Avon 2004 Annual Report Download - page 45
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 45 of the 2004 Avon annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
At December 31, 2004, the maximum remaining term
over which Avon was hedging foreign exchange expo-
sures to the variability of cash flows for all forecasted
transactions was 12 months. As of December 31, 2004,
Avon expects to reclassify $4.7 ($2.8, net of taxes) of net
losses on derivative instruments designated as cash flow
hedges from accumulated other comprehensive loss to
earnings during the next 12 months due to (a) foreign
currency-denominated intercompany royalties, (b) inter-
company loan settlements and (c) foreign currency-
denominated purchases or receipts.
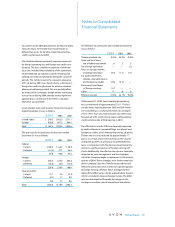
For the years ended December 31, 2004 and 2003, cash
flow hedges impacted accumulated other comprehen-
sive loss as follows:
2004 2003
Net derivative losses at
beginning of year $(1.6) $(2.6)
Net losses on derivative
instruments, net of taxes
of $.5 and $.0 (1.6) —
Reclassification of net losses (gains)
to earnings, net of taxes
of $1.5 and $.6 (1.5) 1.0
Net derivative losses at end of year,
net of taxes of $2.8 and $.8 $(4.7) $(1.6)
Avon uses foreign currency forward contracts and foreign
currency-denominated debt to hedge the foreign cur-
rency exposure related to the net assets of certain of its
foreign subsidiaries. At December 31, 2004, Avon had
a Japanese yen-denominated note payable to hedge
Avon’s net investment in its Japanese subsidiary (see
Note 4, Debt and Other Financing). For the years ended
December 31, 2004, 2003 and 2002, $10.4, $9.2 and $.8,
respectively, related to the effective portions of these
hedges were included in foreign currency translation
adjustments within accumulated other comprehensive
loss on the Consolidated Balance Sheets.
During 2004 and 2003, Avon held foreign currency
forward contracts and options to protect against the
adverse effects that exchange rate fluctuations may
have on the earnings of its foreign subsidiaries. These
derivatives do not qualify for hedge accounting and,
therefore, the gains and losses on these derivatives
have been recognized in earnings each reporting
period and are not material to the Consolidated
Financial Statements.
At December 31, 2004 and 2003, Avon held foreign cur-
rency forward contracts and option contracts with fair
values totaling $5.0 and $2.6, respectively, recorded in
accounts payable. Additionally, certain of Avon’s interna-
tional subsidiaries hold U.S. dollar-denominated assets,
primarily to minimize foreign currency risk and provide
liquidity. At December 31, 2004, Avon subsidiaries that
held U.S. dollar denominated assets included Mexico
($18.0), Venezuela ($11.8), Brazil ($10.0), Argentina ($8.1)
and Hungary ($2.1). At December 31, 2003, Avon’s sub-
sidiary in Argentina held U.S. dollar-denominated assets
totaling $6.0. For the years ended December 31, 2004
and 2003, other expense (income), net, included net
transaction losses of $2.6 and $2.8, respectively, related
to these U.S. dollar-denominated assets.
Credit and Market Risk
Avon attempts to minimize its credit exposure to
counterparties by entering into interest rate swap and
foreign currency forward rate and option agreements
only with major international financial institutions with
“A”or higher credit ratings as issued by Standard &
Poor’s Corporation. Avon’s foreign currency and inter-
est rate derivatives are comprised of over-the-counter
forward contracts, swaps or options with major inter-
national financial institutions. Although the Company’s
theoretical credit risk is the replacement cost at the
then estimated fair value of these instruments, man-
agement believes that the risk of incurring credit risk
losses is remote and that such losses, if any, would not
be material.
Non-performance of the counterparties on the balance
of all the foreign exchange and interest rate swap and
forward rate agreements would result in a write-off of
$27.5 at December 31, 2004. In addition, in the event of
non-performance by such counterparties, Avon would