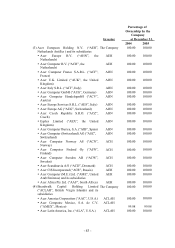
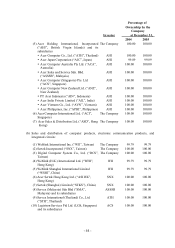
Acer 2005 Annual Report Download - page 53
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 53 of the 2005 Acer annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.- 48 -
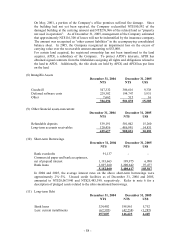
(f) Inventories; land held for sale and development
Inventories are stated at the lower of cost or market value. For Acer brand name information
technology business, costs of inventory are determined using the weighted-average method.
For channel business, costs of inventory are determined using the first-in, first-out method.
Market value represents net realizable value or replacement cost.
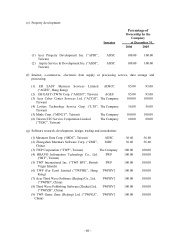
For property development business, land held for the purpose of development and future sale
are stated at the lower of weighted-average cost or market value. The market value of land is
determined by independent appraisers.
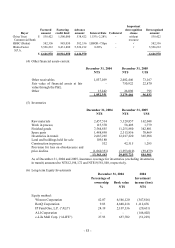
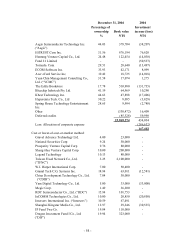
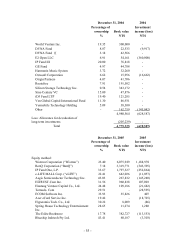
(g) Long-term equity investments
Long-term equity investments in which the Consolidated Companies own less than 20% of the
investee’ s voting shares and are not able to exercise significant influence over the investee’ s
operations and financial policies are accounted for by the cost if the investee is not publicly
traded, otherwise, by the lower-of-cost-or-market method if the investee is publicly traded.
If there is evidence indicating that a decline in the value of an investment is other than
temporary, then the carrying amount of the investment is reduced to reflect its net realizable
value. The related loss is recognized in the accompanying consolidated statements of
income.
Long-term equity investments in which the Consolidated Companies, directly or indirectly,
own 20% or more of the investee’ s voting shares, or less than 20% of the investee’ s voting
shares but are able to exercise significant influence over the investee’ s operations and
financial policies, are accounted for by the equity method. The differences between the
acquisition cost and the net equity of the investee as of the acquisition date are deferred and
amortized over five years using the straight-line method, and the amortization is recorded as
investment income (loss) in the accompanying consolidated statements of income.
Unrealized gains and losses resulted from the transactions between the Consolidated
Companies and investees accounted for under the equity method are deferred. The gains and
losses resulting from depreciated or amortized assets are recognized over their estimated
useful lives. Gains and losses from other assets are recognized when realized.
(h) Leases
In accordance with the nature of the leasing agreement, accounting for capital lease or
operating lease is used.
For capital leases, where the Consolidated Companies act as the lessor, the Consolidated
Companies account for all costs of leased assets and their related imputed interest as lease
receivables and recognizes interest income thereon over the lease terms.
For capital leases where the consolidated companies act as the lessee, the lower of the present
value of rental payables (minus the fulfilled contract costs born by lessor) and bargain
purchase price (or net residual value guaranteed by lessee), or market value of the assets is
recorded as leased assets. If the lease contains a clause that requires transferring ownership
of the property to the lessee at the end of the lease term, or a bargain purchase option, the
leased assets are depreciated over the useful life of the lease. Otherwise, the leased assets are
depreciated over the lease term.
(i) Property and equipment, property leased to others, and property not used in operations
Property and equipment are stated at cost. Interest expense related to the purchase and
construction of property and equipment is capitalized and included in the cost of the related
asset. Significant additions, improvements and replacements are capitalized. Maintenance
and repair costs are expensed in the period incurred. Gains and losses on the disposal of
property and equipment are recorded in the non-operating section in the accompanying
consolidated statements of income.
Property leased to others is classified as other assets. Property not in use is classified to
other assets and stated at the lower of book value or net realizable value.
Depreciation is provided for property and equipment and property leased to others over the
estimated useful life of assets using the straight-line method. If fully depreciated assets
continue to be used, the residual value of the assets is depreciated over the remaining useful
life. The estimated useful lives of the respective classes of assets are as follows: