Samsung 2010 Annual Report Download - page 27
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 27 of the 2010 Samsung annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.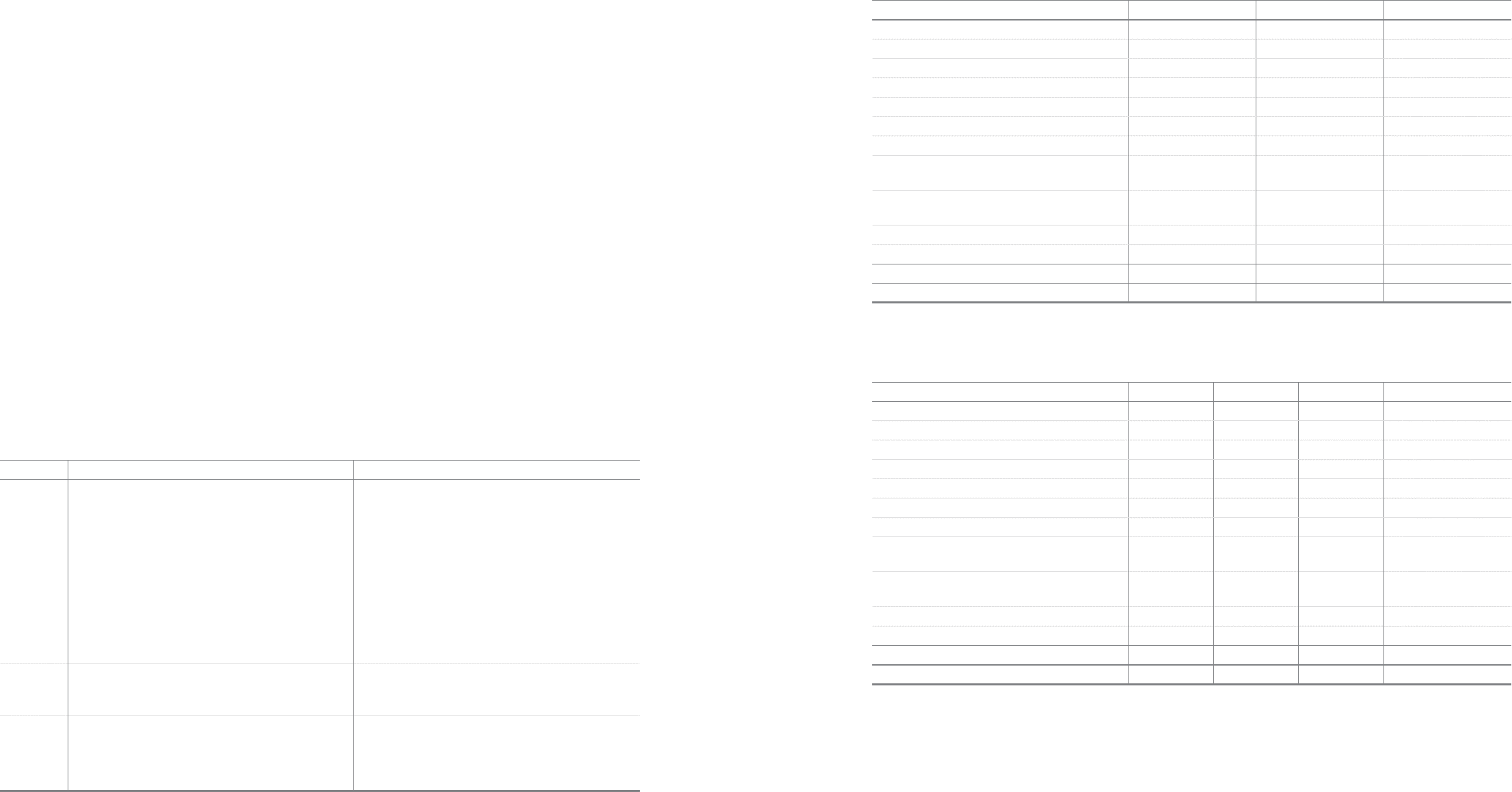
50 51
NOTES TO THE CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
3) Capitalization of development costs
Under Korean GAAP the Company recorded expenditures related to research and development activities as current expense. Under Korean
IFRS if such costs related to development activities meet certain criteria they are recorded as intangible assets.
4) Goodwill or bargain purchase arising from business combinations
Under Korean GAAP, the Company amortizes goodwill or recognizes a gain in relation to bargain purchase (negative goodwill1) acquired as
a result of business combinations on a straight-line method over five years from the year of acquisition. Under Korean IFRS, goodwill is not
amortized but reviewed for impairment annually. Bargain purchase is recognized immediately in the statement of income. The impact of this
adjustment is included within “other” adjustment in the tables below.
5) Derecognition of financial assets
Under Korean GAAP, when the Company transferred a financial asset to financial institutions and it was determined that control over the
asset has been transferred the Company derecognized the financial asset. Under Korean IFRS, if the Company retains substantially all the
risks and rewards of ownership of the asset, the asset is not derecognized but instead the related cash proceeds are recognized as financial
liabilities.
6) Deferred tax
Under Korean GAAP, deferred tax assets and liabilities were classified as either current or non-current based on the classification of their
underlying assets and liabilities. If there are no corresponding assets or liabilities, deferred tax assets and liabilities were classified based on
the periods the temporary differences were expected to reverse. Under Korean IFRS, deferred tax assets and liabilities are all classified as
non-current on the statement of financial position.
In addition, there is a difference between Korean IFRS and Korean GAAP in terms of recognition of deferred tax assets or liabilities relating to
investments in subsidiaries. Under Korean GAAP there is specific criteria as to when deferred tax assets and liabilities relating to investments
in subsidiaries should be recognized, whereas under Korean IFRS, the related deferred tax assets or liabilities are recognized according to
sources of reversal of the temporary differences.
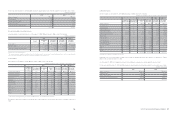
7) Changes in scope of consolidation
At the date of transition, changes in the scope of consolidation as a result of adoption of Korean IFRS are as follows:
Changes Description Name of entity
Newly
added
Under the former ‘Act on External Audit of Stock companies’
in the Republic of Korea, companies those whose total assets are
less than 10 billion Korean Won were not subject to consideration,
but they are subject to consolidation under Korean IFRS.
World Cyber Games,
Samsung Electronics Football Club,
SEMES America, Samsung Electronics Ukraine,
Samsung Electronics Romania,
Samsung Electronics Kazakhstan,
Samsung Electronics Czech and Slovak s.r.o.
Samsung Electronics Levant,
Samsung Electronics European Holding,
Batino Realty Corporation,
Samsung Telecommunications Malaysia,
Samsung Electronics Shenzhen,
Samsung Electronics China R&D Center,
Samsung Electronics Limited,
Samsung Electronics Poland Manufacturing,
Samsung Telecoms (UK)
Newly
added
Under Korean GAAP, a union is not regarded as a legal entity and
excluded from scope of consolidation. However, it is subject to
consolidation under Korean IFRS.
Samsung Venture Capital Union #6, #7 and #14
Excluded
Under Korean GAAP, entities where the Company owns more
than 30% of shares and is the largest shareholder with the largest
voting rights were included in scope of consolidation. Under Korean
IFRS, such entities are not subject to consolidation unless control
over the entity is established.
Samsung Card
1 Negative goodwill under Korean GAAP is referred to as bargain purchase under Korean IFRS
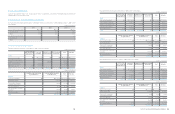
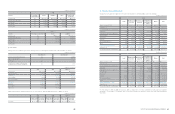
The effects of the adoption of Korean IFRS on financial position, Comprehensive income and cash flows of the Company
(a) Adjustments to the statement of financial position as of the date of transition, January 1, 2009.
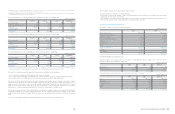
(b) The effect of the adoption of Korean IFRS on financial position and comprehensive income of the Company as of and for the year
ended December 31, 2009.
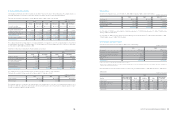
(c) Adjustments to the statement of cash flows for the year ended December 31, 2009
According to Korean IFRS 1007, Cash Flow Statements, cash flows from interest, dividends received and taxes on income shall each be
disclosed separately. The comparison year, 2009, is restated in accordance with Korean IFRS. There are no other significant differences
between cash flows under Korean IFRS and those under previous Korean GAAP for the year ended December 31, 2009.
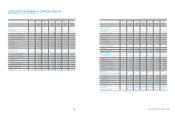
Assets Liabilities Equity Comprehensive income
Korean GAAP
₩
118,281,488
₩
45,227,196
₩
73,054,292
₩
9,700,671
Adjustments:
Change in scope of consolidation (10,120,256) (7,372,830) (2,747,426) (489,504)
Fair valuation of land (*) 3,804,404 924,525 2,879,879 (9,273)
Derecognition of financial assets 754,969 754,969 - -
Capitalization of development costs 214,451 - 214,451 13,973
Pension and compensated absence - 153,357 (153,357) 33,621
Deferred tax on investments in equity and
reclassification to non-current (874,056) (564,016) (310,040) (200,099)
Effect of the adoption of IFRS for jointly
controlled entities and associates 266,742 - 266,742 111,579
Other (143,058) - (143,058) (47,994)
Tax-effect on adjustments (4,895) 11,386 (16,281) (14,130)
Total (6,101,699) (6,092,609) (9,090) (601,827)
Korean IFRS
₩
112,179,789
₩
39,134,587
₩
73,045,202
₩
9,098,844
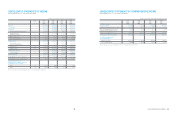
Assets Liabilities Equity
Korean GAAP
₩
105,300,650
₩
42,376,696
₩
62,923,954
Adjustments:
Change in scope of consolidation (12,972,168) (10,649,400) (2,322,768)
Fair valuation of land (*) 3,816,293 927,141 2,889,152
Derecognition of financial assets 1,807,675 1,807,675 -
Capitalization of development costs 200,478 - 200,478
Pension and compensated absence - 186,978 (186,978)
Deferred tax on investments in equity and
reclassification to non-current (1,434,287) (1,332,886) (101,401)
Effect of the adoption of IFRS for jointly
controlled entities and associates 155,163 - 155,163
Other (95,064) - (95,064)
Tax-effect on adjustments (141) 2,010 (2,151)
Total (8,522,051) (9,058,482) 536,431
Korean IFRS
₩
96,778,599
₩
33,318,214
₩
63,460,385
(In millions of Korean Won)
(In millions of Korean Won)
(*) The adjustment includes the effect of deferred tax
(*) The adjustment includes the effect of deferred tax