HTC 2010 Annual Report Download - page 63
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 63 of the 2010 HTC annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
124 2 0 1 0 H T C A N N U A L R E P O R T 125
FINANCIAL INFORMATION
Income Tax
The Company applies intra-year and inter-year allocations for
its income tax, whereby (1) a portion of income tax expense
is allocated to the cumulative eect of changes in accounting
principles; and (2) deferred income tax assets and liabilities are
recognized for the tax eects of temporary dierences, unused
loss carryforward and unused tax credits. Valuation allowances
are provided to the extent, if any, that it is more likely than not
that deferred income tax assets will not be realized. A deferred
tax asset or liability is classified as current or noncurrent in
accordance with the classification of its related asset or liability.
However, if a deferred income tax asset or liability does not
relate to an asset or liability in the financial statements, then
it is classified as either current or noncurrent based on the
expected length of time before it is realized or settled.
Tax credits for purchases of machinery, equipment and
technology, research and development expenditures, and
personnel training expenditures are recognized using the flow-
through method.
Adjustments of prior years’ tax liabilities are added to or
deducted from the current year’s tax provision.
According to the Income Tax Law, an additional tax at 10% of
unappropriated earnings is provided for as income tax in the
year the stockholders approve to retain the earnings.
Treasury Stock
The Company adopted the Statement of Financial Accounting
Standards No. 30 - “Accounting for Treasury Stocks,” which
requires the treasury stock held by the Company to be
accounted for by the cost method. The cost of treasury stock
is shown as a deduction to arrive at stockholders’ equity,
while gain or loss from selling treasury stock is treated as an
adjustment to capital surplus.
When treasury stocks are sold and the selling price is above
the book value, the dierence should be credited to the capital
surplus - treasury stock transactions. If the selling price is
below the book value, the dierence should first be oset
against capital surplus from the same class of treasury stock
transactions, and any remainder should be debited to retained
earnings. The carrying value of treasury stocks should be
calculated using the weighted-average method.
When the Company's treasury stock is retired, the treasury
stock account should be credited, and the capital surplus -
premium on stock account and capital stock account should
be debited proportionately according to the share ratio. The
dierence should be credited to capital surplus or debited to
capital surplus and/or retained earnings.
Foreign Currencies
The financial statements of foreign operations are translated
into New Taiwan dollars at the following exchange rates:
a. Assets and liabilities - at exchange rates prevailing on the
balance sheet date;
b. Stockholders’ equity - at historical exchange rates;
c. Dividends - at the exchange rate prevailing on the dividend
declaration date; and
d. Income and expenses - at average exchange rates for the
year.
Exchange dierences arising from the translation of the
financial statements of foreign operations are recognized as a
separate component of stockholders’ equity. Such exchange
dierences are recognized as gain or loss in the year in which
the foreign operations are disposed of.
Nonderivative foreign-currency transactions are recorded in
New Taiwan dollars at the rates of exchange in eect when
the transactions occur. Exchange dierences arising from
the settlement of foreign-currency assets and liabilities are
recognized as gain or loss.
At the balance sheet date, foreign-currency monetary assets
and liabilities are revalued using prevailing exchange rates and
the exchange dierences are recognized in profit or loss.
At the balance sheet date, foreign-currency nonmonetary assets
(such as equity instruments) and liabilities that are measured at
fair value are revalued using prevailing exchange rates, with the
exchange dierences treated as follows:
a. Recognized in stockholders’ equity if the changes in fair
value are recognized in stockholders’ equity; and
b. Recognized in profit and loss if the changes in fair value is
recognized in profit or loss.
Foreign-currency nonmonetary assets and liabilities that are
carried at cost continue to be stated at exchange rates at the
trade dates.
If the functional currency of an equity-method investee is
a foreign currency, translation adjustments will result from
the translation of the investee’s financial statements into
the reporting currency of the Company. These adjustments
are accumulated and reported as a separate component of
stockholders’ equity.
Reclassifications
Certain 2009 accounts have been reclassified to be consistent
with the presentation of the financial statements as of and for
the year ended December 31, 2010.
3. TRANSLATION INTO U.S. DOLLARS
The financial statements are stated in New Taiwan dollars.
The translation of the 2010 New Taiwan dollar amounts into
U.S. dollar amounts are included solely for the convenience
of readers, using the noon buying rate of NT$29.13 to
US$1.00 quoted by the Bank of Taiwan on December 31,
2010. The convenience translation should not be construed
as representations that the New Taiwan dollar amounts have
been, could have been, or could in the future be, converted into
U.S. dollars at this or any other exchange rate.
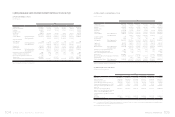
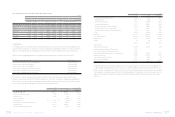
4. CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS
Cash and cash equivalents as of December 31, 2009 and 2010
were as follows:
2009 2010
NT$ NT$ US$(Note 3)
Cash on hand $ 1,000 $ 1,000 $ 34
Cash in banks 561,516 15,491,311 531,800
Time deposits 61,113,948 50,789,765 1,743,555
$ 61,676,464 $ 66,282,076 $ 2,275,389
On time deposits, interest rates ranged from 0.10% to 1.03%
and from 0.14% to 1.50%, as of December 31, 2009 and 2010,
respectively.
On preferential deposits, interest rates ranged from 0.10% to
0.70% and from 0.15% to 0.70% as of December 31, 2009 and
2010, respectively.
5. FINANCIAL ASSETS AND LIABILITIES AT FAIR
VALUE THROUGH PROFIT OR LOSS
Financial assets and liabilities at fair value through profit or loss
as of December 31, 2009 and 2010 were as follows:
2009 2010
NT$ NT$ US$(Note 3)
Derivatives -
financial assets Exchange
contracts $ 18,132 $ 450,276 $ 15,457
The Company had derivative transactions in 2009 and 2010
to manage exposures related to exchange rate fluctuations.
However, these transactions did not meet the criteria for
hedge accounting under Statement of Financial Accounting
Standards No. 34 - “Financial Instruments: Recognition and
Measurement.” Thus, the Company had no hedge accounting
in 2009 and 2010. Outstanding forward exchange contracts as
of December 31, 2009 and 2010 were as follows: