Audi 2009 Annual Report Download - page 226
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 226 of the 2009 Audi annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
223
Consolidated Financial
Statements
178 Income Statement
179 Statement of Recognized
Income and Expense
180 Balance Sheet
181 Cash Flow Statement
182 Statement of Changes in Equity
Notes to the Consolidated
Financial Statements
184 Development of fixed assets
in the 2009 fiscal year
186 Development of fixed assets
in the 2008 fiscal year
188 General information
192 Recognition and
measurement principles
199 Notes to the Income Statement
205 Notes to the Balance Sheet
215 Additional disclosures
236 Events occurring subsequent
to the balance sheet date
237 Statement of Interests
held by the Audi Group
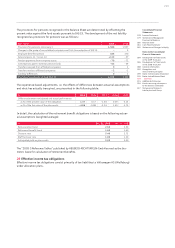
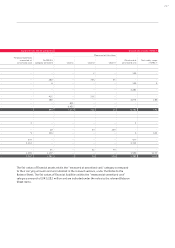
34.3 Market risks
Given the global nature of its operations, the Audi Group is exposed to various market risks,
which are described below. The individual risk types and the respective risk management meas-
ures are also described. Additionally, these risks are quantified by means of sensitivity analyses.
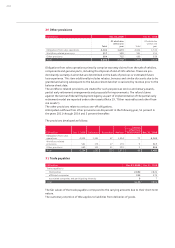
Currency risks
The Audi Group is exposed to exchange rate fluctuations in view of its international business
activities. The measures implemented to hedge against these currency risks are coordinated
regularly between AUDI AG and the Group Treasury of Volkswagen AG (Wolfsburg) in accordance
with Volkswagen’s organizational guideline.
These risks are limited by concluding appropriate hedges for matching amounts and maturities.
The hedging transactions are performed centrally for the Audi Group by Volkswagen AG on the
basis of an agency agreement. The results from hedging contracts are credited or debited to the
Audi Group each month on the basis of the proportionate share of the Volkswagen Group’s over-
all hedging volume.
In accordance with the Volkswagen organizational guideline, AUDI AG additionally concludes
hedging transactions of its own to a limited extent, where this helps to simplify current opera-
tions.
Marketable derivative financial instruments (foreign exchange contracts, currency option trans-
actions and currency swaps) are used for this purpose. Contracts are concluded exclusively with
first-rate national and international banks whose creditworthiness is regularly examined by
leading rating agencies.
For the purpose of managing currency risks, exchange rate hedging in the 2009 fiscal year fo-
cused on the U.S. dollar, the pound sterling, the Japanese yen, the Australian dollar, the Cana-
dian dollar and the Hungarian forint.
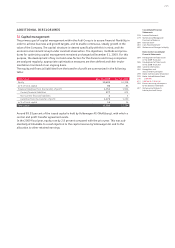
Currency risks pursuant to IFRS 7 arise as a result of financial instruments that are denominated
in a currency other than the functional currency and are of a monetary nature. Exchange rate
variances from the translation of financial statements into the Group currency (translation risk)
are disregarded. Within the Audi Group, the principal non-derivative monetary financial instru-
ments (liquid assets, receivables, securities held and equity instruments held, interest-bearing
liabilities, interest-free liabilities) are either denominated directly in the functional currency or
substantially transferred to the functional currency through the use of derivatives. Above all, the
generally short maturity of the instruments also means that potential exchange rate move-
ments have only a very minor impact on profit or equity.
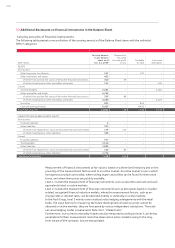
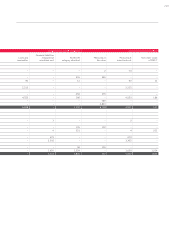
Currency risks are measured using sensitivity analyses, during which the impact on profit and
equity of hypothetical changes to relevant risk variables is assessed. All non-functional curren-
cies in which the Audi Group enters into financial instruments are fundamentally treated as
relevant risk variables.
The periodic effects are determined by applying the hypothetical changes in the risk variables to
the inventory of financial instruments on the reporting date. It is assumed for this purpose that
the inventory on the reporting date is representative of the entire year. Movements in the ex-
change rate against the underlying currencies for the hedged transactions affect the cash flow
hedge reserve in equity and the fair value of these hedging transactions.
Fund price risks
The special mutual funds created using surplus liquidity are exposed, in particular, to an equity
and bond price risk that may arise from fluctuating stock market prices and indices, and market
interest rates. The changes in bond prices resulting from a variation in market interest rates, like
the measurement of currency and other interest rate risks arising from the special funds, are
quantified separately in the corresponding notes on “Currency risks” and “Interest rate risks.”