Qantas 2012 Annual Report Download - page 78
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 78 of the 2012 Qantas annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
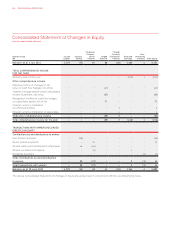
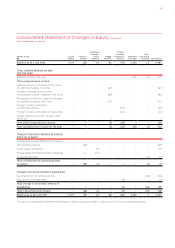
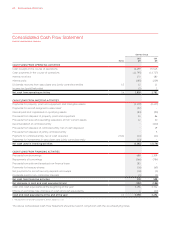
FOR THE YEAR ENDED 30 JUNE 2012
Notes to the Financial Statements continued
which is not depreciated. The depreciation
rates of owned assets are calculated so
as to allocate the cost or valuation of an
asset, less any estimated residual value,
over the asset’s estimated useful life to
the Qantas Group. Assets are depreciated
from the date of acquisition or, with
respect to internally constructed assets,
from the time an asset is completed
and available for use. The costs of
improvements to assets are depreciated
over the remaining useful life of the
asset or the estimated useful life of the
improvement, whichever is the shorter.
Assets under finance lease are
depreciated over the term of the relevant
lease or, where it is likely the Qantas
Group will obtain ownership of the asset,
the life of the asset.
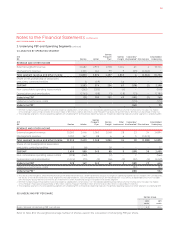
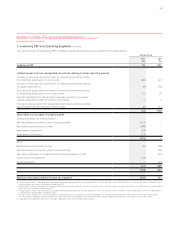
The principal asset depreciation periods
and estimated residual value
percentages are:
Years
Residual
Value (%)
Buildings
and leasehold
improvements –
Plant and equipment –
Passenger aircraft
and engines . – –
Freighter aircraft
and engines . – –
Aircraft spare parts – –
1 Certain leases allow for the sale of leasehold
improvements for fair value. In these instances
the expected fair value is used as the estimated
residual value.
Depreciation rates and residual values
are reviewed annually and reassessed
having regard to commercial and
technological developments, the
estimated useful life of assets to
the Qantas Group and the long-term
fleet plan.
Finance Leased and Hire
Purchase Assets
Leased assets under which the Qantas
Group assumes substantially all the risks
and benefits of ownership are classified
as finance leases. Other leases are
classified as operating leases.
Linked transactions involving the legal
form of a lease are accounted for as one
transaction when a series of transactions
are negotiated as one or take place
concurrently or in sequence and cannot
be understood economically alone.
Finance leases are capitalised. A lease
asset and a lease liability equal to the
present value of the minimum lease
payments and guaranteed residual
value are recorded at the inception
of the lease. Any gains and losses arising
under sale and leaseback arrangements
are deferred and depreciated over the
lease term. Capitalised leased assets
are depreciated on a straight-line basis
over the period in which benefits are
expected to arise from the use of those
assets. Lease payments are allocated
between the reduction in the principal
component of the lease liability and the
interest element.
The interest element is charged to the
Consolidated Income Statement over the
lease term so as to produce a constant
periodic rate of interest on the remaining
balance of the lease liability.
Fully prepaid leases are classified in
the Consolidated Balance Sheet as hire
purchase assets, to recognise that the
financing structures impose certain
obligations, commitments and/or restrictions
on the Qantas Group, which differentiate
these aircraft from owned assets.
Leases are deemed to be non-cancellable
if significant financial penalties associated
with termination are anticipated.
Operating Leases
Rental payments under operating leases
are charged to the Consolidated Income
Statement on a straight-line basis over
the term of the lease.
Any gains and losses arising under sale
and leaseback arrangements where the
sale price is at fair value are recognised
in the Consolidated Income Statement
as incurred. Where the sale price is
below fair value, any gains and losses
are immediately recognised in the
Consolidated Income Statement, except
where the loss is compensated for by
future lease payments at below market
price, it is deferred and amortised in
proportion to the lease payments over
the period for which the asset is expected
to be used. Where the sale price is above
fair value, the excess over fair value is
deferred and amortised over the period
for which the asset is expected to be used.
With respect to any premises rented
under long-term operating leases, which
are subject to sub-tenancy agreements,
provision is made for any shortfall between
primary payments to the head lessor less
any recoveries from sub-tenants. These
provisions are determined on a discounted
cash flow basis, using a rate reflecting
the cost of funds.
Maintenance and Overhaul Costs
An element of the cost of an acquired
aircraft (owned and finance leased
aircraft) is attributed to its service
potential, reflecting the maintenance
condition of its engines and airframe.
This cost is depreciated over the shorter
of the period to the next major inspection
event or the remaining life of the asset
or remaining lease term.
The costs of subsequent major cyclical
maintenance checks for owned and
leased aircraft (including operating
leases) are capitalised and depreciated
over the shorter of the scheduled usage
period to the next major inspection event
or the remaining life of the aircraft or
lease term (as appropriate).
Maintenance checks, which are covered
by the third party maintenance agreements
where there is a transfer of risk and legal
obligation, are expensed on the basis
of hours flown.
All other maintenance costs are expensed
as incurred.
Modifications that enhance the operating
performance or extend the useful lives of
aircraft are capitalised and depreciated
over the remaining estimated useful life
of the asset or remaining lease term (as
appropriate). Manpower costs in relation
to employees who are dedicated to major
modifications to aircraft are capitalised
as part of the cost of the modification to
which they relate.
With respect to operating lease agreements,
where the Qantas Group is required to
return the aircraft with adherence to
certain maintenance conditions, provision
1. Statement of Significant Accounting Policies continued
QANTAS ANNUAL REPORT 2012076