Royal Caribbean Cruise Lines 2009 Annual Report Download - page 82
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 82 of the 2009 Royal Caribbean Cruise Lines annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
ROYAL CARIBBEAN CRUISES LTD.
NOTES TO THE CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
Advertising Costs
Advertising costs are expensed as incurred except those costs which result in tangible assets, such as brochures, which are
treated as prepaid expenses and charged to expense as consumed. Advertising costs consist of media advertising as well as brochure,
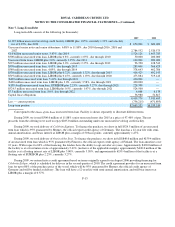
production and direct mail costs. Media advertising was $152.2 million, $152.5 million and $153.4 million, and brochure, production
and direct mail costs were $92.0 million, $100.0 million and $99.0 million for the years 2009, 2008 and 2007, respectively.
Derivative Instruments
We enter into various forward, swap and option contracts to manage our interest rate exposure and to limit our exposure to
fluctuations in foreign currency exchange rates and fuel prices. These instruments are recorded on the balance sheet at their fair value
and the vast majority are designated as hedges. Our derivative instruments are not held for trading or speculative purposes.
At inception of the hedge relationship, a derivative instrument that hedges the exposure to changes in the fair value of a
recognized asset or liability, or a firm commitment is designated as a fair value hedge. A derivative instrument that hedges a
forecasted transaction or the variability of cash flows related to a recognized asset or liability is designated as a cash flow hedge.
Changes in the fair value of derivatives that are designated as fair value hedges are offset against changes in the fair value of the
underlying hedged assets, liabilities or firm commitments. Changes in fair value of derivatives that are designated as cash flow hedges
are recorded as a component of accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) until the underlying hedged transactions are
recognized in earnings.
The foreign-currency transaction gain or loss of our nonderivative financial instruments designated as hedges of our net
investment in our foreign operations or investments are recognized as a component of accumulated other comprehensive income
(loss) along with the associated foreign currency translation adjustment of the foreign operation.
On an ongoing basis, we assess whether derivatives used in hedging transactions are “highly effective” in offsetting changes in
the fair value or cash flow of hedged items. If it is determined that a derivative is not highly effective as a hedge or hedge accounting
is discontinued, any change in fair value of the derivative since the last date at which it was determined to be effective is recognized
in earnings. In addition, the ineffective portion of our highly effective hedges is recognized in earnings immediately and reported in
other income (expense) in our consolidated statements of operations.
Cash flows from derivative instruments that are designated as fair value or cash flow hedges are classified in the same category
as the cash flows from the underlying hedged items. In the event that hedge accounting is discontinued, cash flows subsequent to the
date of discontinuance are classified consistent with the nature of the instrument.
Foreign Currency Translations and Transactions
We translate assets and liabilities of our foreign subsidiaries whose functional currency is the local currency, at exchange rates
in effect at the balance sheet date. We translate revenues and expenses at weighted-average exchange rates for the period. Equity is
translated at historical rates and the resulting foreign currency translation adjustments are included as a component of accumulated
other comprehensive income (loss), which is reflected as a separate component of shareholders’ equity. Exchange gains or losses
arising from the remeasurement of monetary assets and liabilities denominated in a currency other than the functional currency of the
entity involved are immediately included in our earnings, unless certain liabilities have been designated to act as a hedge of a net
investment in a foreign operation or investment. The majority of our transactions are settled in United States dollars. Gains or losses
resulting from transactions denominated in other currencies are recognized in income at each balance sheet date. Exchange gains and
(losses) were ($21.1) million, $23.0 million and ($6.7) million for the years 2009, 2008 and 2007, respectively, and were recorded in
other (expense) income.
F-9