Kia 2005 Annual Report Download - page 85
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 85 of the 2005 Kia annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
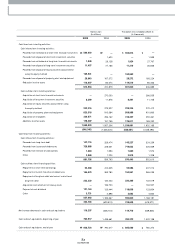
85
2005 Annual Report
INVESTMENTS IN SECURITIES OTHER THAN THOSE ACCOUNTED FOR USING THE EQUITY METHOD
Classification of Securities
At acquisition, the Com pany classifies securities into one of the three categories : trading, held-to-m aturity securities or available-for-sale. Trading securities are those that
were acquired principally to generate profit from short-term fluctuations in prices. Held-to-m aturity securities are those with fixed or determ inable paym ents and fixed
maturity that an enterprise has the positive intent and ability to hold to maturity. Available-for-sale securities are those not classified either as held-to-m aturity or trading
securities. Trading securities are classified as short term investm ent securities, whereas available-for-sale securities and held-to-m aturity securities are classified as long-
term investm ent securities, except for those w hose m aturity dates or whose likelihood of being disposed of are within one year from the balance sheet date, which are
classified as short-term investm ent securities.
Valuation of Securities
Investm ents in securities are initially measured at cost, which consists of the market price of the consideration given to acquire them and incidental expenses. If the
market price of the consideration given is not available, the m arket prices of the securities purchased are used as the basis for measurem ent. If neither the market price of
the consideration given nor those of the acquired securities are available, the acquisition cost is m easured at the best estim ates of its fair value.
After initial recognition, held-to-m aturity securities are valued at am ortized cost. The difference betw een their acquisition costs and face values is amortized over the
rem aining term of the securities by applying the effective interest method and added to or subtracted from the acquisition costs and interest incom e of the rem aining
period. Trading securities are valued at fair value, w ith unrealized gains or losses included in current operations. Available-for-sales securities are also valued at fair value,
with unrealized holding gains or losses recognized in capital adjustm ents, until the securities are sold or if the securities are determ ined to be impaired and the lum p-
sum cum ulative amount of capital adjustm ents are reflected in current operations. How ever, available-for-sales securities that are not traded in an active market and
whose fair value cannot be reliably measured are valued at cost.
If the estim ated recoverable amount of securities is less than the acquisition cost of equity securities or am ortized cost of debt securities and any objective evidence for
such im pairm ent loss exists, im pairm ent loss is recognized in current operations in the period when it arises.
EQUITY SECURITIES ACCOUNTED FOR USING THE EQUITY METHOD
Equity securities held for investm ent in com panies in which the Com pany is able to exercise significant influence over the operating and financial policies of the
investees are accounted for using the equity method. The Company’s share in the net incom e or net loss of investees is reflected in current operations. The changes in
the retained earnings, capital surplus or other capital accounts of investees are accounted for as an adjustm ent to retained earnings or to capital adjustm ents.
The difference betw een the cost of the investm ent and the investor’s share of the net fair value of the investee’s identifiable assets and liabilities at the date of acquisition
is amortized over 5 years for goodw ill or reversed over the rem aining weighted average useful life of the identifiable acquired depreciable assets for negative goodw ill,
using the straight-line m ethod. How ever, the differences occurred from additional purchases of investee’s shares or changes in ratio of shareholding due to capital
increase in investee are reflected in capital adjustm ents.
The Com pany’s portion of profits and losses resulting from inter-com pany transactions that are recognized in assets, such as inventories and fixed assets, are elim inated
and charged to equity securities accounted for using the equity method. How ever, unrealized profits and losses resulting from sales of assets from the Com pany to
investee are elim inated in full.
If an investor’s share of losses of an investee equals or exceeds its interest in the investee, the investor discontinues recognizing its share of further losses. If the investee
subsequently reports profits, the investor resum es recognizing its share of those profits only after its share of the profits equals the share of losses not recognized. Also, if
the recoverable amount of investments in investee becom es less than its carrying amount, the Com pany recognizes im pairm ent loss.
PROPERTY, PLANT AND EQUIPMENT AND RELATED DEPRECIATION
Property, plant and equipm ent are stated at cost, except for assets revalued upw ard in accordance with the Asset Revaluation Law of Korea. Routine maintenance and