Pottery Barn 2004 Annual Report Download - page 99
Download and view the complete annual report
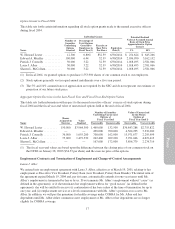
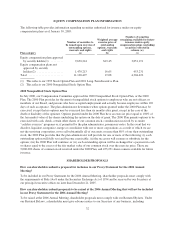
Please find page 99 of the 2004 Pottery Barn annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.• The aggregate total of all outstanding options and awards; and
• The relative value of awards offered by comparable companies to executives in comparable positions.
Special additional stock options may be granted or approved from time to time to executive officers in
connection with promotions, assumption of additional responsibilities and other factors.
Under the company’s existing stock option plans, the exercise price of all stock options is not less than 100% of
the fair market value of the stock (based on the closing sales price of the company’s common stock on the last
market trading day prior to the date of the option grant) or not less than 110% of such fair market value for an
incentive stock option granted to a shareholder with greater than 10% of the voting power of all company stock.
Options granted pursuant to the company’s stock option plans generally vest in five equal annual installments. It
is the company’s policy not to reprice stock options in the event that the fair market value of the common stock
falls below the exercise price of the stock options and not to engage in a stock option exchange program.
How is the Chief Executive Officer compensated?
We determined Edward A. Mueller’s compensation package based, in part, on:
• A review of the compensation paid to chief executive officers of comparable companies (based on the
process described above);
• The compensation packages historically paid to the company’s Chief Executive Officer; and
• Our general compensation philosophy as described above.
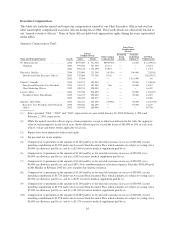
Mr. Mueller’s compensation package for fiscal 2004 included a base salary of $975,000 and a bonus of $731,300.
The bonus portion of Mr. Mueller’s compensation was based on a formula linked to the company’s earnings
performance and Mr. Mueller’s individual performance. As noted previously, Mr. Mueller was paid a full bonus
under the company’s 2001 Incentive Bonus Plan because the Company Objective was exceeded. Since the
performance levels of Mr. Mueller and the company exceeded the company’s targeted goals, the Compensation
Committee determined it also was appropriate to pay Mr. Mueller an additional bonus outside of the 2001
Incentive Bonus Plan. As a result, Mr. Mueller received a bonus under the 2001 Incentive Bonus Plan of
$516,370 plus an additional discretionary bonus of $214,930. Mr. Mueller’s base salary fell within the third
quartile of base salaries paid to chief executive officers at comparable companies, and his bonus fell within the
third quartile with respect to the same group. Together, base salaries and the bonus target place annual cash
compensation within the third quartile of similarly situated executive officers at comparable companies. Mr.
Mueller receives no additional material compensation or benefits not provided to all executives.
Are there any other compensation considerations?
The Company believes its benefit programs generally should be comparable for all employees. However, we
recommend additional benefits for certain individuals from time to time if we determine that the category and
amount of such benefits are reasonable and necessary to provide additional incentives to attract or retain key
executives.
How does the Compensation Committee address Internal Revenue Code Section 162(m)?
Under Section 162(m) of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended, and regulations adopted under it by
the Internal Revenue Service, publicly held companies may be precluded from deducting certain compensation
paid to certain executive officers in excess of $1.0 million in a year. The regulations exclude from this limit
performance-based compensation and stock options, provided certain requirements, such as shareholder
approval, are satisfied. Exceptions to this deductibility limit may be made for various forms of “performance-
based” compensation. The company believes that awards granted under the company’s equity incentive plans can
be excluded from the $1.0 million limit. We believe that bonuses awarded under the 2001 Incentive Bonus Plan
are excluded from calculating the limit. However, the additional, discretionary bonuses granted outside of the
2001 Incentive Bonus Plan to our Chief Executive Officer and four other most highly compensated officers are
22