Kia 2005 Annual Report Download - page 72
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 72 of the 2005 Kia annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
72
KIA MOTORS
Management’s Discussion & Analysis
Profitability
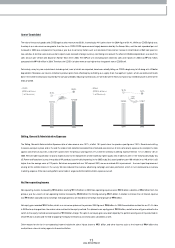
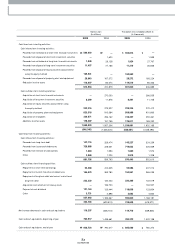
The 2005 operating margin was 0.5%, close to the break even point, and a significant drop off from 3.4% in 2004. The main reason behind this w as the depreciation
of the US dollar. During 2005 the average exchange rate w as 1,022 won, a decline of approxim ately 10% from 2004 in which the average exchange rate stood at
1,135 won. Exports accounted for almost 76% of our 2005 sales, so the rise of the Won hit us hard; the drop in our sales revenue due to the depreciation of the US
dollar reached alm ost ₩1.3 trillion. This problem w as aggravated by the fact that w e currently have only 1 plant overseas, located in China; dom estic plants
represent 91% of our production, and most of our expenses were incurred in Korean Won in 2005. This m ism atch betw een expenses mostly incurred in Won and
sales largely denom inated in US dollar directly hit our operating profit.
For 2006, we estimate the average exchange rate will hover around ₩950 per dollar. This suggests there may be a further 7% appreciation of the Won during 2006.
To counteract this ongoing fallout, w e are in the midst of increasing overseas production so that a large part of increm ental dem and in overseas markets such as
Europe, China and the US can be met by local production in overseas m arkets. With these ends in mind, from December 2006 production in the Slovak plant w ill
commence; production will also take place in the second half of 2007 in the second Chinese plant, follow ed by production in the U.S. plant during the first half of
2009. By 2010, our overseas plants will account for 41% of our total production. We also intend to transform ourselves into more of a high-profit, low -cost
organization. This will be achieved through increasing the average selling price (ASP) of our cars, coupled by cost-saving activities.
Apart from the exchange rate im pact, other causes of the fallen 2005 operating margin included a hike in raw m aterial and secondary parts costs, a shrinking RV
segm ent in the Korean market due to higher oil prices and tax, and the delayed launches of som e of our new models. Nevertheless, the major reason for the 2005
disappointing operating margin was the Korean Won appreciation.
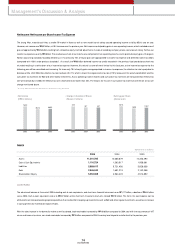
In 2005 the average selling price (ASP) per vehicle sold in the dom estic market was ₩15.5 million, a marginal rise over the previous year (₩15.4 million). Our export
ASP w as $12,300, an increase of 2.6% over the previous year ($12,000).
The m ain reason for the only slight increase in our dom estic ASP was that due to the hike of oil prices and the lifted tax breaks on RVs, the dom estic RV segm ent
shrank sharply, as a result, the sales of our large RVs like Sorento and Carnival dropped off quite a bit. The portion of our large RV sales to total sales fell steeply from
26.8% in 2004 to 16.5% in 2005, fortunately, this w as offset by an increase in our small SUV sales ; the portion of our sm all SUV Sportage, released in 2004, increased
from 11.0% to 21.5%. Given these changes in the sales mix, our dom estic ASP rem ained at a sim ilar level with 2004. How ever, new Carnival released in July 2005 and
a couple of new RV m odels (Sorento face-lift and new Carens) which w ill hit the market in 2006 make us confident that our ASP will rise significantly during 2006.
With regard to exports, the sales of m ini-car Morning in the passenger car segm ent increased greatly in Europe; 132,000 units w ere sold, representing an increase of
38.9% over the previous year. However, the sales of our m id-sized sedan Optima and premium mid-sized sedan Opirus fell by 32.4% and 38.2%, recording sales of
46,000 and 21,000 units respectively. This means that we sold more smaller-sized cars than larger-sized ones. In addition, within the RV segm ent, the launch of new
Carnival was delayed - its shipm ent com menced only after the 4th quarter. These and other factors kept our export ASP to $12,300, a modest rise of only 2.6%
compared to the previous year. In 2006, how ever, KIA expects to see sales rise as w ell as a boost to our export ASP, once we roll out new Carnival, new Carens, and
Sportage.
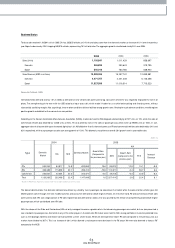
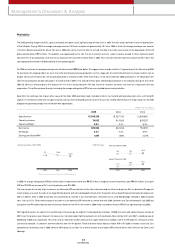
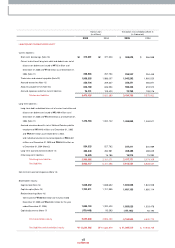
15,999,356
74,002
0.5%
680,904
4.3%
1,967
2005 2004 2003
15,257,742
513,063
3.4%
662,026
4.3%
1,890
12,839,881
805,537
6.3%
752,857
5.9%
2,078
Sales Revenue
Operating Incom e
Operating Margin
Net Incom e
Net Margin
Earnings per Share(KRW)
(Korean w on in m illions)
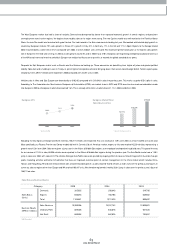
• Exchange Rate (USD/ KRW)
* Based on the Com pany's Transaction Exchange Rate
2003
1,192
2004
1,135
2005
1,022
• ASP Change
2003
15.1
2004
15.4
2005
15.5
11.2 12.0 12.3
Domestic(Million KRW)
Export(Thousand US$)