Entergy 2011 Annual Report Download - page 50
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 50 of the 2011 Entergy annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
MANAGEMENT’S FINANCIAL DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS continued
Entergy Gulf States Louisiana and Entergy Louisiana complied with
this order, but also filed a notice of objection and reservation of rights
in response to the order, stating that the testimony, as well as related
discovery and other proceedings, are not relevant to the decision to
join the MISO RTO. In the APSC proceeding regarding the MISO RTO
proposal, in February 2012 the APSC ordered the parties to consider
to what extent, if any, the proposed spin-off and merger of Entergy’s
transmission business might affect Entergy Arkansas’s membership
in an RTO or otherwise affect the proceeding. The next round of
testimony in the APSC proceeding is scheduled for March 2012.
In June 2011, MISO filed with the FERC a request for a transitional
waiver of provisions of its open access transmission, energy, and
operating reserve markets tariff regarding allocation of transmission
network upgrade costs, in order to establish a transition for the
integration of the Utility operating companies. Several parties
intervened in the proceeding, including Entergy, the APSC, the
LPSC, and the City Council, and some of the parties also filed
comments or protests. In September 2011 the FERC issued an order
denying on procedural grounds MISO’s request, further advising
MISO that submitting modified tariff sheets is the appropriate
method for implementing the transition that MISO seeks for the
Utility operating companies. The FERC did not address the merits
of any transition arrangements that may be appropriate to integrate
the Utility operating companies into the MISO RTO. MISO worked
with its stakeholders to prepare the appropriate changes to its tariff
and filed the proposed tariff changes with the FERC in November
2011. Numerous entities filed interventions and protests to MISO’s
filing. On January 25, 2012, the FERC sent a letter to MISO requesting
additional information relating to MISO’s proposed tariff changes.
NOTICE TO SERC RELIABILITY CORPORATION REGARDING
RELIABILITY STANDARDS AND FERC INVESTIGATION
Entergy has notified the SERC Reliability Corporation (SERC) of
potential violations of certain North American Electric Reliability
Corporation (NERC) reliability standards, including certain Critical
Infrastructure Protection, Facilities Design, Connection and
Maintenance, and System Protection and Control standards. Entergy
is working with the SERC to provide information concerning these
potential violations. In addition, FERC’s Division of Investigations
is conducting an investigation of certain issues relating to the Utility
operating companies compliance with certain Reliability Standards
related to protective system maintenance, facility ratings and modeling,
training, and communications. The Energy Policy Act of 2005 provides
authority to impose civil penalties for violations of the Federal Power
Act and FERC regulations.
U.S. DEPARTMENT OF JUSTICE INVESTIGATION
In September 2010, Entergy was notified that the U.S. Department
of Justice had commenced a civil investigation of competitive
issues concerning certain generation procurement, dispatch, and
transmission system practices and policies of the Utility operating
companies. The investigation is ongoing.
MARKET AND CREDIT RISK SENSITIVE
INSTRUMENTS
Market risk is the risk of changes in the value of commodity and
financial instruments, or in future net income or cash flows, in
response to changing market conditions. Entergy holds commodity
and financial instruments that are exposed to the following
significant market risks:
n The commodity price risk associated with the sale of electricity
by the Entergy Wholesale Commodities business.
n The interest rate and equity price risk associated with Entergy’s
investments in pension and other postretirement benefit trust
funds. See Note 11 to the financial statements for details
regarding Entergy’s pension and other postretirement benefit
trust funds.
n The interest rate and equity price risk associated with Entergy’s
investments in nuclear plant decommissioning trust funds,
particularly in the Entergy Wholesale Commodities business. See
Note 17 to the financial statements for details regarding Entergy’s
decommissioning trust funds.
n The interest rate risk associated with changes in interest rates
as a result of Entergy’s issuances of debt. Entergy manages its
interest rate exposure by monitoring current interest rates and
its debt outstanding in relation to total capitalization. See Notes 4
and 5 to the financial statements for the details of Entergy’s
debt outstanding.
The Utility business has limited exposure to the effects of market
risk because it operates primarily under cost-based rate regulation.
To the extent approved by their retail rate regulators, the Utility
operating companies hedge the exposure to natural gas price
volatility of their fuel and gas purchased for resale costs, which are
recovered from customers.
Entergy’s commodity and financial instruments are exposed
to credit risk. Credit risk is the risk of loss from nonperformance
by suppliers, customers, or financial counterparties to a contract
or agreement. Entergy is also exposed to a potential demand on
liquidity due to credit support requirements within its supply or
sales agreements.
Commodity Price Risk
POWER GENERATION
As a wholesale generator, Entergy Wholesale Commodities core
business is selling energy, measured in MWh, to its customers.
Entergy Wholesale Commodities enters into forward contracts with
its customers and sells energy in the day ahead or spot markets.
In addition to selling the energy produced by its plants, Entergy
Wholesale Commodities sells unforced capacity, which allows load-
serving entities to meet specified reserve and related requirements
placed on them by the ISOs in their respective areas. Entergy
Wholesale Commodities’ forward fixed price power contracts consist
of contracts to sell energy only, contracts to sell capacity only, and
bundled contracts in which it sells both capacity and energy. While the
terminology and payment mechanics vary in these contracts, each of
these types of contracts requires Entergy Wholesale Commodities to
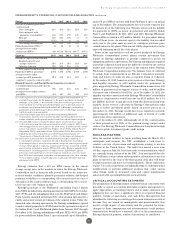
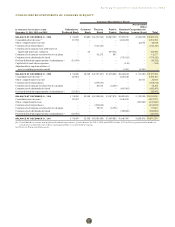
deliver MWh of energy, make capacity available, or both. The following
is a summary as of December 31, 2011 of the amount of Entergy
Wholesale Commodities’ nuclear power plants’ planned energy output
that is sold forward under physical or financial contracts:
48