Vodafone 2001 Annual Report Download - page 65
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 65 of the 2001 Vodafone annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
Vodafone Group Plc
Annual Report & Accounts
for the year ended
31 March 2001
63
UNITED STATES ACCOUNTING PRINCIPLES continued
Min ority in terests
The adjustments in respect of minority interests relate to provisions for deferred tax which have been recognised for US GAAP purposes by a less
than 100% owned subsidiary undertaking.
Oth er adju stm en ts
Licence fee amortisation – Under UK GAAP, Vodafone has adopted a policy of amortising licence fees in proportion to the expected usage of the
network during the start up period and then on a straight line basis. Under US GAAP, licence fees are amortised on a straight line basis from the
date that operations commence to the date the licence expires.
Pension costs – Under both UK GAAP and US GAAP pension costs are provided so as to provide for future pension liabilities. However, there are
differences in the prescribed methods of valuation, which give rise to GAAP adjustments to the pension cost and the pension prepayment.
Defeasance of liabilities – Under UK GAAP, liabilities which have been unconditionally satisfied by monetary assets placed in trust and other set
off arrangements are considered to be extinguished. Under US GAAP, the offsetting of assets and liabilities is generally not allowed and, therefore,
the non-recognition of a liability is permissible only if the liability has been legally extinguished.
Capitalisation of computer software costs – Under UK GAAP, costs that are directly attributable to the development of computer software for
continuing use in the business, whether purchased from external sources or developed internally, are capitalised. Under US GAAP data conversion
costs and costs incurred during the research stage of software projects are not capitalised.
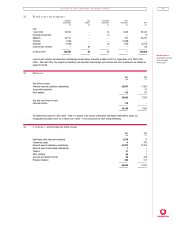
Gain on disposal of fixed assets and fixed asset investments – Under US GAAP, the net gain on disposal of fixed assets and fixed asset
investments of £6m and £6m, respectively (2000 – £Nil and £954m) would be included within operating income.
Investments in own shares – Investments in the Company’s own shares are included within other fixed asset investments under UK GAAP. US
GAAP requires investments in own shares to be shown as a deduction from equity.
Prop osed dividen ds
Under UK GAAP, final dividends are included in the financial statements when recommended by the Board of directors to the shareholders
in respect of the results for a financial year. Under US GAAP, dividends are included in the financial statements when declared by the Board
of directors.
Equity accoun tin g
UK GAAP requires the investor’s share of operating profit or loss, exceptional items and interest income or expense of associated undertakings
and joint ventures to be shown separately from those of the Group on the face of the profit and loss account. The charges for interest and
taxation for associated undertakings and joint ventures may be aggregated within the Group interest and taxation amounts shown on the face of
the profit and loss account, but must be disclosed in the notes to the accounts. The Group’s share of the turnover of joint ventures and associated
undertakings is also permitted to be disclosed on the face of the profit and loss account. In addition, the Group’s share of gross assets and gross
liabilities of joint ventures are shown on the face of the consolidated balance sheet. Under US GAAP, the after-tax profits or losses (i.e. operating
results after exceptional items, interest and taxation) are included in the income statement as a single line item and the investments in associated
undertakings and joint ventures are included in the consolidated balance sheet as a single line item. US GAAP does not permit the Group’s share
of turnover of joint ventures and associated undertakings to be disclosed on the face of the income statement, nor does it permit the Group’s
share of gross assets and gross liabilities of joint ventures to be shown on the face of the consolidated balance sheet.
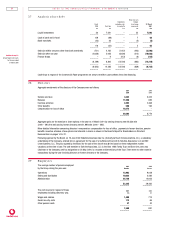
Earn in gs per ordin ary sh are
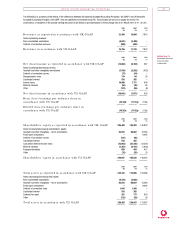
Earnings per ordinary share information is calculated based on:
2001 2001 2000
$m £m £m
Net (loss)/income in accordance with US GAAP (10,041) (7,071) 553
Weighted average number of ordinary shares in issue 61,439 61,439 27,100
Basic (loss)/earnings per ordinary share (16.34)¢ (11.51)p 2.04p
Diluted weighted average number of ordinary shares 61,398 61,398 27,360
Diluted (loss)/earnings per ordinary share (16.35)¢ (11.52)p 2.02p
The presentation of adjusted basic earnings per share is not permitted under US GAAP.