Qantas 2012 Annual Report Download - page 73
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 73 of the 2012 Qantas annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
FOR THE YEAR ENDED 30 JUNE 2012
Notes to the Financial Statements
Qantas Airways Limited (Qantas) is
a for-profit company limited by shares,
incorporated in Australia whose shares
are publicly traded on the Australian
Securities Exchange (ASX) and which
is subject to the operation of the Qantas
Sale Act as described in the Corporate
Governance Statement.
The Consolidated Financial Statements
for the year ended 30 June 2012 comprise
Qantas and its controlled entities (together
referred to as the Qantas Group) and the
Qantas Group’s interest in associates and
jointly controlled entities.
The Financial Statements of Qantas for the
year ended 30 June 2012 were authorised
for issue in accordance with a resolution
of the Directors on 14 September 2012.
A STATEMENT OF COMPLIANCE
The Consolidated Financial Statements
are general purpose financial statements
which have been prepared in accordance
with Australian Accounting Standards
(AASBs) adopted by the Australian
Accounting Standards Board and the
Corporations Act 2001. The Consolidated
Financial Statements also comply with
International Financial Reporting
Standards (IFRSs) and interpretations
adopted by the International Accounting
Standards Board.
B BASIS OF PREPARATION
The Consolidated Financial Statements
are presented in Australian dollars, which
is the functional currency of the Group,
and have been prepared on the basis
of historical cost except in accordance
with relevant accounting policies where
assets and liabilities are stated at their
fair values. Assets classified as held for
sale are stated at the lower of carrying
amount and fair value less costs to sell.
Qantas is a company of the kind referred
to in Australian Securities and Investments
Commission (ASIC) Class Order 98/100
dated 10 July 1998. In accordance with
that Class Order, all financial information
presented has been rounded to the nearest
million dollars, unless otherwise stated.
The accounting policies set out in Note 1
have been consistently applied to all
periods presented in the Consolidated
Financial Statements.
C CRITICAL ACCOUNTING ESTIMATES
AND JUDGEMENTS
The preparation of the Consolidated
Financial Statements in conformity with
AASBs requires management to make
judgements, estimates and assumptions
that affect the application of accounting
policies and reported amounts of assets,
liabilities, income and expenses. The
estimates and associated assumptions
are based on historical experience and
various other factors that are believed to
be reasonable under the circumstances,
the results of which form the basis for
making the judgements about carrying
values of assets and liabilities that are not
readily apparent from other sources. Actual
results may differ from these estimates.
Estimates and underlying assumptions
are reviewed on an ongoing basis.
Revisions to accounting estimates are
recognised in the period in which the
estimate is revised and in any future
periods affected. Judgements made by
management in the application of AASBs
that have a significant effect on the
Financial Statements and estimates with
a significant risk of material adjustment
in future periods are highlighted below.
Change in accounting estimates
– Discount Rates
Qantas has changed its estimate of
the discount rates used to calculate the
present value of provisions and employee
benefits in accordance with AASB 137:
Provisions, Contingent Liabilities and
Contingent Assets and AASB 119:
Employee Benefits respectively.
AASB 137 requires that where the effect
of the time value of money is material,
provisions should be discounted to their
present value at the end of the reporting
period using a pre-tax rate that reflects
current market assessments of the time
value of money and the risks specific to
the liability. AASB 119 requires employee
benefit provisions to be discounted to
their present value using a discount rate
determined by reference to market yields
at the end of the reporting period on
high quality corporate bonds. In countries
where there is no deep market for such
bonds, the market yields at the end of
the reporting period for government
bonds shall be used.
The discount rates were re-estimated due
to changes in market yields and the Group’s
assessment of the time value of money
and risk in accordance with AASB 137 and
AASB 119. In addition, when discounting
using government bond yields in
accordance with AASB 119, Qantas
now uses the State Government Bond
yields rather than Federal Government
Bond yields.
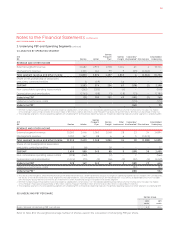
The changes in discount rates resulted in
a decrease in the Workers’ Compensation
provision of $15 million (2011: decrease
of $1 million) and an increase in the long
service leave provision of $45 million
(2011: decrease of $4 million). No other
provisions were materially impacted by
a change in the estimate of discount rates.
The net effect of these changes was a
$30 million increase in provisions as at
30 June 2012 (2011: decrease in provisions
of $5 million).
Change in accounting estimates
– Qantas Frequent Flyer
Qantas Frequent Flyer changed the
accounting estimates of the fair value
of points and breakage expectation
effective 1 January 2009. The effect of
this change was applied prospectively
from 1 January 2009 for new points issued.
Unredeemed points as at 1 January 2009
remained deferred at the previous
estimate and were redeemed at this
value until the points were extinguished.
The unredeemed points as at 1 January
2009 were extinguished during the year
(April 2011 for the Qantas Frequent Flyer
segment) on a first-in-first-out basis. As
a result, the revenue was recognised at
a lower average value per point redeemed
compared to the year ended 30 June 2011.
The effect of this difference was that
revenue was $5 million (2011: $172 million)
higher than it would have been had the
1 January 2009 unredeemed points been
redeemed at the weighted average
value per point prevailing at the time
of redemption.
D PRINCIPLES OF CONSOLIDATION
Controlled Entities
Controlled entities are entities controlled
by Qantas. Control exists when Qantas
has the power, directly or indirectly,
1. Statement of Significant Accounting Policies
071