Energizer 2011 Annual Report Download - page 64
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 64 of the 2011 Energizer annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
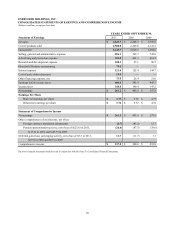
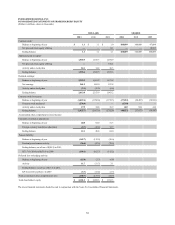
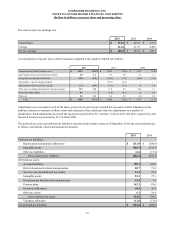
ENERGIZER HOLDINGS, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Dollars in millions, except per share and percentage data)
(1) Basis of Presentation and Use of Estimates
The financial statements include the accounts of the Company and its majority-owned subsidiaries. All significant
intercompany transactions are eliminated. The Company has no material equity method or variable interests.
Preparation of the financial statements in conformity with generally accepted accounting principles in the U.S. (GAAP)
requires Energizer Holdings, Inc. and its subsidiaries (the Company) to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported
amounts of assets and liabilities, disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities and the reported amounts of revenues and
expenses. On an ongoing basis, the Company evaluates its estimates, including those related to customer programs and
incentives, product returns, bad debts, inventories, intangible and other long-lived assets, income taxes, financing, pensions and
other postretirement benefits, contingencies and acquisitions. Actual results could differ from those estimates.
(2) Summary of Significant Accounting Policies
The Company's significant accounting policies, which conform to GAAP and are applied on a consistent basis among all years
presented, except as indicated, are described below.
Foreign Currency Translation - Financial statements of foreign operations where the local currency is the functional currency
are translated using end-of-period exchange rates for assets and liabilities, and average exchange rates during the period for
results of operations. Related translation adjustments are reported as a component within accumulated other comprehensive
income in the shareholders’ equity section of the Consolidated Balance Sheets.
For foreign operations that are considered highly inflationary, translation practices differ in that inventories, properties,
accumulated depreciation and depreciation expense are translated at historical rates of exchange, and translation adjustments
for monetary assets and liabilities are included in earnings. Gains and losses from foreign currency transactions are generally
included in earnings.
Effective January 1, 2010, the financial statements for our Venezuela subsidiary are consolidated under the rules governing the
translation of financial information in a highly inflationary economy based on the use of the blended National Consumer Price
Index in Venezuela. Under GAAP, an economy is considered highly inflationary if the cumulative inflation rate for a three year
period meets or exceeds 100 percent. If a subsidiary is considered to be in a highly inflationary economy, the financial
statements of the subsidiary must be re-measured into our reporting currency (U.S. dollar) and future exchange gains and losses
from the re-measurement of monetary assets and liabilities are reflected in current earnings, rather than exclusively in the
equity section of the balance sheet, until such time as the economy is no longer considered highly inflationary. For further
information regarding the Company’s Venezuela affiliate, see Note 5 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
Financial Instruments and Derivative Securities - The Company uses financial instruments, from time to time, in the
management of foreign currency, interest rate and other risks that are inherent to its business operations. Such instruments are
not held or issued for trading purposes.
Foreign exchange (F/X) instruments, including currency forwards, are used primarily to reduce transaction exposures and, to a
lesser extent, to manage other translation exposures. F/X instruments used are selected based on their risk reduction attributes
and the related market conditions. The Company has designated certain foreign currency contracts as cash flow hedges for
accounting purposes as of September 30, 2011.
The Company also holds a derivative instrument contract to mitigate the risk of its deferred compensation liabilities.
The Company uses raw materials that are subject to price volatility. The Company uses hedging instruments as it desires to
reduce exposure to variability in cash flows associated with future purchases of zinc or other commodities. These instruments
are designated as cash flow hedges for accounting purposes at September 30, 2011.
The Company has interest rate risk with respect to interest expense on variable rate debt. During fiscal 2009, the Company
entered into interest rate swap agreements which have been designated as cash flow hedges with two major financial
institutions that fixed the variable benchmark component (LIBOR) of the Company’s interest rate on $300 of the Company’s
variable rate debt through December 2012.
54