Entergy 2002 Annual Report Download - page 70
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 70 of the 2002 Entergy annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
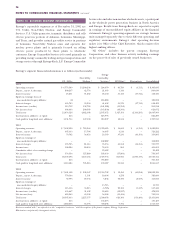
The planned construction and capital investments do not
include potential investments in new businesses or assets.
Entergy will also require $2.6 billion during the period 2003-
2005 to meet long-term debt and preferred stock maturities
and cash sinking fund requirements. Entergy plans to meet
these requirements primarily with internally generated funds
and cash on hand, supplemented by proceeds from the
issuance of debt and outstanding credit facilities. In the fourth
quarter of 2002, the U.S. Utility issued $640 million of debt
with maturities ranging from 2007 to 2032. Approximately
$71 million of the proceeds of the debt issued in the fourth
quarter were used to retire, in 2002, debt that was scheduled
to mature in 2003, and the remainder will be used to meet
certain 2003 maturities as they occur. Entergy Mississippi
issued an additional $100 million of debt in January 2003 that
matures in 2013. The proceeds will be used to repay, prior
to maturity, debt of Entergy Mississippi that is scheduled to
mature in 2003 and 2004. Certain domestic utility companies
may also continue the reacquisition or refinancing of all or a
portion of certain outstanding series of preferred stock and
long-term debt.
SALES WARRANTIES AND INDEMNITIES
In the CitiPower sales transaction, Entergy or its subsidiaries
made certain warranties to the purchaser. These warranties
include representations regarding litigation, accuracy of
financial accounts, and the adequacy of existing tax provisions.
The purchasers of CitiPower have asserted notice of claims
against Entergy under the terms of the Tax Warranty Deed
dated November 23, 1998 between them and Entergy. The Tax
Warranty Deed includes a reservation of rights relating to a
potential liability in the event of an adverse tax ruling. In
November 2002, the Australian Taxation Office assessed
CitiPower for taxes for the years 1997 through 1999.
Management believes it has adequately provided for the
ultimate resolution of this matter.
In the Saltend sales transaction, Entergy or its subsidiaries
made certain warranties to the purchasers relating primarily to
the performance of certain remedial work on the facility and the
assumption of responsibility for certain contingent liabilities.
Entergy believes that it has provided adequately for the warranties
as of December 31, 2002.
POWER PURCHASE AGREEMENTS
Entergy Louisiana has an agreement extending through the
year 2031 to purchase energy generated by a hydroelectric
facility known as the Vidalia project. Entergy Louisiana made
payments under the contract of approximately $104.2 million
in 2002, $86.0 million in 2001, and $58.6 million in 2000. If the
maximum percentage (94%) of the energy is made available to
Entergy Louisiana, current production projections would
require estimated payments of approximately $79.5 million in
2003, and a total of $2.7 billion for the years 2004 through
2031. Entergy Louisiana currently recovers the costs of the
purchased energy through its fuel adjustment clause. In an
LPSC-approved settlement related to tax benefits from the
treatment of the Vidalia contract, Entergy Louisiana agreed to
credit monthly rates by $11 million each year for up to ten
years, beginning in October 2002.
NUCLEAR INSURANCE
The Price-Anderson Act limits public liability of a nuclear
plant owner for a single nuclear incident to approximately
$9.5 billion. Protection for this liability is provided through a
combination of private insurance underwritten by American
Nuclear Insurers (ANI) (currently $300 million for each
reactor) and an industry assessment program. In addition,
liability arising out of terrorist acts will be covered by ANI sub-
ject to one industry aggregate limit of $300 million, with a
conditional option for one shared industry aggregate limit
reinstatement of $300 million. (There are no terrorism
limitations under the Price-Anderson Secondary Financial
Protection program, which responds upon the exhaustion of
ANI coverage). Under the assessment program, the maximum
payment requirement for each nuclear incident would be
$88.1 million per reactor, payable at a rate of $10 million per
licensed reactor per incident per year. Entergy has ten
licensed reactors, with five each in the U.S. Utility segment
and the Non-Utility Nuclear segment. As a co-licensee of
Grand Gulf 1 with System Energy, South Mississippi Electric
Power Agency (SMEPA) would share in 10% of this obligation.
In addition, each owner/licensee of Entergy’s ten nuclear
units participates in a private insurance program that provides
coverage for worker tort claims filed for bodily injury caused
by radiation exposure. The program provides for a maximum
assessment of approximately $3 million for each licensed reactor
in the event that losses exceed accumulated reserve funds.
Entergy’s nuclear owner/licensee subsidiaries are also
members of certain insurance programs that provide coverage
for property damage, including decontamination and prema-
ture decommissioning expense, to members’ nuclear generating
plants. These programs are underwritten by Nuclear Electric
Insurance, Limited (NEIL). As of December 31, 2002, Entergy
was insured against such losses up to $2.3 billion for each of its
nuclear units, except for Pilgrim and Vermont Yankee which are
insured for $1.115 billion in property damages. In addition,
Entergy’s nuclear owner/licensee subsidiaries are members of
the NEIL insurance program that covers certain replacement
power and business interruption costs incurred due to
prolonged nuclear unit outages. Under the property damage
and replacement power/business interruption insurance pro-
grams, these Entergy subsidiaries could be subject to assess-
ments if losses exceed the accumulated funds available to the
insurers. As of December 31, 2002, the maximum amounts of
such possible assessments were $81.4 million for the U.S. Utility
segment and $68.9 million for the Non-Utility Nuclear segment.
Entergy maintains property insurance for each of its nuclear
units in excess of the Nuclear Regulatory Commission’s (NRC)
minimum requirement for nuclear power plant licensees
of $1.06 billion per site. NRC regulations provide that
the proceeds of this insurance must be used, first, to
render the reactor safe and stable, and second, to complete
68
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS continued