Cisco 2007 Annual Report Download - page 63
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 63 of the 2007 Cisco annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
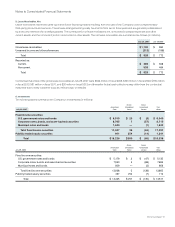
66 Cisco Systems, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
The Company enters into foreign exchange forward contracts to reduce the short-term effects of foreign currency fluctuations on foreign
currency receivables, investments, and payables. The gains and losses on the foreign exchange forward contracts offset the transaction
gains and losses on foreign currency receivables, investments, and payables recognized in earnings. Gains and losses on the contracts are
included in other income, net, and offset foreign exchange gains and losses from the revaluation of intercompany balances or other current
assets, investments, or liabilities denominated in currencies other than the functional currency of the reporting entity. The Company’s
foreign exchange forward contracts related to current assets and liabilities generally range from one to three months in original maturity.
Additionally, the Company has entered into foreign exchange forward contracts with maturities of up to two years related to long-term
customer financings. The foreign exchange forward contracts related to investments generally have maturities of less than 18 months.
The Company hedges certain foreign currency forecasted transactions related to certain operating expenses with currency options
and forward contracts. These transactions are designated as cash flow hedges. The effective portion of the derivative’s gain or loss
is initially reported as a component of accumulated other comprehensive income and subsequently reclassified into earnings when the
hedged exposure affects earnings. The ineffective portion, if any, of the gain or loss is reported in earnings immediately. These currency
option contracts and forward contracts generally have maturities of less than 18 months.
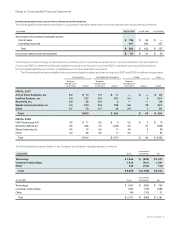
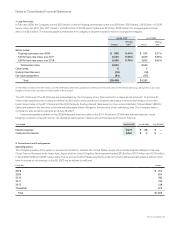
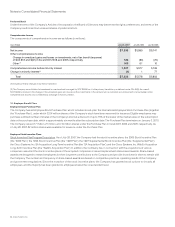
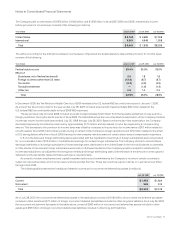
Interest Rate Derivatives The Company’s interest rate derivatives are summarized as follows (in millions):
July 28, 2007 July 29, 2006
Notional
Amount Fair Value
Notional
Amount Fair Value
Interest rate swaps—investments $ 1,000 $ 29 $ 1,000 $ 45
Interest rate swaps—long-term debt $ 6,000 $ (81) $ 6,000 $ (155)
The Company’s primary objective for holding fixed income securities is to achieve an appropriate investment return consistent with
preserving principal and managing risk. To realize these objectives, the Company may utilize interest rate swaps or other derivatives
designated as fair value or cash flow hedges.
The Company has entered into $1.0 billion of interest rate swaps designated as fair value hedges of its investment portfolio. Under
these interest rate swap contracts, the Company makes fixed-rate interest payments and receives interest payments based on LIBOR. The
effect of these swaps is to convert fixed-rate returns to floating-rate returns based on LIBOR for a portion of the Company’s fixed income
portfolio. The gains and losses related to changes in the value of the interest rate swaps are included in other income, net, and offset
the changes in fair value of the underlying hedged investment. The fair values of the interest rate swaps designated as hedges of the
Company’s investments are reflected in prepaid expenses and other current assets.
In conjunction with its issuance of fixed-rate senior notes in February 2006, the Company entered into $6.0 billion of interest rate
swaps designated as fair value hedges of the fixed-rate debt. Under these interest rate swap contracts, the Company receives fixed-rate
interest payments and makes interest payments based on LIBOR. The effect of these swaps is to convert fixed-rate interest expense to
floating-rate interest expense based on LIBOR. The gains and losses related to changes in the value of the interest rate swaps are included
in other income, net, and offset the changes in fair value of the underlying debt. The fair values of the interest rate swaps designated as
hedges of the Company’s debt are reflected in other long-term liabilities.
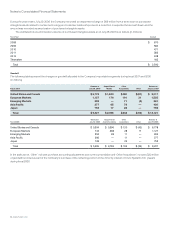
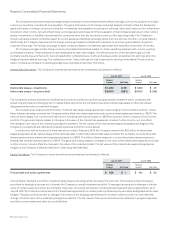
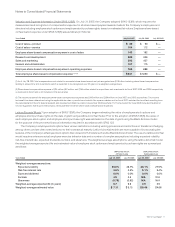
Equity Derivatives The Company’s equity derivatives are summarized as follows (in millions):
July 28, 2007 July 29, 2006
Notional
Amount Fair Value
Notional
Amount Fair Value
Forward sale and option agreements $ 458 $ 1 $ 164 $ 93
The Company maintains a portfolio of publicly traded equity securities which are subject to price risk. The Company may hold equity
securities for strategic purposes or to diversify the Company’s overall investment portfolio. To manage its exposure to changes in the fair
value of certain equity securities, the Company may enter into equity derivatives, including forward sale and option agreements. As of
July 28, 2007, the Company had entered into forward sale agreements on certain publicly traded equity securities designated as fair value
hedges. The gains and losses due to changes in the value of the hedging instruments are included in other income, net, and offset the
change in the fair value of the underlying hedged investment. The fair values of the equity derivatives are reflected in prepaid expenses
and other current assets and other accrued liabilities.