Tyson Foods 2013 Annual Report Download - page 52
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 52 of the 2013 Tyson Foods annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
52
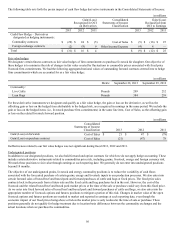
During fiscal 2013, the domestic production deduction and estimated general business credits decreased tax expense by $40 million
and $17 million, respectively.
During fiscal 2012, foreign valuation allowances increased tax expense by $10 million, and the domestic production deduction
decreased tax expense by $17 million.
During fiscal 2011, the domestic production deduction and estimated general business credits decreased tax expense by $25 million
and $9 million, respectively.
Approximately $53 million, $2 million and $36 million of income from continuing operations before income taxes for fiscal 2013,
2012 and 2011, respectively, were from operations based in countries other than the United States.
We recognize deferred income taxes for the future tax consequences attributable to differences between the financial statement
carrying amounts of existing assets and liabilities and their respective tax bases. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are measured using
tax rates expected to apply to taxable income in the years in which those temporary differences are expected to be recovered or settled.
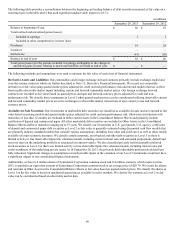
The tax effects of major items recorded as deferred tax assets and liabilities as of September 28, 2013, and September 29, 2012, are as
follows:
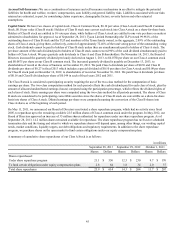
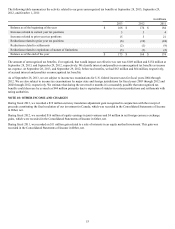
in millions
2013 2012
Deferred Tax Deferred Tax
Assets Liabilities Assets Liabilities
Property, plant and equipment $ — $ 525 $ — $ 542
Suspended taxes from conversion to accrual method — 71 — 76
Intangible assets — 29 — 35
Inventory 8 110 9 105
Accrued expenses 209 — 193 —
Net operating loss and other carryforwards 77 — 101 —
Insurance reserves 22 — 21 —
Other 60 98 69 90
$ 376 $ 833 $ 393 $ 848
Valuation allowance $(77) $ (78)
Net deferred tax liability $ 534 $ 533
We record deferred tax amounts in Other current assets, Other Assets, Other current liabilities and Deferred Income Taxes in the
Consolidated Balance Sheets.
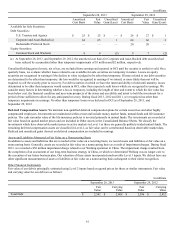
The deferred tax liability for suspended taxes from conversion to accrual method represents the 1987 change from the cash to accrual
method of accounting and will be recognized by 2027.
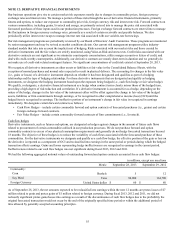
At September 28, 2013, our gross state tax net operating loss carryforwards approximated $457 million and expire in fiscal years 2014
through 2033. Gross foreign net operating loss carryforwards approximated $116 million, of which $27 million expire in fiscal years
2017 through 2022, and the remainder has no expiration. We also have tax credit carryforwards of approximately $22 million that
expire in fiscal years 2014 through 2027.
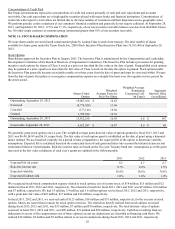
We have accumulated undistributed earnings of foreign subsidiaries aggregating approximately $351 million and $230 million at
September 28, 2013, and September 29, 2012, respectively. These earnings are expected to be indefinitely reinvested outside of the
United States. If those earnings were distributed in the form of dividends or otherwise, we would be subject to federal income taxes
(subject to an adjustment for foreign tax credits), state income taxes and withholding taxes payable to the various foreign countries. It
is not currently practicable to estimate the tax liability that might be payable on the repatriation of these foreign earnings.