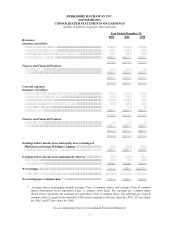
Berkshire Hathaway 2002 Annual Report Download - page 33
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 33 of the 2002 Berkshire Hathaway annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.32
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
(1) Significant accounting policies and practices (Continued)
(d) Investments (Continued)
Other investments include investments in commodities, limited partnerships, and equity warrants, which are
carried at fair value in the accompanying Consolidated Balance Sheets. Realized and unrealized gains
and losses associated with these investments are included in the Consolidated Statements of Earnings as
a component of realized investment gains. Other investments also include commercial loans, which are
carried at amortized cost.
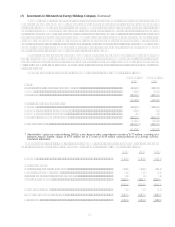
Berkshire utilizes the equity method of accounting with respect to investments where it exercises significant
influence, but not control, over the policies of the investee. A voting interest of at least 20% and no
greater than 50% is normally a prerequisite for utilizing the equity method. However Berkshire may
apply the equity method with less than 20% voting interests based upon the facts and circumstances
including representation on the Board of Directors, contractual veto or approval rights, participation in
policy making processes, the existence or absence of other significant owners and the expected duration
of the investment. Berkshire applies the equity method to investments in common stock and investments
in preferred stock when such preferred stock possesses substantially identical subordinated interests to
common stock.
In applying the equity method, investments are recorded at cost and subsequently increased or decreased by
the proportionate share of net earnings or losses of the investee. Berkshire also records its proportionate
share of other comprehensive income items of the investee as a component of its comprehensive income.
Dividends or other equity distributions are recorded as a reduction of the investment. In the event that
net losses of the investee have reduced the equity method investment to zero, additional net losses may
be recorded if additional investments in the investee are at-risk, even if Berkshire has not committed to
provide financial support to the investee. Berkshire bases such additional equity method loss amounts, if
any, on the change in its claim on the investees book value.
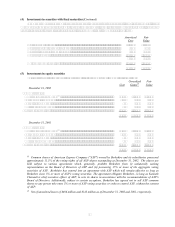
(e) Finance and financial products
Certain Berkshire finance affiliates utilize derivative instruments as risk management tools. Such
instruments include interest rate, currency and equity swaps and options, interest rate caps and floors,
futures and forward contracts and foreign exchange contracts. Trading account assets and liabilities are
marked-to-market on a daily basis and represent the estimated fair values of derivatives in net gain
positions (assets) and in net loss positions (liabilities) and reflect reductions permitted under master
netting agreements with counterparties. The fair values of these instruments represent the present value
of expected future cash flows under the contract, which is a function of underlying interest rates,
currency rates, security values, related volatility, the creditworthiness of counterparties and duration of
the contract. Future changes in these factors or a combination thereof may affect the fair value of these
instruments. Changes in fair value of trading account assets and liabilities during the period are included
in the Consolidated Statements of Earnings. The carrying values of trading account assets and trading
account liabilities reflect a net decrease of $19.1 billion at December 31, 2002 and $17.5 billion at
December 31, 2001 as a result of the netting arrangements.
Securities purchased under agreements to resell (assets) and securities sold under agreements to repurchase
(liabilities) are accounted for as collateralized investments and borrowings and are recorded at the
contractual resale or repurchase amounts. Other investment securities owned and liabilities associated
with investment securities sold but not yet purchased are carried at fair value. Loans and finance
receivables are principally commercial and consumer loans, which are carried at amortized cost.
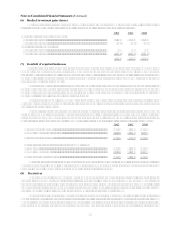
(f) Inventories
Inventories are stated at the lower of cost or market. Cost with respect to manufactured goods includes raw
materials, direct and indirect labor and factory overhead. As of December 31, 2002, approximately 44%
of the total inventory cost was determined using the last-in-first-out (LIFO) method, 33% using the
first-in-first-out (FIFO) method, with the remainder using the specific identification method. With
respect to inventories carried at LIFO cost, the aggregate difference in value between LIFO cost and
cost determined under FIFO methods was not material as of December 31, 2002 and December 31,
2001.