Qantas 2016 Annual Report Download - page 80
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 80 of the 2016 Qantas annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
Notes to the Financial Statements continued
For the year ended 30 June 2016
20 FINANCIAL RISK MANAGEMENT CONTINUED
(B) FAIR VALUE
The fair value of cash, cash equivalents and non-interest-bearing financial assets and liabilities approximates their carrying value
due to their short maturity. The fair value of financial assets and liabilities is determined by valuing them at the present value of
future contracted cash flows. Cash flows are discounted using standard valuation techniques at the applicable market yield, having
regard to the timing of the cash flows.
The fair value of forward foreign exchange and fuel contracts is determined as the unrealised gain/loss at balance date by reference
to market exchange rates and fuel prices. The fair value of interest rate swaps is determined as the present value of future contracted
cash flows. Cash flows are discounted using standard valuation techniques at the applicable market yield, having regard to the timing
of the cash flows. The fair value of options is determined using standard valuation techniques. Other financial assets and liabilities
represent the fair value of derivative financial instruments recognised on the Consolidated Balance Sheet in accordance with
AASB9. Refer to Note 29(E) for a definition of the fair value hierarchy.
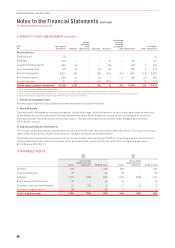
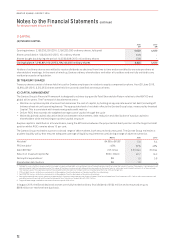
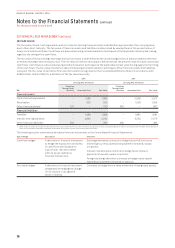
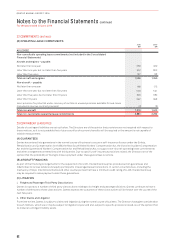
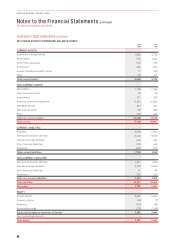
2016 2015
Carrying Amount Held at Carrying Amount Held at
$M
Fair Value
Through Profit
and Loss Amortised Cost Fair Value
Fair Value
Through Profit
and Loss Amortised Cost Fair Value
Financial assets
Cash and cash equivalents –1,980 1,986 –2,908 2,917
Receivables –929 929 –1,093 1,093
Other financial assets1275 –275 662 –662
Financial liabilities
Payables –1,986 1,986 –1,881 1,881
Interest-bearing liabilities –4,862 4,952 –5,562 5,575
Other financial liabilities1264 –264 484 –484
1 Other financial assets and liabilities represent the fair value of derivative financial instruments recognised on the Consolidated Balance Sheet in accordance with AASB 9. These derivative
financial instruments have been measured at fair value using Level 2 inputs in estimating their fair values.
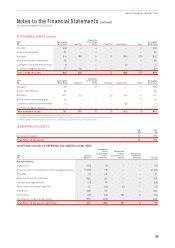
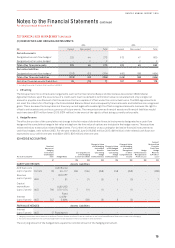
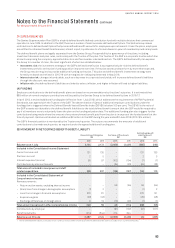
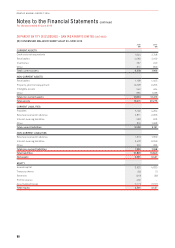
The following section summarises derivative financial instruments in the Consolidated Financial Statements:
Type of Hedge Description Derivative
Cash flow hedges A derivative or financial instrument
to hedge the exposure to variability
i
n cash flows attributable to
a particular risk associated
with an asset, liability or
forecasttransaction.
Exchange derivative contracts to hedge future AUD fuel costs
and foreign currency operational payments (forwards, swaps
oroptions).
Interest rate derivative contracts to hedge future interest
payments (forwards, swaps or options).
Foreign exchange derivative contracts to hedge future capital
expenditure payments (forwards or options).
Fair value hedges A derivative or financial instrument
designated as hedging the change
in fair value of a recognised
assetorliability.
Contracts to hedge the fair value movement of designated assets.
78
QANTAS ANNUAL REPORT 2016