectively converted approximately 74% at December 31, 2011 and 2010, of our outstanding long-term, fixed-
rate borrowings to a variable interest rate based on LIBOR. Our total exposure to floating interest rates was approximately 82% at
December 31, 2011, and 81% at December 31, 2010.
We had interest-rate swap agreements designated as fair value hedges of fixed-rate debt, with notional amounts totaling $1,725 at
December 31, 2011. Unrealized gains were $147.6 at December 31, 2011, and $94.4 at December 31, 2010, and were included within
long-term debt. During 2011, we recorded a net gain of $53.2 in interest expense for these interest-rate swap agreements designated as fair
value hedges. During 2010, we recorded a net gain of $66.8 in interest expense for these interest-rate swap agreements designated as fair