IHOP 2014 Annual Report Download - page 85
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 85 of the 2014 IHOP annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.66
DineEquity, Inc. and Subsidiaries
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
1. The Company
The first International House of Pancakes® (“IHOP®”) restaurant opened in 1958 in Toluca Lake, California. Shortly
thereafter, the Company began developing and franchising additional restaurants. The Company was incorporated as IHOP
Corp. under the laws of the State of Delaware in 1976. In November 2007, the Company acquired Applebee's
International, Inc., which became a wholly-owned subsidiary of the Company. Effective June 2, 2008, the name of the
Company was changed to DineEquity, Inc. (“DineEquity”). The Company owns, franchises and operates two restaurant
concepts: Applebee's Neighborhood Grill and Bar® (“Applebee's®”), in the bar and grill segment within the casual dining
category of the restaurant industry, and IHOP in the family dining category of the restaurant industry.
As of December 31, 2014, there were a total of 1,650 IHOP restaurants, of which 1,472 were subject to franchise
agreements, 167 were subject to area license agreements and 11 were company-operated restaurants. These IHOP restaurants
were located in all 50 states of the United States, the District of Columbia, two United States territories and eight countries
outside of the United States. As of December 31, 2014, there were a total of 2,017 Applebee's restaurants, of which 1,994 were
subject to franchise agreements and 23 were company-operated restaurants. These Applebee's restaurants were located in 49
states of the United States, two United States territories and 15 countries outside of the United States.
References herein to Applebee's and IHOP restaurants are to these restaurant concepts, whether operated by franchisees,
area licensees or the Company. Retail sales at restaurants that are owned by franchisees and area licensees are not attributable
to the Company.
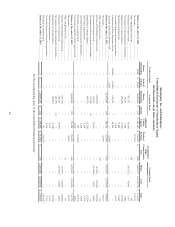
2. Basis of Presentation and Summary of Significant Accounting Policies
Principles of Consolidation
The consolidated financial statements include the accounts of DineEquity, Inc. and its wholly-owned subsidiaries. All
intercompany accounts and transactions have been eliminated in consolidation.
Fiscal Periods
The Company has a 52/53 week fiscal year that ends on the Sunday nearest to December 31 of each year. In a 52-week
fiscal year, each fiscal quarter contains 13 weeks, comprised of two, four-week fiscal months followed by a five-week fiscal
month. In a 53-week fiscal year, the last month of the fourth fiscal quarter contains six weeks. For convenience, the Company
refers to all fiscal years as ending on December 31 and fiscal quarters as ending on March 31, June 30 and September 30. The
2014, 2013 and 2012 fiscal years presented herein ended December 28, 2014, December 29, 2013 and December 30, 2012,
respectively, and each contained 52 weeks.
Use of Estimates
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with United States generally accepted accounting principles
(“U.S. GAAP”) requires the Company's management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of
assets and liabilities, disclosures of contingent assets and liabilities, if any, at the date of the consolidated financial statements,
and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting period. Significant estimates are made in the
calculation and assessment of the following: (a) impairment of tangible and intangible assets, (b) income taxes, (c) allowance
for doubtful accounts and notes receivables, (d) lease accounting estimates and (e) contingencies. On an ongoing basis, the
Company evaluates its estimates based on historical experience, current conditions and various other assumptions that are
believed to be reasonable under the circumstances. The Company adjusts such estimates and assumptions when facts and
circumstances dictate. Actual results could differ from those estimates.
Concentration of Credit Risk
The Company's cash, cash equivalents and accounts receivable are potentially subject to concentration of credit risk. Cash
and cash equivalents are placed with financial institutions that management believes are creditworthy. The Company does not
believe that it is exposed to any significant credit risk on cash and cash equivalents. At times, cash and cash equivalent balances
may be in excess of FDIC insurance limits.
Accounts receivable are derived from revenues earned from franchisees and area licensees located primarily in the United
States. Financing receivables arise from the financing of restaurant equipment, leases or franchise fees by IHOP franchisees.
The Company is subject to a concentration of credit risk with respect to receivables from franchisees that own a large number
of Applebee's or IHOP restaurants. As of December 31, 2014, there were 15 franchisees that owned 54 or more restaurants each