Proctor and Gamble 2016 Annual Report Download - page 69
Download and view the complete annual report
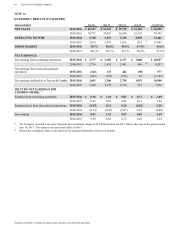
Please find page 69 of the 2016 Proctor and Gamble annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.The Procter & Gamble Company 55
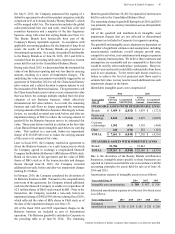
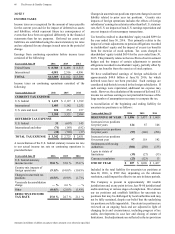
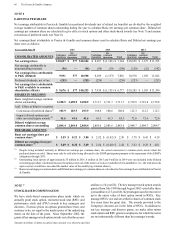
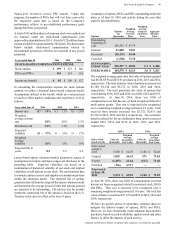
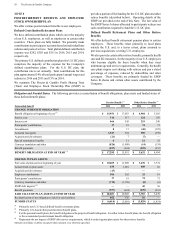
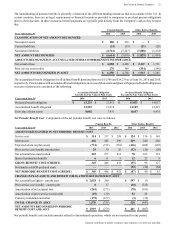
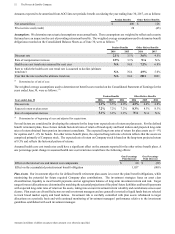
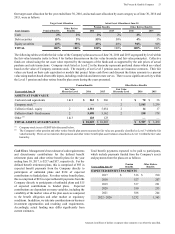
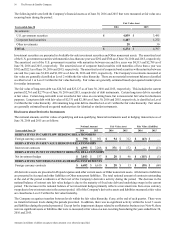
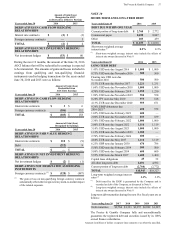
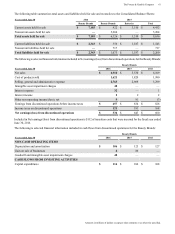
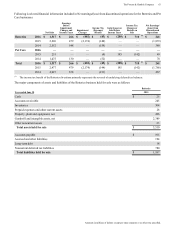
Amounts in millions of dollars except per share amounts or as otherwise specified.
Interest rate swaps that meet specific accounting criteria are
accounted for as fair value or cash flow hedges. For fair value
hedges, the changes in the fair value of both the hedging
instruments and the underlying debt obligations are
immediately recognized in Interest expense. For cash flow
hedges, the effective portion of the changes in fair value of the
hedging instrument is reported in OCI and reclassified into
Interest expense over the life of the underlying debt obligation.
The ineffective portion for both cash flow and fair value
hedges, which was not material for any year presented, was
immediately recognized in Interest expense.
Foreign Currency Risk Management
We manufacture and sell our products and finance our
operations in a number of countries throughout the world. As
a result, we are exposed to movements in foreign currency
exchange rates.
To manage the exchange rate risk primarily associated with the
financing of our operations, we have historically used a
combination of forward contracts, options and currency swaps.
As of June 30, 2016, we had currency swaps with original
maturities up to five years, which are intended to offset the
effect of exchange rate fluctuations on intercompany loans
denominated in foreign currencies. These swaps are accounted
for as cash flow hedges. The effective portion of the changes
in fair value of these instruments is reported in OCI and
reclassified into SG&Aand Interest expense in the same period
or periods during which the related hedged transactions affect
earnings. The ineffective portion, which was not material for
any year presented, was immediately recognized in SG&A.
The change in fair values of certain non-qualifying instruments
used to manage foreign exchange exposure of intercompany
financing transactions and certain balance sheet items subject
to revaluation are immediately recognized in earnings,
substantially offsetting the foreign currency mark-to-market
impact of the related exposures.
Net Investment Hedging
We hedge certain net investment positions in foreign
subsidiaries. To accomplish this, we either borrow directly in
foreign currencies and designate all or a portion of the foreign
currency debt as a hedge of the applicable net investment
position or we enter into foreign currency swaps that are
designated as hedges of net investments. Changes in the fair
value of these instruments are recognized in OCI to offset the
change in the value of the net investment being hedged. The
ineffective portion of these hedges, which was not material in
any year presented, was immediately recognized in Interest
expense.
Commodity Risk Management
Certain raw materials used in our products or production
processes are subject to price volatility caused by weather,
supply conditions, political and economic variables and other
unpredictable factors. To manage the volatility related to
anticipated purchases of certain of these materials, we have
historically, on a limited basis, used futures and options with
maturities generally less than one year and swap contracts with
maturities up to five years. As of and during the years ended
June 30, 2016 and 2015, we did not have any commodity
hedging activity.
Insurance
We self-insure for most insurable risks. However, we purchase
insurance for Directors and Officers Liability and certain other
coverage where it is required by law or by contract.
Fair Value Hierarchy
Accounting guidance on fair value measurements for certain
financial assets and liabilities requires that financial assets and
liabilities carried at fair value be classified and disclosed in
one of the following categories:
• Level 1: Quoted market prices in active markets for
identical assets or liabilities.
• Level 2: Observable market-based inputs or unobservable
inputs that are corroborated by market data.
• Level 3: Unobservable inputs reflecting the reporting
entity's own assumptions or external inputs from inactive
markets.
When applying fair value principles in the valuation of assets
and liabilities, we are required to maximize the use of quoted
market prices and minimize the use of unobservable inputs.
The Company has not changed its valuation techniques used
in measuring the fair value of any financial assets or liabilities
during the year. Our fair value estimates take into consideration
the credit risk of both the Company and our counterparties.
When active market quotes are not available for financial assets
and liabilities, we use industry standard valuation models.
Where applicable, these models project future cash flows and
discount the future amounts to a present value using market-
based observable inputs including credit risk, interest rate
curves, foreign currency rates and forward and spot prices for
currencies. In circumstances where market-based observable
inputs are not available, management judgment is used to
develop assumptions to estimate fair value. Generally, the fair
value of our Level 3 instruments is estimated as the net present
value of expected future cash flows based on external inputs.