Pentax 2009 Annual Report Download - page 67
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 67 of the 2009 Pentax annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
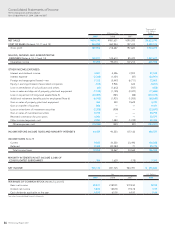
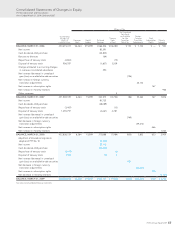
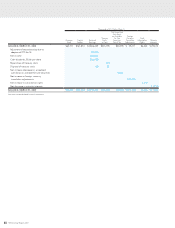
65
HOYA Annual Report 2009
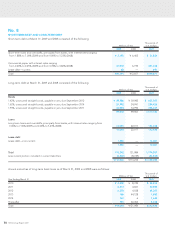
No. 3
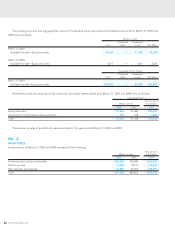
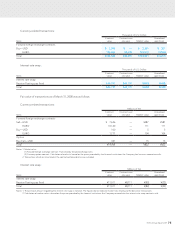
INVESTMENT SECURITIES
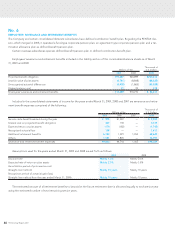
Investment securities as of March 31, 2009 and 2008 consisted of the following:
Millions of Yen
Thousands of
U.S. Dollars
2009 2008 2009
Marketable equity securities ¥2,050 ¥3,616 $20,865
Non-marketable equity securities 1,500 1,308 15,278
Total ¥3,550 ¥4,924 $36,143
On December 26, 2008, the ASBJ issued ASBJ Statement No.
16 (Revised 2008), “Revised Accounting Standard for Equity
Method of Accounting for Investments.” The new standard
requires adjustments to be made to conform the associate’s
accounting policies for similar transactions and events under
similar circumstances to those of the parent company when the
associate’s financial statements are used in applying the equity
method unless it is impracticable to determine adjustments. In
addition, financial statements prepared by foreign associated
companies in accordance with either International Financial
Reporting Standards or the generally accepted accounting prin-
ciples in the United States tentatively may be used in applying
the equity method if the following items are adjusted so that net
income is accounted for in accordance with Japanese GAAP,
unless they are not material: 1) amortization of goodwill; 2)
scheduled amortization of actuarial gain or loss of pensions that
has been directly recorded in the equity; 3) expensing capitalized
development costs of R&D; 4) cancellation of the fair value model
accounting for property, plant, and equipment and investment
properties and incorporation of the cost model accounting; 5)
recording the prior years’ effects of changes in accounting poli-
cies in the income statement where retrospective adjustments to
the financial statements have been incorporated; and 6) exclu-
sion of minority interests from net income, if contained.
This standard is applicable to equity method of accounting
for investments effective on or after April 1, 2010 with early adop-
tion permitted for fiscal years beginning on or after April 1, 2009.
Asset Retirement Obligations—On March 31, 2008, the ASBJ
published a new accounting standard for asset retirement obli-
gations, ASBJ Statement No. 18 “Accounting Standard for Asset
Retirement Obligations” and ASBJ Guidance No. 21 “Guidance
on Accounting Standard for Asset Retirement Obligations.”
Under this accounting standard, an asset retirement obligation is
defined as a legal obligation imposed either by law or contract
that results from the acquisition, construction, development and
the normal operation of a tangible fixed asset and is associated
with the retirement of such tangible fixed asset.
The asset retirement obligation is recognized as the sum of
the discounted cash flows required for the future asset retire-
ment and is recorded in the period in which the obligation is
incurred if a reasonable estimate can be made. If a reasonable
estimate of the asset retirement obligation cannot be made in
the period the asset retirement obligation is incurred, the liabil-
ity should be recognized when a reasonable estimate of asset
retirement obligation can be made. Upon initial recognition of a
liability for an asset retirement obligation, an asset retirement
cost is capitalized by increasing the carrying amount of the
related fixed asset by the amount of the liability. The asset
retirement cost is subsequently allocated to expense through
depreciation over the remaining useful life of the asset. Over
time, the liability is accreted to its present value each period.
Any subsequent revisions to the timing or the amount of the
original estimate of undiscounted cash flows are reflected as an
increase or a decrease in the carrying amount of the liability and
the capitalized amount of the related asset retirement cost. This
standard is effective for fiscal years beginning on or after April
1, 2010 with early adoption permitted for fiscal years beginning
on or before March 31, 2010.