Audi 2009 Annual Report Download - page 200
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 200 of the 2009 Audi annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
197
Consolidated Financial
Statements
178 Income Statement
179 Statement of Recognized
Income and Expense
180 Balance Sheet
181 Cash Flow Statement
182 Statement of Changes in Equity
Notes to the Consolidated
Financial Statements
184 Development of fixed assets
in the 2009 fiscal year
186 Development of fixed assets
in the 2008 fiscal year
188 General information
192 Recognition and
measurement principles
192 Recognition of income
and expenses
193 Intangible assets
193 Property, plant
and equipment
194 Investment property
194 Investments accounted for
using the equity method
194 Impairment tests
195 Financial instruments
197 Other receivables and
financial assets
197 Deferred tax
197 Inventories
198 Securities, cash and
cash equivalents
198 Provisions for pensions
198 Other provisions
198 Management’s estimates
and assessments
199 Notes to the Income Statement
205 Notes to the Balance Sheet
215 Additional disclosures
236 Events occurring subsequent
to the balance sheet date
237 Statement of Interests
held by the Audi Group
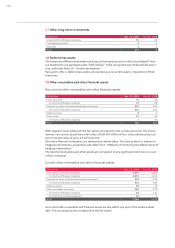
OTHER RECEIVABLES AND FINANCIAL ASSETS
Other receivables and financial assets (except for derivatives) are recognized at amortized cost.
Provision is made for discernible non-recurring risks and general credit risks in the form of corre-
sponding value adjustments.
DEFERRED TAX
Pursuant to IAS 12, deferred tax is determined according to the balance sheet-focused liability
method. This method specifies that tax deferrals are to be created for all temporary differences
between the tax base of assets and liabilities and their carrying amounts in the Consolidated
Balance Sheet (temporary concept). Deferred tax assets relating to carryforward of unused tax
losses must also be recognized.
Deferrals amounting to the anticipated tax burden or tax relief in subsequent fiscal years are
created on the basis of the anticipated tax rate at the time of realization. In accordance with
IAS 12, the tax consequences of distributions of profit are not recognized until the resolution on
the appropriation of profits is adopted.
Deferred tax assets include future tax relief resulting from temporary differences between the
carrying amounts in the Consolidated Balance Sheet and the valuations in the Balance Sheet for
tax purposes. Deferred tax assets for carrying forward unused tax losses that can be realized in
the future and from tax relief are also recognized.
Deferred tax assets and deferred tax liabilities are netted if the tax creditors and maturities are
identical.
Pursuant to IAS 1.70, deferred tax is reported as non-current.
The carrying amount is reduced for deferred tax assets that are unlikely to be realized.
INVENTORIES
Raw materials and supplies are measured at the lower of average cost of acquisition or fair value
(net realizable value). Generally, an average value or a value calculated on the basis of the FIFO
(first in, first out) process is used. Other costs of purchase and purchase cost reductions are
taken into account as appropriate.
Work in progress and finished goods are valued at the lower of cost of conversion or fair value.
Cost of conversion includes direct materials and direct productive wages, as well as a directly
attributable portion of the necessary indirect materials and indirect labor costs, production-
related depreciation, and expenses attributable to the products from the amortization of capi-
talized production development costs. Distribution costs, general administrative expenses and
interest on borrowings are not capitalized.
Merchandise is valued at the lower of cost of purchase or fair value.
Provision has been made for all discernible storage and inventory risks in the form of appropriate
reductions in the carrying amounts. Individual adjustments are made on all inventories as soon
as the probable proceeds realizable from their sale or use are lower than the carrying amounts
of the inventories. The fair value is deemed to be the estimated proceeds of sale less the esti-
mated costs incurred up until the sale.
Current leased assets comprise leased vehicles with an operating lease of up to one year and
vehicles which are subject to a buy-back obligation for within one year (owing to buy-back
agreements). These vehicles are capitalized at cost of sales and depreciated over the contractual
term to:
–the calculated residual value (vehicles with an operating lease)
–the buy-back price (buy-back vehicles)