Foot Locker 2013 Annual Report Download - page 66
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 66 of the 2013 Foot Locker annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.Foot Locker, Inc.
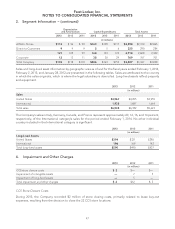
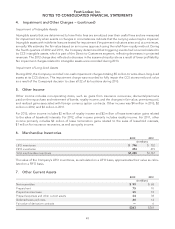
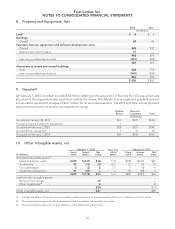
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
1. Summary of Significant Accounting Policies − (continued)
intangible asset is greater than its carrying value, the two-step test is performed. If the carrying value of the
asset exceeds its fair value, an impairment loss is recognized in the amount of the excess. The fair value of each
reporting unit is determined using a combination of market and discounted cash flow approaches.
Derivative Financial Instruments
All derivative financial instruments are recorded in the Company’s Consolidated Balance Sheets at their fair
values. For derivatives designated as a hedge, and effective as part of a hedge transaction, the effective portion
of the gain or loss on the hedging derivative instrument is reported as a component of other comprehensive
income/loss or as a basis adjustment to the underlying hedged item and reclassified to earnings in the period
in which the hedged item affects earnings. The effective portion of the gain or loss on hedges of foreign net
investments is generally not reclassified to earnings unless the net investment is disposed of.
To the extent derivatives do not qualify or are not designated as hedges, or are ineffective, their changes in fair
value are recorded in earnings immediately, which may subject the Company to increased earnings volatility.
Fair Value
The Company categorizes its financial instruments into a three-level fair value hierarchy that prioritizes the
inputs to valuation techniques used to measure fair value into three broad levels. The fair value hierarchy gives
the highest priority to quoted prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilities (Level 1) and the lowest
priority to unobservable inputs (Level 3). If the inputs used to measure fair value fall within different levels of the
hierarchy, the category level is based on the lowest priority level input that is significant to the fair value mea-
surement of the instrument. Fair value is determined based upon the exit price that would be received to sell
an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between market participants exclusive of any
transaction costs.
The Company’s financial assets recorded at fair value are categorized as follows:
Level 1 − Quoted prices for identical instruments in active markets.
Level 2 − Quoted prices for similar instruments in active markets; quoted prices for identical or similar
instruments in markets that are not active; and model-derived valuations in which all significant inputs or
significant value-drivers are observable in active markets.
Level 3 − Model-derived valuations in which one or more significant inputs or significant value-drivers are
unobservable.
Income Taxes
The Company accounts for its income taxes under the asset and liability method, which requires the recogni-
tion of deferred tax assets and liabilities for the expected future tax consequences of events that have been
included in the financial statements. Under this method, deferred tax assets and liabilities are determined on
the basis of the differences between the financial statements and the tax basis of assets and liabilities using
enacted tax rates in effect for the year in which the differences are expected to reverse. The effect of a change
in tax rates on deferred tax assets and liabilities is recognized in income in the period that includes the enact-
ment date. Deferred tax assets are recognized for tax credits and net operating loss carryforwards, reduced by
a valuation allowance, which is established when it is more likely than not that some portion or all of the deferred
tax assets will not be realized. The effect on deferred tax assets and liabilities of a change in tax rates is recog-
nized in income in the period that includes the enactment date.
The Company recognizes net deferred tax assets to the extent that it believes these assets are more likely than
not to be realized. In making such a determination, the Company considers all available positive and negative
evidence, including future reversals of existing taxable temporary differences, projected future taxable income,
43