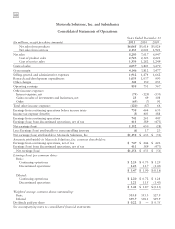
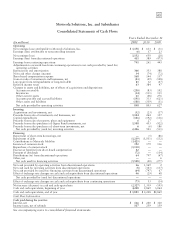
Motorola 2011 Annual Report Download - page 63
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 63 of the 2011 Motorola annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
57
labor, (j) the seasonality of the business, (k) the firmness of the segment’s backlog, (l) the competitiveness of the
patent portfolio, and (m) the impact of research and development; (2) “Properties,” about the consequences of a
disruption in manufacturing; (3) “Legal Proceedings,” about the ultimate disposition of pending legal matters and
timing; (4) “Management’s Discussion and Analysis,” about: (a) market growth/contraction, demand, spending and
resulting opportunities, (b) the return of capital to shareholders through dividends and/or repurchasing shares,
(c) the success of our business strategy and portfolio (d) future payments, charges, use of accruals and expected cost-
saving and profitability benefits associated with our reorganization of business programs and employee separation
costs, (e) our ability and cost to repatriate funds, including our ability to contribute cash to Motorola Mobility in
2012, (f) the impact of the timing and level of sales and the geographic location of such sales, (g) the impact of
maintaining inventory, (h) future cash contributions to pension plans or retiree health benefit plans, (i) our ability to
collect on our Sigma Fund and other investments, (j) our ability and cost to access the capital markets, (k) our
ability to borrow and the amount available under our credit facilities, (l) our ability to retire outstanding debt,
(m) our ability and cost to obtain performance related bonds, (n) adequacy of resources to fund expected working
capital and capital expenditure measurements, (o) expected payments pursuant to commitments under long-term
agreements, (p) the ability to meet minimum purchase obligations, (q) our ability to sell accounts receivable and the
terms and amounts of such sales, (r) the outcome and effect of ongoing and future legal proceedings, (s) the impact
of recent accounting pronouncements on our financial statements, (t) the impact of the loss of key customers, and
(u) the expected effective tax rate and deductibility of certain items; and (5) “Quantitative and Qualitative
Disclosures about Market Risk,” about: (a) the impact of foreign currency exchange risks, (b) future hedging
activity and expectations of the Company, and (c) the ability of counterparties to financial instruments to perform
their obligations.
Some of the risk factors that affect the Company’s business and financial results are discussed in “Item 1A:
Risk Factors.” We wish to caution the reader that the risk factors discussed in “Item 1A: Risk Factors,” and those
described elsewhere in this report or in our other Securities and Exchange Commission filings, could cause our
actual results to differ materially from those stated in the forward-looking statements.
Item 7A. Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk
Interest Rate Risk
As of December 31, 2011, we have $1.5 billion of long-term debt, including the current portion of long-term
debt, which is primarily priced at long-term, fixed interest rates. Of this total long-term debt amount, a $44 million
Euro-denominated variable interest loan has a hedge that changes the interest rate characteristics from variable to
fixed-rate. A hypothetical unfavorable movement of 10% in the interest rates would have an immaterial impact on
the hedge’s fair value.
Foreign Currency Risk
We use financial instruments to reduce our overall exposure to the effects of currency fluctuations on cash
flows. Our policy prohibits speculation in financial instruments for profit on exchange rate price fluctuations,
trading in currencies for which there are no underlying exposures, or entering into transactions for any currency to
intentionally increase the underlying exposure. Instruments that are designated as part of a hedging relationship
must be effective at reducing the risk associated with the exposure being hedged and are designated as part of a
hedging relationship at the inception of the contract. Accordingly, changes in the market values of hedge
instruments must be highly correlated with changes in market values of the underlying hedged items both at the
inception of the hedge and over the life of the hedge contract.
Our strategy related to foreign exchange exposure management is to offset the gains or losses on the financial
instruments against losses or gains on the underlying operational cash flows or investments based on our operating
assessment of risk. We enter into derivative contracts for some of our non-functional currency receivables and
payables, which are primarily denominated in major currencies that can be traded on open markets. We typically
use forward contracts and options to hedge these currency exposures. In addition, we enter into derivative contracts
for some forecasted transactions, which are designated as part of a hedging relationship if it is determined that the
transaction qualifies for hedge accounting under the provisions of the authoritative accounting guidance for
derivative instruments and hedging activities. A portion of our exposure is from currencies that are not traded in
liquid markets and these are addressed, to the extent reasonably possible, by managing net asset positions, product
pricing and component sourcing.