Motorola 2015 Annual Report Download - page 57
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 57 of the 2015 Motorola annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.56
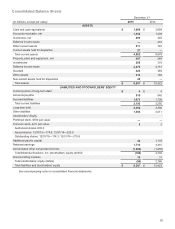
in effect during the period. The resulting translation adjustments are included as a component of Accumulated other
comprehensive loss in the Company’s consolidated balance sheets. For those operations that have the U.S. dollar as their
functional currency, transactions denominated in the local currency are measured in U.S. dollars using the current rates of
exchange for monetary assets and liabilities and historical rates of exchange for nonmonetary assets. Gains and losses from
remeasurement of monetary assets and liabilities are included in Other within Other income (expense) within the Company’s
consolidated statements of operations.
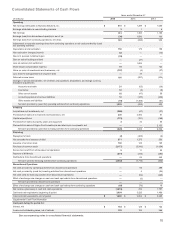
Derivative Instruments: Gains and losses on hedges of existing assets or liabilities are marked-to-market and the
result is included in Other within Other income (expense) within the Company’s consolidated statements of operations. Certain
financial instruments are used to hedge firm future commitments or forecasted transactions. Gains and losses pertaining to
those instruments that qualify for hedge accounting are deferred until such time as the underlying transactions are recognized
and subsequently recognized in the same line within the consolidated statements of operations as the hedged item. Gains and
losses pertaining to those instruments that do not qualify for hedge accounting are recorded immediately in Other income
(expense) within the consolidated statements of operations.
Earnings Per Share: The Company calculates its basic earnings (loss) per share based on the weighted-average
number of common shares issued and outstanding. Net earnings (loss) attributable to Motorola Solutions, Inc. is divided by the
weighted average common shares outstanding during the period to arrive at the basic earnings (loss) per share. Diluted
earnings (loss) per share is calculated by dividing net earnings (loss) attributable to Motorola Solutions, Inc. by the sum of the
weighted average number of common shares used in the basic earnings (loss) per share calculation and the weighted average
number of common shares that would be issued assuming exercise or conversion of all potentially dilutive securities, excluding
those securities that would be anti-dilutive to the earnings (loss) per share calculation. Both basic and diluted earnings (loss) per
share amounts are calculated for earnings (loss) from continuing operations and net earnings attributable to Motorola Solutions,
Inc. for all periods presented.
Share-Based Compensation Costs: The Company grants share-based compensation awards and offers an
employee stock purchase plan. The amount of compensation cost for these share-based awards is generally measured based
on the fair value of the awards as of the date that the share-based awards are issued and adjusted to the estimated number of
awards that are expected to vest. The fair values of stock options and stock appreciation rights are generally determined using a
Black-Scholes option pricing model which incorporates assumptions about expected volatility, risk free rate, dividend yield, and
expected life. Performance based stock options, performance-contingent stock options, and market stock units vest based on
market conditions and are therefore measured under a Monte Carlo simulation in order to simulate a range of possible future
unit prices for Motorola Solutions over the performance period. Compensation cost for share-based awards is recognized on a
straight-line basis over the vesting period.
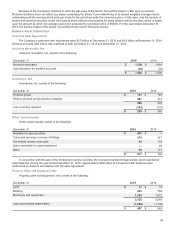
Retirement Benefits: The Company records annual expenses relating to its pension benefit and postretirement plans
based on calculations which include various actuarial assumptions, including discount rates, assumed asset rates of return,
compensation increases, and turnover rates. The Company reviews its actuarial assumptions on an annual basis and makes
modifications to the assumptions based on current rates and trends. The effects of the gains, losses, and prior service costs and
credits are amortized either over the average service life or over the average remaining lifetime of the participants, depending on
the number of active employees in the plan. The funded status, or projected benefit obligation less plan assets, for each plan, is
reflected in the Company’s consolidated balance sheets using a December 31 measurement date.
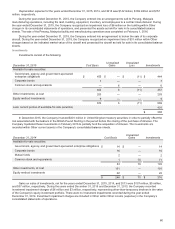
Recent Accounting Pronouncements: In May 2014, the Financial Accounting Standards Board ("FASB") issued
Accounting Standards Update ("ASU") No. 2014-09, "Revenue from Contracts with Customers." This new standard will replace
most existing revenue recognition guidance in U.S. GAAP. The core principle of the ASU is that an entity should recognize
revenue for the transfer of goods or services equal to the amount it expects to receive for those goods and services. This ASU
requires additional disclosures about the nature, amount, timing and uncertainty of revenue and cash flows arising from
customer contracts, including significant judgments and estimates and changes in those estimates. In August 2015, the FASB
issued ASU 2015-14, "Revenue from Contracts with Customers: Deferral of the Effective Date" that delayed the effective date of
ASU 2014-09 by one year to January 1, 2018, as the Company’s annual reporting period begins after December 15, 2017. ASU
2014-09 allows for both retrospective and modified retrospective methods of adoption. The Company is in the process of
determining the method of adoption it will elect and is currently assessing the impact of this ASU on its consolidated financial
statements and footnote disclosures.
In April 2015, the FASB issued ASU No. 2015-03, "Interest-Imputation of Interest (Subtopic 835-30): Simplifying the
Presentation of Debt Issuance Costs." Under this guidance, debt issuance costs related to a recognized debt liability are
required to be presented in the balance sheet as a direct reduction from the carrying amount of such debt liability, consistent with
debt discounts. The recognition and measurement guidance for debt issuance costs are not affected by this guidance. In
adopting the ASU, the Company will be required to apply a full retrospective approach to all periods presented. This guidance
will be effective January 1, 2016 and, upon adoption, debt issuance costs capitalized in other assets in the consolidated balance
sheet will be reclassified and presented as a reduction to long-term debt. As of December 31, 2015, debt issuance costs, net of
accumulated amortization, recognized in the consolidated balance sheet were $41 million.
On November 20, 2015, the FASB issued ASU No. 2015-17, "Balance Sheet Classification of Deferred Taxes," which
amends existing guidance on income taxes to require the classification of all deferred tax assets and liabilities as non-current on
the balance sheet. The ASU will be effective for the Company beginning January 1, 2017, including interim periods in its fiscal
year 2017, and allows for both retrospective and prospective methods of transition upon adoption. The Company has adopted