Western Union 2007 Annual Report Download - page 20
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 20 of the 2007 Western Union annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.18
WESTERN UNION 2007 Annual Report
Industry Trends
We participate in a large and growing market for money transfer.
Growth in the money transfer business tends to correlate to
immigration and related employment rates worldwide. Therefore,
an indicator for future growth is the size of the international
migrant population, which to a certain extent follows economic
opportunity worldwide. According to The World Bank, the number
of worldwide immigrants is nearly 200 million or approximately
3% of the world’s population. The top three remittance markets
in the world, the countries of India, China and Mexico, each
receive $25 billion or more annually according to The World
Bank. We anticipate that demand for money transfer services
will continue to grow as people continue to migrate from their
country of origin.
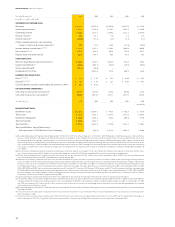
In 2007, consumers transferred $64 billion in consumer-to-
consumer transactions through our company in both cross-border
and intra-country transactions, of which $57 billion related to
cross-border transactions. Funds transferred through our agent
network have increased at a compound annual growth rate of
23% from 2005 to 2007, with cross-border money transfers
increasing at a compound annual growth rate of 27% during the
same period.
Another signifi cant trend impacting the money transfer
industry is the increase in regulation in recent years. Regulation
in the United States and elsewhere focuses, in part, on anti-money
laundering and anti-terrorist activities. Regulations require
money transfer providers, banks and other fi nancial institutions,
to develop systems to monitor and report appropriately on
certain transactions.
Competition
We face robust competition in the highly-fragmented consumer-
to-consumer money transfer industry. We compete with a variety
of money transfer service providers, including:
||
GLOBAL MONEY TRANSFER PROVIDERS —
Global money transfer
providers allow consumers to send money to a wide variety
of locations, in both their home countries and abroad.
||
REGIONAL MONEY TRANSFER PROVIDERS —
Regional money transfer
companies, or “niche” players, provide the same services as
global money transfer providers, but focus on a small group
of corridors or services within one region, such as North Amer-
ica to the Caribbean, Central or South America, or western
Europe to North Africa.
|| BANKS — Banks of all sizes compete with us in a number of
ways, including bank wire services and card-based services.
We believe that banks often use wire transfer services
and other money transfer methods to attract immigrant con-
sumers to their banks so they can sell them other services
and products.
|| INFORMAL NETWORKS — Informal networks enable people to
transfer funds without formal mechanisms, such as receipts,
and, often, without compliance with government reporting
requirements. However, we believe that such networks com-
prise a signifi cant share of the market.
|| ELECTRONIC COMMERCE — Online money transfer services
allowing consumers the ability to send and receive money
electronically using the internet.
||
ALTERNATIVE CHANNELS — Alternative channels, including mail
and commercial courier services, money transfers using mobile
phones, and card-based options, such as ATM cards and stored-
value cards, allow consumers to send or receive money.
The most signifi cant competitive factors in consumer-to-consumer
remittances relate to brand recognition, distribution network,
consumer experience and price.
For additional details regarding our consumer-to-consumer
segment, including fi nancial information regarding our interna-
tional and United States operations, see Management’s Discussion
and Analysis Financial Condition and Results of Operations and
our financial statements and the notes to those statements
included elsewhere in this Annual Report.
Consumer-to-Business Segment
We provide a portfolio of electronic and cash payment options
that provide consumers with fast and convenient ways to make
one-time or recurring payments to billers. Revenues from this
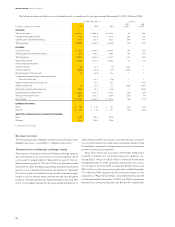
segment represented 15% of our revenue in 2007.
Operations
Our revenue in this segment is derived primarily from transaction
fees paid by the consumer or the biller. These fees are typically
less than the fees charged in our consumer-to-consumer segment.
In order to make an electronic payment, the consumer or biller
initiates a transaction over the telephone or the internet which
we process using the consumer’s credit card, debit card or ACH.
In order to make a cash payment, the consumer goes to an agent
location and makes the payment to the agent.
In addition, we generate revenue from upfront enrollment
fees received for our Equity Accelerator service, and we earn
investment income on funds received from services sold in advance
of settlement with payment recipients. The segment’s revenue
was primarily generated in the United States for all periods pre-
sented. No individual biller accounted for greater than 10% of
this segment’s revenue during all periods presented.
Services
Our consumer-to-business services strive to give consumers
choices as to the payment channel and method of payment, and
include the following:
ELECTRONIC PAYMENTS. Consumers use our Speedpay service
principally in the United States to make payments to a variety of
billers using credit cards, debit cards and ACH. Payments are
initiated over the telephone or the internet.
Our Equity Accelerator service is provided in the mortgage
service industry, enabling consumers to make mortgage payments
by ACH. It is marketed as a convenient way for homeowners to
schedule additional recurring principal payments on their mort-
gages. Consumers who enroll in this service make mortgage
payments based on a customized payment program, which results
in interest savings and a lower mortgage balance.