Kodak 2002 Annual Report Download - page 37
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 37 of the 2002 Kodak annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
Financials
37
CAUTIONARY STATEMENT PURSUANT TO SAFE HARBOR
PROVISIONS OF THE PRIVATE SECURITIES LITIGATION
REFORM ACT OF 1995
Certain statements in this report may be forward-looking in
nature, or “forward-looking statements” as defined in the United
States Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995. For
example, references to the Company’s revenue and cash flow
expectations for 2003 are forward-looking statements.
Actual results may differ from those expressed or implied in
forward-looking statements. The forward-looking statements
contained in this report are subject to a number of risk factors,
including the successful: implementation of product strategies
(including category expansion, digitization, OLED, and digital
products); implementation of intellectual property licensing
strategies; development and implementation of e-commerce
strategies; completion of information systems upgrades, including
SAP; completion of various portfolio actions; reduction of
inventories; improvement in manufacturing productivity;
improvement in receivables performance; reduction in capital
expenditures; improvement in supply chain efficiency; development
of the Company’s business in emerging markets like China, India,
Brazil, Mexico, and Russia. The forward-looking statements
contained in this report are subject to the following additional
risk factors: inherent unpredictability of currency fluctuations and
raw material costs; competitive actions, including pricing; the
nature and pace of technology substitution, including the analog-
to-digital shift; continuing customer consolidation and buying
power; general economic and business conditions; and other risk
factors disclosed herein and from time to time in the Company’s
filings with the Securities and Exchange Commission, including
but not limited to the items discussed in “Risk Factors” as set
forth in “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial
Condition and Results of Operations” in this report.
Any forward-looking statements in this report should be
evaluated in light of these important risk factors.
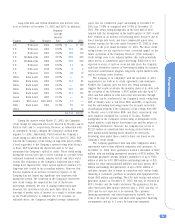
MARKET PRICE DATA
2002 2001
Price per share: High Low High Low
1st Quarter $ 34.30 $ 25.58 $ 46.65 $ 38.19
2nd Quarter 35.49 28.15 49.95 37.76
3rd Quarter 32.36 26.30 47.38 30.75
4th Quarter 38.48 25.60 36.10 24.40
SUMMARY OF OPERATING DATA
A summary of operating data for 2002 and for the four years
prior is shown on page 78.
QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE DISCLOSURES
ABOUT MARKET RISK
The Company, as a result of its global operating and financing
activities, is exposed to changes in foreign currency exchange
rates, commodity prices, and interest rates, which may adversely
affect its results of operations and financial position. In seeking
to minimize the risks and/or costs associated with such activities,
the Company may enter into derivative contracts.
Foreign currency forward contracts are used to hedge
existing foreign currency denominated assets and liabilities,
especially those of the Company’s International Treasury Center,
as well as forecasted foreign currency denominated intercompany
sales. Silver forward contracts are used to mitigate the
Company’s risk to fluctuating silver prices. The Company’s
exposure to changes in interest rates results from its investing
and borrowing activities used to meet its liquidity needs. Long-
term debt is generally used to finance long-term investments,
while short-term debt is used to meet working capital
requirements. An interest rate swap agreement was used to
convert some floating-rate debt to fixed-rate debt. The Company
does not utilize financial instruments for trading or other
speculative purposes.
Using a sensitivity analysis based on estimated fair value of
open forward contracts using available forward rates, if the U.S.
dollar had been 10% weaker at December 31, 2002 and 2001,
the fair value of open forward contracts would have increased
$13 million, and decreased $25 million, respectively. Such gains
or losses would be substantially offset by losses or gains from the
revaluation or settlement of the underlying positions hedged.
Using a sensitivity analysis based on estimated fair value of
open forward contracts using available forward prices, if available
forward silver prices had been 10% lower at December 31, 2002
and 2001, the fair value of open forward contracts would have
decreased $4 million and $11 million, respectively. Such losses in
fair value, if realized, would be offset by lower costs of
manufacturing silver-containing products.
The Company is exposed to interest rate risk primarily
through its borrowing activities and, to a lesser extent, through
investments in marketable securities. The Company utilizes U.S.
dollar denominated and foreign currency denominated borrowings
to fund its working capital and investment needs. The majority of
short-term and long-term borrowings are in fixed-rate
instruments. There is inherent roll-over risk for borrowings and
marketable securities as they mature and are renewed at current
market rates. The extent of this risk is not predictable because of
the variability of future interest rates and business financing
requirements.