Chevron 2005 Annual Report Download - page 65
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 65 of the 2005 Chevron annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
CHEVRON CORPORATION 2005 ANNUAL REPORT 63
engaged in more than one outstanding derivative transaction
with the same counterparty and also has a legally enforceable
netting agreement with that counterparty, the net marked-
to-market exposure represents the netting of the positive and
negative exposures with that counterparty and is a reason-
able measure of the company’s credit risk exposure. The
company also uses other netting agreements with certain
counterparties with which it conducts signifi cant transactions
to mitigate credit risk.
The fair values of the outstanding contracts are reported
on the Consolidated Balance Sheet as “Accounts and notes
receivable,” “Accounts payable,” “Long-term receivables – net”
and “Deferred credits and other noncurrent obligations.”
Gains and losses on the company’s risk management activi-
ties are reported as either “Sales and other operating revenues”
or “Purchased crude oil and products,” whereas trading gains
and losses are reported as “Other income.” These activities
are reported under “Operating activities” in the Consolidated
Statement of Cash Flows.
Foreign Currency The company enters into forward exchange
contracts, generally with terms of 180 days or less, to man-
age some of its foreign currency exposures. These exposures
include revenue and anticipated purchase transactions,
including foreign currency capital expenditures and lease com-
mitments, forecasted to occur within 180 days. The forward
exchange contracts are recorded at fair value on the balance
sheet with resulting gains and losses refl ected in income.
The fair values of the outstanding contracts are reported
on the Consolidated Balance Sheet as “Accounts and notes
receivable” or “Accounts payable,” with gains and losses
reported as “Other income.” These activities are reported
under “Operating activities” in the Consolidated Statement
of Cash Flows.
Interest Rates The company enters into interest rate swaps as
part of its overall strategy to manage the interest rate risk on
its debt. Under the terms of the swaps, net cash settlements
are based on the difference between fi xed-rate and fl oat-
ing-rate interest amounts calculated by reference to agreed
notional principal amounts. Interest rate swaps related to a
portion of the company’s fi xed-rate debt are accounted for
as fair value hedges, whereas interest rate swaps related to a
portion of the company’s fl oating-rate debt are recorded at
fair value on the balance sheet with resulting gains and losses
refl ected in income.
Fair values of the interest rate swaps are reported on the
Consolidated Balance Sheet as “Accounts and notes receiv-
able” or “Accounts payable,” with gains and losses reported
directly in income as part of “Interest and debt expense.”
These activities are reported under “Operating activities” in
the Consolidated Statement of Cash Flows.
Fair Value Fair values are derived either from quoted market
prices or, if not available, the present value of the expected cash
fl ows. The fair values refl ect the cash that would have been
received or paid if the instruments were settled at year-end.
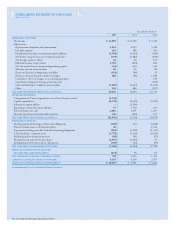
Year ended December 31
2005 2004 2003
Sales and other operating revenues $ 640 $ 660 $ 601
Total costs and other deductions 509 495 535
Net income 113 160 50
At December 31
2005 2004
Current assets $ 358 $ 292
Other assets 283 219
Current liabilities 119 67
Other liabilities 243 278
Net equity 279 166
There were no restrictions on CTC’s ability to pay divi-
dends or make loans or advances at December 31, 2005.
NOTE 6.
STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY
Retained earnings at December 31, 2005 and 2004, included
approximately $5,000 and $3,950, respectively, for the com-
pany’s share of undistributed earnings of equity affiliates.
At December 31, 2005, about 142 million shares of Chev-
ron’s common stock remained available for issuance from the
160 million shares that were reserved for issuance under the
Chevron Corporation Long-Term Incentive Plan (LTIP), as
amended and restated, which was approved by the stockhold-
ers in 2004. In addition, approximately 561 thousand shares
remain available for issuance from the 800 thousand shares of
the company’s common stock that were reserved for awards
under the Chevron Corporation Non-Employee Directors’
Equity Compensation and Deferral Plan (Non-Employee
Directors’ Plan), which was approved by stockholders in 2003.
Refer to Note 26, on page 86, for a discussion of the compa-
ny’s common stock split in 2004.
NOTE 7.
FINANCIAL AND DERIVATIVE INSTRUMENTS
Commodity Derivative Instruments Chevron is exposed to mar-
ket risks related to price volatility of crude oil, refi ned products,
natural gas, natural gas liquids and refi nery feedstocks.
The company uses derivative commodity instruments to
manage these exposures on a portion of its activity, includ-
ing: fi rm commitments and anticipated transactions for the
purchase or sale of crude oil; feedstock purchases for company
refi neries; crude oil and refi ned products inventories; and
fi xed-price contracts to sell natural gas and natural gas liquids.
The company also uses derivative commodity instruments for
limited trading purposes.
The company uses Inter national Swaps Dealers Associa-
tion agreements to govern derivative contracts with certain
counterparties to mitigate credit risk. Depending on the
nature of the derivative transactions, bilateral collateral
arrangements may also be required. When the company is
NOTE 5. SUMMARIZED FINANCIAL DATA – CHEVRON
TRANSPORT CORPORATION LTD. – Continued