Albertsons 2004 Annual Report Download - page 59
Download and view the complete annual report
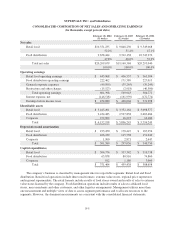
Please find page 59 of the 2004 Albertsons annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.SUPERVALU INC. and Subsidiaries
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
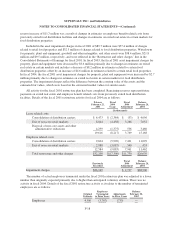
workers’ compensation and general and automobile liability is subject to a considerable degree of variability.
Among the causes of this variability are unpredictable external factors affecting future inflation rates, discount
rates, litigation trends, legal interpretations, benefit level changes and claim settlement patterns.
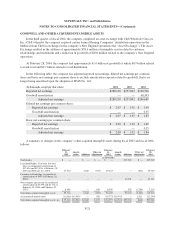
Property, Plant and Equipment:
Property, plant and equipment are carried at cost. Depreciation, as well as amortization of assets under
capital leases, are based on the estimated useful lives of the assets using the straight-line method. Estimated
useful lives generally are 10 to 40 years for buildings and major improvements, 3 to 10 years for equipment, and
the shorter of the term of the lease or expected life for leasehold improvements. Interest on property under
construction of $0.4 million, $5.9 million and $5.7 million was capitalized in fiscal years 2004, 2003 and 2002,
respectively.
Goodwill and Other Intangible Assets:
Goodwill represents the excess of costs over fair value of assets of businesses acquired. The company
adopted the provisions of Statement of Financial Accounting Standards (SFAS) No. 142, “Goodwill and Other
Intangible Assets”, as of February 24, 2002. Pursuant to SFAS No. 142, goodwill and intangible assets acquired
in a purchase business combination and determined to have an indefinite useful life are not amortized, but instead
are tested for impairment at least annually in accordance with the provisions of SFAS No. 142. SFAS No. 142
also requires that intangible assets with estimable useful lives be amortized over their respective estimated useful
lives to their estimated residual values, and be reviewed for impairment in accordance with SFAS No. 144,
“Accounting for Impairment or Disposal of Long-Lived Assets”.
Retirement Plans:
The company sponsors pension and other retirement plans in various forms covering substantially all
employees who meet eligibility requirements. The determination of the company’s obligation and expense for
pension and other post retirement benefits is dependent, in part, on management’s selection of certain
assumptions used by actuaries in calculating such amounts. These assumptions are described in the Retirement
Plans note in the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements and include, among other things, the discount rate,
the expected long-term rate of return on plan assets, and the rates of increases in compensation and healthcare
costs.
Financial Instruments:
The company accounts for derivative financial instruments pursuant to SFAS No. 133, “Accounting for
Derivatives and Hedging Activities”, and SFAS No. 138, “Accounting for Certain Derivative Instruments and
Certain Hedging Activity, an Amendment of SFAS No. 133”. SFAS No. 133 and No. 138 require that all
derivative financial instruments are recorded on the balance sheet at their respective fair value.
The company has only limited involvement with derivative financial instruments and uses them only to
manage well-defined interest rate risks. The derivatives used have included interest rate caps, collars and swap
agreements. The company does not use financial instruments or derivatives for any trading or other speculative
purposes.
Stock-based Compensation:
The company has stock based employee compensation plans, which are described more fully in the Stock
Option Plans note in the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements. The company utilizes the intrinsic value-
based method, per Accounting Principles Board (APB) Opinion No. 25, “Accounting for Stock Issued to
F-12