MasterCard 2015 Annual Report Download - page 62
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 62 of the 2015 MasterCard annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.56
MASTERCARD INCORPORATED
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
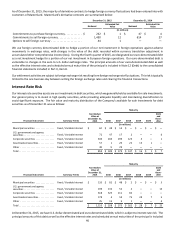
Note 1. Summary of Significant Accounting Policies
Organization
MasterCard Incorporated and its consolidated subsidiaries, including MasterCard International Incorporated (“MasterCard
International” and together with MasterCard Incorporated, “MasterCard” or the “Company”), is a technology company in the
global payments industry that connects consumers, financial institutions, merchants, governments and businesses worldwide,
enabling them to use electronic forms of payment instead of cash and checks. The Company facilitates the processing of payment
transactions including authorization, clearing and settlement, and delivers related products and services. The Company makes
payments easier and more efficient by creating a wide range of payment solutions and services through a family of well-known
brands, including MasterCard, Maestro and Cirrus. The Company also provides value-added offerings such as loyalty and reward
programs, information services and consulting. The Company’s network is designed to ensure safety and security for the global
payments system. A typical transaction on the Company’s network involves four participants in addition to the Company:
cardholder, merchant, issuer (the cardholder’s financial institution) and acquirer (the merchant’s financial institution). The
Company’s customers encompass a vast array of entities, including financial institutions and other entities that act as “issuers”
and “acquirers”, as well as merchants, governments, telecommunication companies and other businesses. The Company does
not issue cards, extend credit, determine or receive revenue from interest rates or other fees charged to cardholders by issuers,
or establish the rates charged by acquirers in connection with merchants’ acceptance of the Company’s branded cards.
Significant Accounting Policies
Consolidation and basis of presentation - The consolidated financial statements include the accounts of MasterCard and its
majority-owned and controlled entities, including any variable interest entities (“VIEs”) for which the Company is the primary
beneficiary. Investments in VIEs for which the Company is not considered the primary beneficiary are not consolidated and are
accounted for as equity method or cost method investments and recorded in other assets on the consolidated balance sheet.
At December 31, 2015 and 2014, there were no significant VIEs which required consolidation and the investments were not
considered material to the consolidated financial statements. Intercompany transactions and balances have been eliminated in
consolidation. Certain prior period amounts have been reclassified to conform to the 2015 presentation. In 2014 and 2013, net
revenue and general and administrative expenses were revised to correctly classify $32 million and $34 million, respectively, of
customer incentive expenses as contra revenue instead of general and administrative expenses. This revision had no impact on
net income. The Company follows accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America (“GAAP”).
Non-controlling interests represent the equity interest not owned by the Company and are recorded for consolidated entities in
which the Company owns less than 100% of the interests. Changes in a parent’s ownership interest while the parent retains its
controlling interest are accounted for as equity transactions, and upon loss of control, retained ownership interests are
remeasured at fair value, with any gain or loss recognized in earnings. For 2015, 2014 and 2013, income from non-controlling
interests was de minimis and, as a result, amounts are included in the consolidated statement of operations within other income
(expense).
The Company accounts for investments in common stock or in-substance common stock under the equity method of accounting
when it has the ability to exercise significant influence over the investee, generally when it holds between 20% and 50% ownership
in the entity. In addition, investments in flow-through entities such as limited partnerships and limited liability companies are
also accounted for under the equity method when the Company has the ability to exercise significant influence over the investee,
generally when the investment ownership percentage is equal to or greater than 5% of the outstanding ownership interest. The
excess of the cost over the underlying net equity of investments accounted for under the equity method is allocated to identifiable
tangible and intangible assets and liabilities based on fair values at the date of acquisition. The amortization of the excess of the
cost over the underlying net equity of investments and MasterCard’s share of net earnings or losses of entities accounted for
under the equity method of accounting is included in other income (expense) on the consolidated statement of operations.
The Company accounts for investments in common stock or in-substance common stock under the cost method of accounting
when it does not exercise significant influence, generally when it holds less than 20% ownership in the entity or when the interest
in a limited partnership or limited liability company is less than 5% and the Company has no significant influence over the operation
of the investee. Investments in companies that MasterCard does not control, but that are not in the form of common stock or
in-substance common stock, are also accounted for under the cost method of accounting. Investments for which the equity
method or cost method of accounting is used are recorded in other assets on the consolidated balance sheet.