Energizer 2011 Annual Report Download - page 84
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 84 of the 2011 Energizer annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
ENERGIZER HOLDINGS, INC.
(Dollars in millions, except per share and percentage data)
Commodity Price Risk The Company uses raw materials that are subject to price volatility. At times, hedging instruments are
used by the Company to reduce exposure to variability in cash flows associated with future purchases of zinc or other
commodities. The fair market value of the Company's outstanding hedging instruments included in Accumulated other
comprehensive loss on the Consolidated Balance Sheets was an unrealized pre-tax loss of $6.2 and pre-tax gain of $1.0 at
September 30, 2011 and 2010, respectively. Over the next twelve months, approximately $5.6 of the loss included in
Accumulated other comprehensive loss will be recognized in earnings. Contract maturities for these hedges extend into fiscal
year 2013. There were 18 open contracts at September 30, 2011. These hedge contracts cover approximately 90% of estimated
zinc purchases in fiscal 2012.
Foreign Currency Risk A significant portion of Energizer’s product cost is more closely tied to the U.S. dollar than to the
local currencies in which the product is sold. As such, a weakening of currencies relative to the U.S. dollar, results in margin
declines unless mitigated through pricing actions, which are not always available due to the competitive environment.
Conversely, a strengthening in currencies relative to the U.S. dollar, and to a lesser extent, the Euro can improve margins. As a
result, the Company has entered into a series of forward currency contracts to hedge the cash flow uncertainty of forecasted
inventory purchases due to short term currency fluctuations. The Company’s primary foreign affiliates, which are exposed to
U.S. dollar purchases, have the Euro, the Japanese yen, the British pound, the Canadian dollar and the Australian dollar as their
local currencies. At September 30, 2011 and 2010, respectively, the Company had an unrealized pre-tax gain on these forward
currency contracts accounted for as cash flow hedges of $3.3 and unrealized pre-tax loss of $16.8 included in Accumulated
other comprehensive loss on the Consolidated Balance Sheets. Assuming foreign exchange rates versus the U.S. dollar remain
at September 30, 2011 levels, over the next twelve months, approximately $2.7 of the pre-tax gain included in Accumulated
other comprehensive loss will be included in earnings. Contract maturities for these hedges extend into fiscal year 2013. There
were 64 open contracts at September 30, 2011 with a total notional value of approximately $360.
Interest Rate Risk The Company has interest rate risk with respect to interest expense on variable rate debt. At September 30,
2011, the Company had $503.5 of variable rate debt outstanding. During fiscal 2009, the Company entered into interest rate
swap agreements with two major financial institutions that fixed the variable benchmark component (LIBOR) of the
Company’s interest rate on $300 of the Company’s variable rate debt through December 2012. At September 30, 2011 and
2010, respectively, the Company had an unrealized pre-tax loss on these interest rate swap agreements of $4.7 and $7.8
included in Accumulated other comprehensive loss on the Consolidated Balance Sheets.
Cash Flow Hedges The Company maintains a number of cash flow hedging programs, as discussed above, to reduce risks
related to commodity, foreign currency and interest rate risk. Each of these derivative instruments have a high correlation to the
underlying exposure being hedged and have been deemed highly effective for accounting purposes in offsetting the associated
risk.
Derivatives not Designated in Hedging Relationships The Company holds a share option with a major financial institution to
mitigate the impact of changes in certain of the Company’s deferred compensation liabilities, which are tied to the Company’s
common stock price. Period activity related to the share option is classified in the same category in the cash flow statement as
the period activity associated with the Company’s deferred compensation liability, which was cash flow from operations.
In addition, the Company enters into foreign currency derivative contracts which are not designated as cash flow hedges for
accounting purposes to hedge existing balance sheet exposures. Any losses on these contracts would be offset by exchange
gains on the underlying exposures; thus, they are not subject to significant market risk.
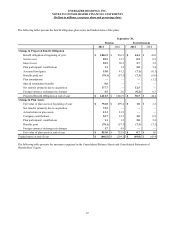
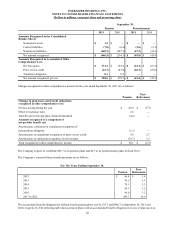
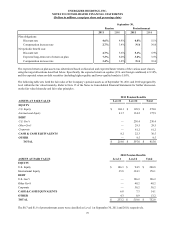
The following table provides fair values as of September 30, 2011 and 2010, and the amounts of gains and losses on derivative
instruments classified as cash flow hedges as of and for the twelve months ended September 30, 2011 and 2010, respectively.
Derivatives designated as
Cash Flow Hedging Relationships
Foreign currency contracts
Commodity contracts (6)
Interest rate contracts
Total
At September 30, 2011
Fair Value
Asset(Liability) (1) (2)
$ 3.3
(6.2)
(4.7)
$ (7.6)
For Twelve Months Ended
September 30, 2011
Gain/(Loss)
Recognized
in OCI(3)
$ (4.5)
(5.2)
3.1
$ (6.6)
Gain/(Loss)
Reclassified From
OCI into Income
(Effective Portion) (4) (5)
$ (24.6)
1.0
—
$ (23.6)
74