Pitney Bowes 2014 Annual Report Download - page 52
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 52 of the 2014 Pitney Bowes annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.PITNEY BOWES INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Tabular dollars in thousands, except per share amounts)
42
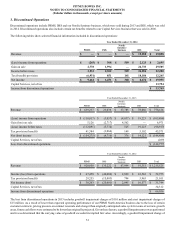
1. Summary of Significant Accounting Policies
Basis of Presentation
The accompanying Consolidated Financial Statements of Pitney Bowes Inc. (we, us, our, or the company) and its wholly owned subsidiaries
have been prepared in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America (GAAP). Intercompany
transactions and balances have been eliminated. Certain prior year amounts have been reclassified to conform to the current year
presentation.
In April 2014, Pitney Bowes of Canada Ltd., a wholly owned subsidiary, completed the sale of its Document Imaging Solutions (DIS)
business, which consisted of hardware (copiers and printers) and document management software solutions to Konica Minolta Business
Solutions (Canada) Ltd. and the related lease portfolio to a business equipment leasing services provider in two separate transactions.
Accordingly, the results of operations of DIS were reclassified as discontinued operations (see Note 3). The cash flows from discontinued
operations are not separately stated or reclassified in the accompanying Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows.
In 2013, we sold our Management Services business (PBMS), Nordic furniture business and International Mailing Services business
(IMS). Further, we made certain organizational changes and realigned our business units and segment reporting to reflect the clients we
serve, the solutions we offer, and how we manage, review, analyze and measure our operations. Historical results have been recast to
present the operating results of these divested businesses as discontinued operations and our segment results have been recast to conform
to the new segment reporting.
Use of Estimates
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with GAAP requires the use of estimates and assumptions that affect the reported
amounts of assets, liabilities, revenues, expenses and accompanying disclosures, including the disclosure of contingent assets and
liabilities. These estimates and assumptions are based on management's best knowledge of current events, historical experience and other
information available when the financial statements are prepared. These estimates include, but are not limited to, revenue recognition for
multiple element arrangements, goodwill and intangible asset impairment review, allowance for doubtful accounts and credit losses,
residual values of leased assets, useful lives of long-lived and intangible assets, restructuring costs, pensions and other postretirement
costs, income tax reserves, deferred tax asset valuation allowance, stock-based compensation expense and loss contingencies. Actual
results could differ from those estimates and assumptions.
Cash Equivalents and Short-Term Investments
Cash equivalents include short-term, liquid investments with maturities of three months or less at the date of purchase. Short-term
investments include investments with a maturity of greater than three months but less than one year from the reporting date.
Investment Securities
Investment securities that management has the positive intent and ability to hold to maturity are classified as held-to-maturity and are
carried at amortized cost. Investment securities not classified as held-to-maturity are classified as available-for-sale and recorded at fair
value, with unrealized gains and losses excluded from earnings and reported in other comprehensive income, net of tax. Purchase premiums
and discounts are recognized in interest income using the effective interest method over the terms of the securities. Gains and losses on
the sale of available-for-sale securities are recorded on the trade date and are determined using the specific identification method.
Investment securities are recorded in the Consolidated Balance Sheets as cash and cash equivalents, short-term investments and other
assets depending on the type of investment and maturity.
During 2014, we determined that for years ended December 31, 2013 and 2012 certain non-cash exchanges of investments were reported
as cash used for purchases of available-for-sale investment securities and cash provided by proceeds from sales/maturities of available-
for-sale investment securities. The Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows for the years ended December 31, 2013 and 2012 have been
revised in this Form 10-K by decreasing cash used for purchases of available-for-sale investment securities and cash provided by proceeds
from sales/maturities of available-for-sale investment securities by $28 million and $64 million, respectively. We have determined that
these adjustments are not material to our consolidated financial statements for any of the affected periods.
Accounts Receivable and Allowance for Doubtful Accounts
We estimate our accounts receivable risks and provide an allowance for doubtful accounts accordingly. We evaluate the adequacy of the
allowance based on historical loss experience, aging of receivables, adverse situations that may affect a customer's ability to pay and
prevailing economic conditions and make adjustments to the allowance as necessary. This evaluation is inherently subjective and actual
results may differ significantly from estimated reserves. Accounts receivable are generally due within 30 days after the invoice date.
Accounts deemed uncollectible are written off against the allowance after all collection efforts have been exhausted and management