Kia 2005 Annual Report Download - page 87
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 87 of the 2005 Kia annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
87
2005 Annual Report
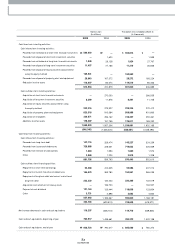
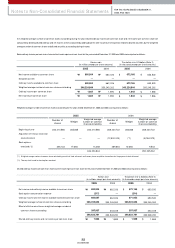
Before April 1999, the Com pany and its em ployees paid 3 percent and 6 percent, respectively, of monthly pay (as defined) to the National Pension Fund in accordance
with the National Pension Law of Korea. The Com pany paid half of the em ployees’ 6 percent portion and is paid back at the term ination of service by offsetting the
receivable against the severance payment. Such receivables, totalling ₩34,418 million (US
$33,976 thousand) and ₩39,691 million (US
$39,182 thousand) as of
Decem ber 31, 2005 and 2004, respectively, are presented as a deduction from accrued severance benefits. Since April 1999, according to a revision in the National
Pension Law, the Com pany and its employees each pay 4.5 percent of monthly pay to the Fund.
STOCK OPTIONS
The Com pany com putes total com pensation expense to stock options, which are granted to employees and directors, by fair value method using the option-pricing
model. The com pensation expense has been accounted for as a charge to current operations and a credit to capital adjustm ents from the grant date using the straight-
line m ethod.
DERIVATIVE INSTRUMENTS
All derivative instruments are accounted for at fair value with the valuation gain or loss recorded as an asset or liability. If the derivative instrum ent is not part of a
transaction qualifying as a hedge, the adjustm ent to fair value is reflected in current operations. The accounting for derivative transactions that are part of a qualified
hedge based both on the purpose of the transaction and on m eeting the specified criteria for hedge accounting differs depending on w hether the transaction is a fair
value hedge or a cash flow hedge. Fair value hedge accounting is applied to a derivative instrum ent designated as hedging the exposure to changes in the fair value of
an asset or a liability or a firm com mitm ent (hedged item ) that is attributable to a particular risk. The gain or loss both on the hedging derivative instrum ents and on the
hedged item attributable to the hedged risk is reflected in current operations. Cash flow hedge accounting is applied to a derivative instrument designated as hedging
the exposure to variability in expected future cash flow s of an asset or a liability or a forecasted transaction that is attributable to a particular risk. The effective portion of
gain or loss on a derivative instrum ent designated as a cash flow hedge is recorded as a capital adjustm ent and the ineffective portion is recorded in current operations.
The effective portion of gain or loss recorded as a capital adjustm ent is reclassified to current earnings in the sam e period during which the hedged forecasted
transaction affects earnings. If the hedged transaction results in the acquisition of an asset or the incurrence of a liability, the gain or loss in capital adjustm ent is added to
or deducted from the asset or the liability.
ACCOUNTING FOR FOREIGN CURRENCY TRANSACTIONS AND TRANSLATION
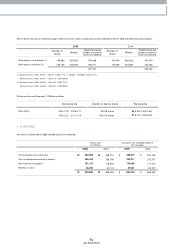
The Com pany maintains its accounts in Korea w on. Transactions in foreign currencies are recorded in Korean w on based on the prevailing rates of exchange on the
transaction date. Monetary accounts with balances denom inated in foreign currencies are recorded and reported in the accom panying non-consolidated financial
statem ents at the exchange rates prevailing at the balance sheet dates. The balances have been translated using the Basic Rate announced by Seoul Money Brokerage
Services, Ltd., which was ₩1,013.00 and ₩1,043.80 to US$1.00 at Decem ber 31, 2005 and 2004, respectively, and the translation loss and gain is reflected in current
operations.
INCOME TAX EXPENSE
The Com pany recognizes deferred incom e taxes. Accordingly, incom e tax expense is determ ined by adding or deducting the total income tax and surtaxes to be paid
for the current period and the changes in deferred incom e tax debits (credits). The difference betw een the income tax expense and the am ount of incom e tax show n in
the current period’s tax return will be offset against the deferred incom e tax credits (debits), w hich will occur in subsequent periods. The Com pany recognizes deferred
tax liabilities basically for all taxable tem porary differences, but recognizes deferred tax assets for all deductible tem porary differences to the extent that it is probable that
taxable profit will be available against which the deductible tem porary difference can be utilized. Also, the Com pany recognizes deferred tax assets for all deductible
tem porary differences arising from investm ents in subsidiaries and associates to the extent that it is probable that the tem porary difference will be reversed in the
foreseeable future and taxable profit will be available against which the tem porary difference can be utilized. In addition, current tax and deferred tax is charged or
credited directly to equity if the tax relates to items that are credited or charged directly to equity in the same or different period.
ORDINARY (NET) INCOME PER COMMON SHARE
Basic ordinary incom e per com m on share and net income per com mon share are com puted by dividing ordinary and net incom e available to com mon shareholders by