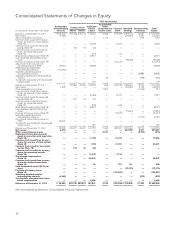
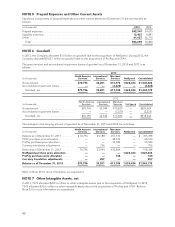
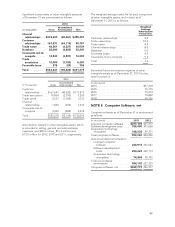
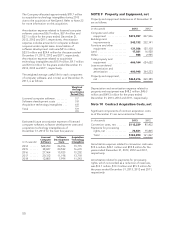
NetSpend 2013 Annual Report Download - page 47
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 47 of the 2013 NetSpend annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.issuance is recognized as compensation expense
immediately for vested awards and over the vesting
period of the nonvested awards. For nonvested
award grants that have pro rata vesting, the
Company recognizes compensation expense using
the straight-line method over the vesting period of
the award.
LEASES: The Company is obligated under
noncancelable leases for computer equipment and
facilities. As these leases expire, they will be
evaluated and renewed or replaced by similar leases
based on need. A lease is an agreement conveying
the right to use property, plant, or equipment (land
and/or depreciable assets) usually for a stated period
of time. For purposes of applying the accounting and
reporting standards, leases are classified from the
standpoint of the lessee as capital or operating
leases.
Rental payments on operating leases are charged to
expense over the lease term. If rental payments are
not made on a straight-line basis, rental expense
nevertheless shall be recognized on a straight-line
basis unless another systematic and rational basis is
more representative of the time pattern in which use
benefit is derived from the leased property, in which
case that basis shall be used.
Certain of the Company’s operating leases are for
office space. The Company will make various
alterations (leasehold improvements) to the office
space and capitalize these costs as part of property
and equipment. Leasehold improvements are
amortized on a straight-line basis over the useful life
of the improvement or the term of the lease,
whichever is shorter.
ADVERTISING: Advertising costs, consisting mainly
of advertising in trade publications, are expensed as
incurred or the first time the advertising takes place
except for direct-response advertising and television
advertising production costs. Direct-response
advertising consists of commission paid to affiliate
marketers for the new funded customer accounts
generated by them. Direct-response advertising costs
are capitalized and amortized over the average life of
the new accounts, which is approximately one year.
Television advertising production costs consist of the
costs of developing and filming television ads.
Television advertising production costs are
capitalized when the production services are received
and expensed in the period when the advertising first
takes place. Advertising expense for 2013, 2012 and
2011 was $1.3 million, $1.0 million and $813,000,
respectively.
INCOME TAXES: Income taxes reflected in TSYS’
consolidated financial statements are computed
based on the taxable income of TSYS and its
affiliated subsidiaries. A consolidated U.S. federal
income tax return is filed for TSYS and its majority
owned U.S. subsidiaries. Additionally, income tax
returns are also filed in states where TSYS and its
subsidiaries have filing obligations and in foreign
jurisdictions where TSYS has a foreign affiliate.
The Company accounts for income taxes in
accordance with the asset and liability method.
Deferred income tax assets and liabilities are
recognized for the future tax consequences
attributable to differences between the financial
statement carrying amounts of existing assets and
liabilities and their respective tax basis and operating
loss and tax credit carry forwards. Deferred tax assets
and liabilities are measured using enacted tax rates
expected to apply to taxable income in the years in
which those temporary differences are expected to
be recovered or settled. Reserves against the
carrying value of a deferred tax asset are established
when necessary to reflect the decreased likelihood of
realization of a deferred asset in the future. The effect
on deferred income tax assets and liabilities of a
change in tax rates is recognized in income in the
period that includes the enactment date.
Income tax provisions require the use of
management judgments, which are subject to
challenge by various taxing authorities. Contingency
reserves are periodically established where the
amount of the contingency can be reasonably
determined and is likely to occur. Reductions in
contingency reserves are recognized when tax
disputes are settled or examination periods lapse.
Significant estimates used in accounting for income
taxes relate to the determination of taxable income,
the determination of temporary differences between
book and tax basis, as well as estimates on the
realizability of tax credits and net operating losses.
TSYS recognizes potential interest and penalties
related to the underpayment of income taxes as
income tax expense in the Consolidated Statements
of Income.
EARNINGS PER SHARE: The guidance under
ASC 260, “Earnings Per Share,” holds that unvested
share-based payment awards that contain
nonforfeitable rights to dividends or dividend
equivalents are “participating securities” as defined
in ASC 260, and therefore should be included in EPS
using the two-class method.
45