Kia 2007 Annual Report Download - page 68
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 68 of the 2007 Kia annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
068_
Kia Motors Annual Report 2007
Presentation
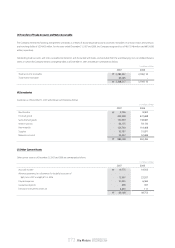
Trading securities are classified as current assets, whereas available-for-sale securities and held-to-maturity securities are classified as long-term investments.
However, available-for-sale securities whose maturity dates are due within one year from the balance sheet date or whose likelihood of being disposed of within
one year from the balance sheet date is probable are classified as current assets. Likewise, held-to-maturity securities whose maturity dates are due within one year
from the balance sheet date are classified as current assets.
Impairment
A decline in market value of any available-for-sale or held-to-maturity security below cost that is deemed to be other-than-temporary results in a reduction in
carrying amount to fair value and the impairment loss is charged to current results of operations.
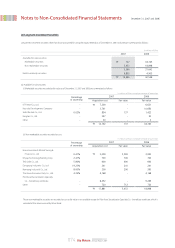
(i) Investments in Associates and Subsidiaries
Associates are all entities over which the Company has the ability to significantly influence the financial and operating policies and procedures, generally through 20
per cent to 50 per cent of the voting rights. Subsidiaries are entities controlled by the Company, generally through greater than 50 per cent voting rights.
Investments in associates and subsidiaries are accounted for using the equity method of accounting and are initially recognized at cost.
The Company’s investments in associates and subsidiaries include goodwill identified on acquisition (net of any accumulated impairment loss). Goodwill is
calculated as the excess of the acquisition cost of an investment in an associate or subsidiary over the Company’s share of the fair value of the identifiable net assets
acquired. Goodwill is amortized using the straight-line method over its estimated useful life. Amortization of goodwill is recorded together with equity income
(losses).
When events or circumstances indicate that the carrying value of goodwill may not be recoverable, the Company reviews goodwill for impairment and records any
impairment loss immediately in the statement of income.
The Company’s share of its post-acquisition profits or losses in investments in associates and subsidiaries is recognized in the income statement, and its share of
post-acquisition movements in equity is recognized in equity. The cumulative post-acquisition movements are adjusted against the carrying amount of each
investment. Changes in the carrying amount of an investment resulting from dividends by an associate or subsidiary are recognized when the associate or
subsidiary declares the dividend. When the Company’s share of losses in an associate or subsidiary equals or exceeds its interest in the associate or subsidiary,
including preferred stock or other long term loans and receivables issued by the associate or subsidiary, the Company does not recognize further losses, unless it
has incurred obligations or made payments on behalf of the associate or subsidiary.
Unrealized gains on transactions between the Company and its associates or subsidiaries are eliminated to the extent of the Company’s interest in each associate or
subsidiary.
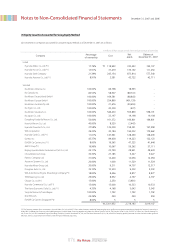
(j) Property, Plant and Equipment
Property, plant and equipment are stated at cost, except in the case of revaluation made in accordance the Asset Revaluation Law which allowed for asset
revaluation prior to the Law being revoked.
Significant additions or improvements extending useful lives of assets are capitalized. However, normal maintenance and repairs are charged to expense as
incurred.
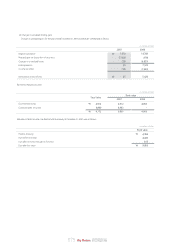
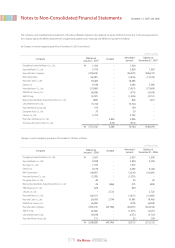
Depreciation is computed by the straight-line method over the estimated useful lives of the respective assets as follows:
December 31, 2007 and 2006
Notes to Non-Consolidated Financial Statements
Useful lives (years)
Buildings and structures
Machinery and equipment
Dies, molds and tools
Vehicles
Other equipment
20-40
15
5
5
5