Cisco 2007 Annual Report Download - page 70
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 70 of the 2007 Cisco annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
2007 Annual Report 73
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
Accuracy of Fair Value Estimates The Company uses third-party analyses to assist in developing the assumptions used in, as well as
calibrating, its lattice-binomial model. The Company is responsible for determining the assumptions used in estimating the fair value
of its share-based payment awards.
The Company’s determination of the fair value of share-based payment awards is affected by assumptions regarding a number of
highly complex and subjective variables. These variables include, but are not limited to, the Company’s expected stock price volatility over
the term of the awards, and actual and projected employee stock option exercise behaviors. Option-pricing models were developed for
use in estimating the value of traded options that have no vesting or hedging restrictions and are fully transferable. Because the Company’s
employee stock options have certain characteristics that are significantly different from traded options, and because changes in the
subjective assumptions can materially affect the estimated value, in management’s opinion, the existing valuation models may not provide
an accurate measure of the fair value of the Company’s employee stock options. Although the fair value of employee stock options is
determined in accordance with SFAS 123(R) and SAB 107 using an option-pricing model, that value may not be indicative of the fair value
observed in a willing buyer/willing seller market transaction.
Employee 401(k) Plans
The Company sponsors the Cisco Systems, Inc. 401(k) Plan (the “Plan”) to provide retirement benefits for its employees. As allowed
under Section 401(k) of the Internal Revenue Code, the Plan provides for tax-deferred salary contributions for eligible employees. The
Plan allows employees to contribute from 1% to 25% of their annual compensation to the Plan on a pretax and after-tax basis. Employee
contributions are limited to a maximum annual amount as set periodically by the Internal Revenue Code. The Company matches pretax
employee contributions up to 100% of the first 4% of eligible earnings that are contributed by employees. Therefore, the maximum
matching contribution that the Company may allocate to each participant’s account will not exceed $9,000 for the 2007 calendar year due
to the $225,000 annual limit on eligible earnings imposed by the Internal Revenue Code. All matching contributions vest immediately. The
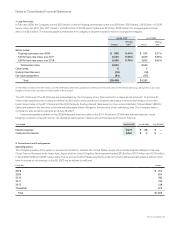
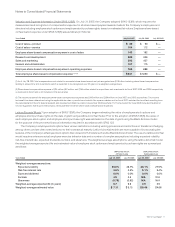
Company’s matching contributions to the Plan totaled $131 million, $96 million, and $84 million in fiscal 2007, 2006, and 2005, respectively.
The Plan allows employees who meet the age requirements and reach the Plan contribution limits to make a catch-up contribution not
to exceed the lesser of 50% of their eligible compensation or the limit set forth in the Internal Revenue Code. The catch-up contributions
are not eligible for matching contributions. In addition, the Plan provides for discretionary profit-sharing contributions as determined by the
Board of Directors. Such contributions to the Plan are allocated among eligible participants in the proportion of their salaries to the total
salaries of all participants. There were no discretionary profit-sharing contributions made in fiscal 2007, 2006, or 2005.
The Company also sponsors other 401(k) plans that arose from acquisitions of other companies. The Company’s contributions to
these plans were not material to the Company on either an individual or aggregate basis for any of the fiscal years presented.
Deferred Compensation Plans
The Company also maintains a deferred compensation plan for certain employees and directors of Scientific-Atlanta (the “SA Plan”).
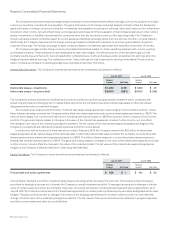
The deferred compensation liability under the SA Plan was approximately $109 million and $100 million, as of July 28, 2007 and July 29,
2006, respectively, and was recorded in current and long-term liabilities. In March 2007, the Board of Directors approved a new nonqualified
deferred compensation plan, the Cisco Systems, Inc. Deferred Compensation Plan (the “Deferred Compensation Plan”), which became
effective June 25, 2007. As required by applicable law, participation in the Deferred Compensation Plan is limited to a group of the Company’s
management employees, which group includes each of the Company’s named executive officers. Under the Deferred Compensation Plan,
which is an unfunded and unsecured deferred compensation arrangement, a participant may elect to defer base salary, bonus, and/or
commissions, pursuant to such rules as may be established by the Company, up to the maximum percentages for each deferral election as
described in the plan. This operates in a manner similar to the way in which the Company’s 401(k) plan operates, but without regard to the
maximum deferral limitations imposed on 401(k) plans by the Code. The Company may also, at its discretion, make a matching contribution
to the employee under the Deferred Compensation Plan. A matching contribution, equal to 4% of eligible compensation over the Internal
Revenue Code limit for calendar year 2007 which is deferred by participants under the Deferred Compensation Plan will be made to
eligible participants’ accounts at the end of calendar year 2007. The deferred compensation liability under this plan was not material as
of July 28, 2007.