Asus 2013 Annual Report Download - page 110
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 110 of the 2013 Asus annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
106
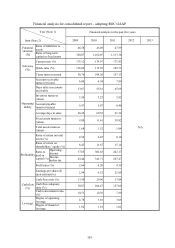
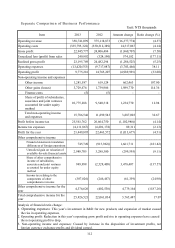
The root causes of the financial ratio change in the last two years:
Times interest earned: At the expiration of current CB, the reduction in amortized value decreased (the CB and
ECB issued by the company does not pay out relevant interests. However, to cooperate with the
regulations of new Financial Reporting, the amortized expense resulting from the discount on
b
onds is recognized as interest expense without the actual cash payout) has caused the interest
protection multiples to increase.
Ratio of return on total assets: The increase in this year’s net profit caused the return on total asset ratio to
increase.
Ratio of return on shareholders’ equity: Last year’s capital reduction and growing revenue causing the rise
ration of return on shareholders’ equity to rise.
Ratio of operating income to Paid-in capital: The increase in this year’s operating income was smaller than the
increase in additional paid-in capital caused the ratio of operating income to paid-in capital to
drop.
Cash flow ratio: This year’s revenue growth, increase in account receivable resulting from sales of goods, and
increase in inventory net balance have caused the net cash inflow from current operating
activities to drop, therefore the cash flow ratio declined accordingly.
Cash flow adequacy ratio: The competent authority actively controls the inventory quantity, causing reduction in
inventory increase in the last 5 years while the net cash inflow resulting from the total operating
activities in the last 5 years to rise, therefore the cash flow adequacy increased accordingly.
Cash reinvestment ratio: This year’s revenue growth, increase in account receivable resulting from sales of
goods, and increase in inventory net balance have caused the net cash inflow from current
operating activities to drop, when compared with last period.
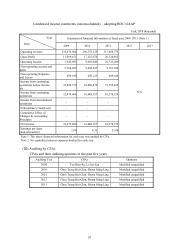
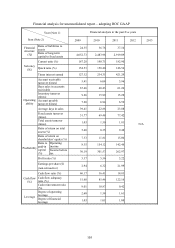
Note: The notes are the same as Financial analysis for consolidated report – adopting ROC GAAP
III. Supervisors’ report in the most recent years
ASUSTek Computer Inc.
SUPERVISORS’ REPORT
The Board of Director has prepared the Company’s 2013 business report, financial
statements and distribution of profits. All of the above have been reviewed and determined
to be correct and accurate by the undersigned. According to Article 219 of the Company Act,
we hereby submit this report.
ASUSTek Computer Inc.
Supervisors: Tze-Kaing Yang
Chung-Jen Cheng
L.H. Yang
March 27 2014