Pentax 2009 Annual Report Download - page 65
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 65 of the 2009 Pentax annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
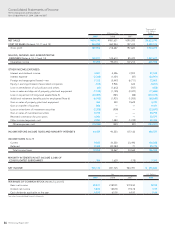
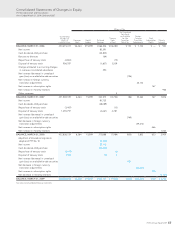
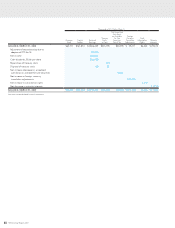
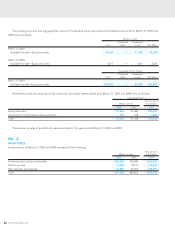
63
HOYA Annual Report 2009
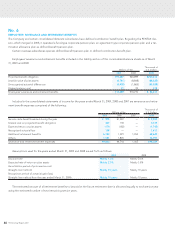
on a straight-line basis over 10 years, which is less than the
expected average remaining working lives of the employees.
Actuarial gains and losses are also amortized on a straight-
line basis over 10 years, which is less than the expected aver-
age remaining working lives of the employees, commencing
with the following fiscal year.
(Changes in accounting policies)
In July 2008, The Accounting Standards Board of Japan (ASBJ)
issued an Accounting Standard—ASBJ Statement No.19 “Par-
tial Amendments to Accounting Standard for Retirement Ben-
efits (Part 3)”. The above accounting standards were therefore
applied from the fiscal year under review.
This had no effect on income before adjustment of income
taxes and other items for the fiscal year under review,
because its impact, including actuarial differences that
accrued during the fiscal year under review, will be treated as
costs in and after the following fiscal year.
iv) Reserve for periodic repairs: Reserve for periodic repairs is
provided at amount estimated based on the expenses of the
latest extensive repairs for continuous melting furnaces.
v) Allowance for product warranties: To prepare for after-sales
service expenses that are anticipated to arise within product
warranty periods, an allowance is provided on the basis of
results for past fiscal years and forecasts for future warranty
expenses. Some of the overseas subsidiaries primarily record
estimates based on their net sales.
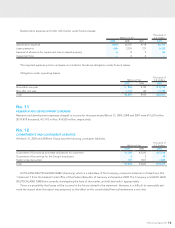
j. Research and Development Expenses—Research and devel-
opment expenses are charged to income when incurred.
k. Leases—In March 2007, the ASBJ issued ASBJ Statement No.
13, “Accounting Standard for Lease Transactions,” which
revised the previous accounting standard for lease transactions
issued in June 1993. The revised accounting standard for lease
transactions was effective for fiscal years beginning on or after
April 1, 2008 with early adoption permitted for fiscal years
beginning on or after April 1, 2007.
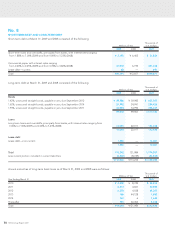
Under the previous accounting standard, finance leases that
deemed to transfer ownership of the leased property to the
lessee were capitalized. However, other finance leases were
accounted for as operating lease transactions if certain “as if
capitalized” information was disclosed in the note to the les-
see’s financial statements. The revised accounting standard
requires that all finance lease transactions be capitalized to
recognize lease assets and lease obligations in the balance
sheet. In addition, the revised accounting standard permits
leases which existed at the transition date and do not transfer
ownership of the leased property to the lessee to continue to
be accounted for as operating lease transactions.
The Company applied the revised accounting standard effec-
tive April 1, 2008. In addition, the Company continues to account
for leases which existed at the transition date and do not transfer
ownership of the leased property to the lessee as operating lease
transactions. The effect of this change in accounting methods on
profit or loss and business segment information was minimal.
l. Bonuses to Directors—Bonuses to directors are accrued at
the year end to which such bonuses are attributable.
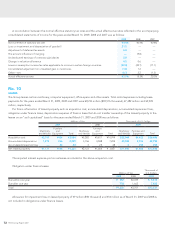
m. Income Taxes—The provision for income taxes is computed
based on the pretax income included in the consolidated state-
ments of income. The asset and liability approach is used to
recognize deferred tax assets and liabilities for the expected
future tax consequences of temporary differences between the
carrying amounts and the tax bases of assets and liabilities.
Deferred taxes are measured by applying currently enacted tax
laws to the temporary differences.
n. Foreign Currency Translations—All short-term and long-term
monetary receivables and payables denominated in foreign
currencies are translated into Japanese yen at the exchange
rates at the balance sheet date. The foreign exchange gains
and losses from translation are recognized in the statements of
income to the extent that they are not hedged by forward
exchange contracts.
o. Foreign Currency Financial Statements—The balance sheet
accounts of the consolidated overseas subsidiaries and associ-
ated companies are translated into Japanese yen at the current
exchange rates as of the balance sheet dates except for equity,
which is translated at historical exchange rates. Differences
arising from such translation are shown as “Foreign currency
translation adjustments” in a separate component of equity.
Revenue and expense accounts of consolidated overseas sub-
sidiaries are translated into Japanese yen at the monthly aver-
age exchange rates.