Oracle 2005 Annual Report Download - page 94
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 94 of the 2005 Oracle annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.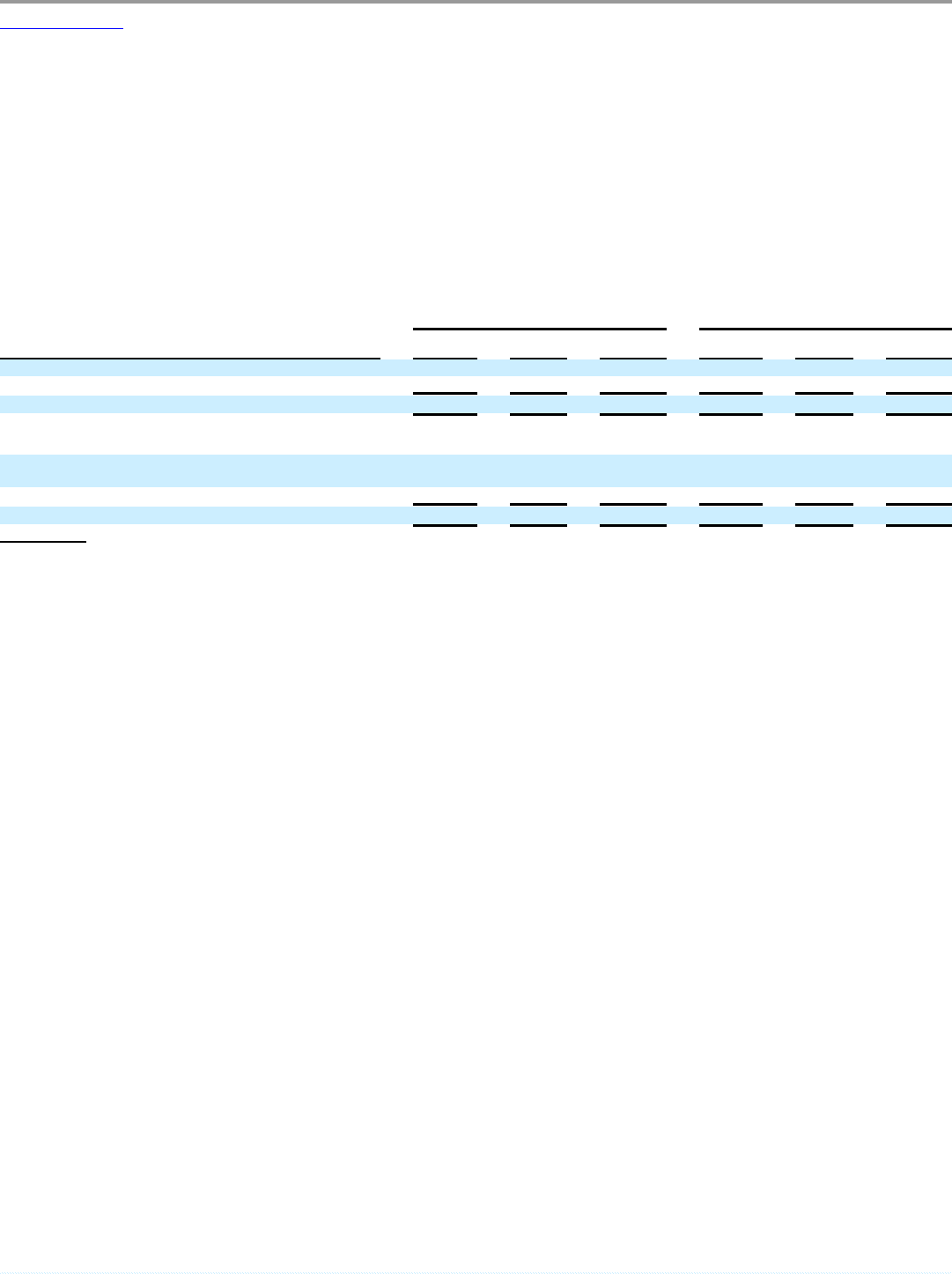
Table of Contents
ORACLE CORPORATION
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS—(Continued)
May 31, 2006
11. CASH, CASH EQUIVALENTS AND MARKETABLE SECURITIES
Cash and cash equivalents consist primarily of highly liquid investments in time deposits held at major banks, commercial paper, United States government
agency discount notes, money market mutual funds and other money market securities with original maturities of 90 days or less. Marketable securities primarily
consist of commercial paper, corporate notes and Unites States government agency notes. In accordance with Statement 115 and based on our intentions
regarding these instruments, we classify certain of our debt securities as available-for-sale and account for these marketable securities at market value. We
classify all of our other investments in debt securities as held-to-maturity and account for these marketable securities at amortized cost.
The amortized principal amount of cash and cash equivalents at May 31, 2006 and 2005 was $6.7 billion and $3.9 billion, which approximates fair value, and the
weighted average interest rates were 4.08% and 2.32%, respectively.
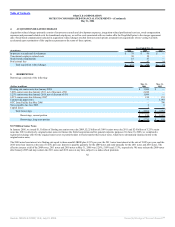
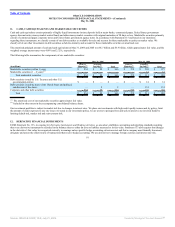
The following table summarizes the components of our marketable securities:
May 31, 2006 May 31, 2005
(in millions)
Held-to-
Maturity(1)
Available-
for-Sale(1) Total
Held-to-
Maturity(1)
Available-
for-Sale(1) Total
Marketable securities (within 1 year) $ 854 $ 92 $ 946 $ 578 $ 299 $ 877
Marketable securities (1 – 2 years)(2) — — — — 12 12
Total marketable securities $ 854 $ 92 $ 946 $ 578 $ 311 $ 889
Debt securities issued by U.S. Treasury and other U.S.
governmental entities $ — $ — $ — $ — $ 14 $ 14
Debt securities issued by states of the United States and political
subdivisions of the states. — 2 2 — 131 131
Corporate and other debt securities 854 90 944 578 166 744
Total $ 854 $ 92 $ 946 $ 578 $ 311 $ 889
(1) The amortized cost of our marketable securities approximates fair value.
(2) Included in other assets in the accompanying consolidated balance sheets.
Our investment portfolio is subject to market risk due to changes in interest rates. We place our investments with high credit quality issuers and, by policy, limit
the amount of credit exposure to any one issuer. As stated in our investment policy, we are averse to principal loss and seek to preserve our invested funds by
limiting default risk, market risk and reinvestment risk.
12. DERIVATIVE FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS
FASB Statement No. 133, Accounting for Derivative Instruments and Hedging Activities, as amended, establishes accounting and reporting standards requiring
that every derivative instrument be recorded in the balance sheet as either an asset or liability measured at its fair value. Statement 133 also requires that changes
in the derivative’s fair value be recognized currently in earnings unless specific hedge accounting criteria are met and that a company must formally document,
designate and assess the effectiveness of transactions that receive hedge accounting. We use derivatives to manage foreign currency and interest rate risk.
91
Source: ORACLE CORP, 10-K, July 21, 2006 Powered by Morningstar® Document Research℠