PG&E 2008 Annual Report Download - page 140
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 140 of the 2008 PG&E annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
138
Renewable Energy Contracts — California law requires
that each California retail seller of electricity, except for
municipal utilities, increase its purchases of renewable
energy (such as biomass, small hydroelectric, wind, solar,
and geothermal energy) by at least 1% of its retail sales
per year, so that the amount of electricity delivered from
renewable resources equals at least 20% of its total retail
sales by the end of 2010. The Utility has entered into new
renewable power purchase contracts that will help the Utility
meet this renewable portfolio standard (“RPS”) by 2010.
Long-Term Power Purchase Agreements — In accordance
with the Utility’s CPUC-approved long-term procurement
plans, the Utility has entered into several power purchase
agreements with third parties. The Utility’s obligations
under a portion of these agreements are contingent on
the third party’s development of a new generation facility
to provide the power to be purchased by the Utility under
the agreements.
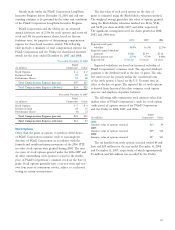
Annual Receipts and Payments — The payments made under
QFs, irrigation district and water agency, renewable energy,
and other power purchase agreements during 2008, 2007, and
2006 were as follows:
(in millions) 2008 2007 2006
Qualifying facility energy payments $ 969 $ 812 $661
Qualifying facility capacity payments 343 363 366
Irrigation district and water agency
payments 69 72 64
Renewable energy and capacity
payments 714 604 429
Other power purchase agreement
payments 2,036 1,166 670
The amounts above do not include payments related
to DWR purchases for the benefi t of the Utility’s customers,
as the Utility only acts as an agent for the DWR.
The Energy Policy Act of 2005 signifi cantly amended the
purchase requirements of PURPA. As amended, Section 210(m)
of PURPA authorizes the FERC to waive the obligation of
an electric utility under Section 210 of PURPA to purchase
the electricity offered to it by a QF (under a new contract or
obligation) if the FERC fi nds the QF has nondiscriminatory
access to one of three defi ned categories of competitive
wholesale electricity markets. The statute permits such waivers
to a particular QF or on a “service territory-wide basis.” The
Utility plans to wait until after the new day-ahead market
structure provided for in the CAISO’s MRTU initiative to
restructure the California electricity market becomes effective
to assess whether it will fi le a request with the FERC to
terminate its obligations under PURPA and to enter into
new QF purchase obligations.
As of December 31, 2008, the Utility had agreements with
246 QFs for approximately 3,900 MW that are in operation.
Agreements for approximately 3,600 MW expire at various
dates between 2009 and 2028. QF power purchase agreements
for approximately 300 MW have no specifi c expiration dates
and will terminate only when the owner of the QF exercises
its termination option. The Utility also has power purchase
agreements with 74 inoperative QFs. The total of approxi-
mately 3,900 MW consists of approximately 2,500 MW
from cogeneration projects, 600 MW from wind projects
and 800 MW from projects with other fuel sources,
including biomass, waste-to-energy, geothermal, solar, and
hydroelectric. QF power purchase agreements accounted
for approximately 18%, 20%, and 20% of the Utility’s 2008,
2007, and 2006 electricity sources, respectively. No single
QF accounted for more than 5% of the Utility’s 2008, 2007,
or 2006 electricity sources.
Irrigation Districts and Water Agencies — The Utility has
contracts with various irrigation districts and water agencies
to purchase hydroelectric power. Under these contracts, the
Utility must make specifi ed semi-annual minimum payments
based on the irrigation districts’ and water agencies’ debt
service requirements, whether or not any hydroelectric
power is supplied, and variable payments for operation and
maintenance costs incurred by the suppliers. These contracts
expire on various dates from 2010 to 2031. The Utility’s
irrigation district and water agency contracts accounted for
approximately 2%, 3%, and 6% of the Utility’s electricity
sources in 2008, 2007, and 2006, respectively.