Cisco 2008 Annual Report Download - page 47
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 47 of the 2008 Cisco annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
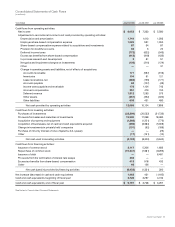
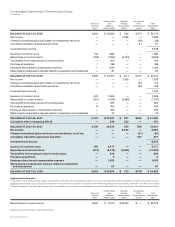
52 Cisco Systems, Inc.
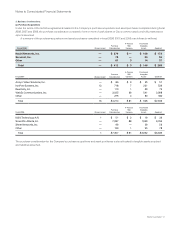
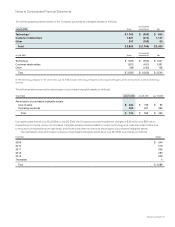
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(f) Depreciation and Amortization Property and equipment are stated at cost, less accumulated depreciation and amortization.
Depreciation and amortization are computed using the straight-line method over the following periods:
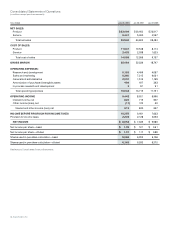
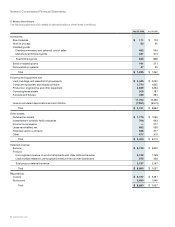
Period
Buildings 25 years
Furniture and fixtures 5 years
Production, engineering, and other equipment Up to 5 years
Computer equipment and related software 30 to 36 months
Operating lease assets Based on lease term—
generally up to 3 years
Depreciation and amortization of leasehold improvements Shorter of remaining lease term
or 5 years
(g) Goodwill and Purchased Intangible Assets Goodwill is tested for impairment on an annual basis and during the period between annual
tests in certain circumstances, and written down when impaired. Based on the impairment tests performed, there was no impairment of
goodwill in fiscal 2008, 2007, or 2006. Purchased intangible assets other than goodwill are amortized over their useful lives unless these
lives are determined to be indefinite. Purchased intangible assets are carried at cost, less accumulated amortization. Amortization is
computed over the estimated useful lives of the respective assets, generally two to seven years.
(h) Impairment of Long-Lived Assets Long-lived assets and certain identifiable intangible assets to be held and used are reviewed for
impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of such assets may not be recoverable.
Determination of recoverability of long-lived assets is based on an estimate of undiscounted future cash flows resulting from the use of the
asset and its eventual disposition. Measurement of an impairment loss for long-lived assets and certain identifiable intangible assets that
management expects to hold and use is based on the fair value of the asset. Long-lived assets and certain identifiable intangible assets to
be disposed of are reported at the lower of carrying amount or fair value less costs to sell.
(i) Derivative Instruments The Company recognizes derivative instruments as either assets or liabilities and measures those instruments
at fair value. The accounting for changes in the fair value of a derivative depends on the intended use of the derivative and the resulting
designation. For a derivative instrument designated as a fair value hedge, the gain or loss is recognized in earnings in the period of change
together with the offsetting loss or gain on the hedged item attributed to the risk being hedged. For a derivative instrument designated
as a cash flow hedge, the effective portion of the derivative’s gain or loss is initially reported as a component of accumulated other
comprehensive income and subsequently reclassified into earnings when the hedged exposure affects earnings. The ineffective portion
of the gain or loss is reported in earnings immediately. For derivative instruments that are not designated as accounting hedges, changes in
fair value are recognized in earnings in the period of change.
(j) Fair Value of Financial Instruments The fair value of certain of the Company’s financial instruments, including cash and cash equivalents,
accrued compensation, and other current liabilities, approximates the carrying amount because of their short maturities. In addition, the
fair value of the Company’s loan receivables and financed service contracts also approximate the carrying amount. The fair values of fixed
income investments, publicly traded equity securities, and the Company’s long-term debt are determined using quoted market prices for
those securities or similar financial instruments.