Salesforce.com 2004 Annual Report Download - page 71
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 71 of the 2004 Salesforce.com annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
Table of Contents
salesforce.com, inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements—(Continued)
issued with an exercise price of ¥4,000 per share (approximately $37 per share), ¥3,500 per share (approximately $31 per share) and ¥3,500 per share
(approximately $30 per share) and vest over a two-year period. As a result of these stock option grants, the joint venture recorded $88,000, $13,000 and
$162,000 of deferred stock-based compensation during fiscal 2005, 2004 and 2003, respectively. The joint venture amortized $23,000, $274,000 and
$544,000 of deferred stock-based compensation expense during fiscal 2005, 2004 and 2003, respectively. The joint venture reversed $2,000, zero and $34,000
of deferred stock-based compensation related to terminated employees during fiscal 2005, 2004 and 2003, respectively. Additionally, as a result of an
employee termination, during fiscal 2005 the joint venture reversed compensation expense of $475,000, which had been previously recognized.
Given the Company's majority ownership interest in the joint venture, the accounts of the joint venture have been consolidated with the accounts of the
Company, and a minority interest has been recorded for the third party's interest in the net assets and operations of the joint venture to the extent of the
minority partners' individual investments. All intercompany transactions have been eliminated, with the exception of minority interest.
Under the terms of the joint venture agreement, the joint venture will terminate if the joint venture becomes a public company or is sold to a third party,
or upon the mutual agreement of the parties. In addition, if the Company commits a breach of, or if the Company fails to perform, its material obligations
under the joint venture agreement, which are not cured in a timely manner, SunBridge can require the Company to purchase all of its shares in the joint
venture. The purchase price for SunBridge's shares would be the then fair market value plus a specified premium. In the event that SunBridge commits a
breach of, or if it fails to perform, its material obligations under the joint venture agreement, which it does not cure in a timely manner, or if SunBridge enters
into bankruptcy proceedings, the Company can require SunBridge to sell to it all of their shares in the joint venture. The purchase price for SunBridge's shares
would be the then fair market value less a specified discount. Additionally, if the Company and SunBridge are unable to agree on certain operational matters,
either party can require the other to purchase all of its shares of the joint venture at a price equal to the then fair value market value. Fair market value is to be
determined by mutual agreement of the parties, or if the parties are unable to agree, by an independent appraiser.
3. Balance Sheet Accounts
Marketable Securities
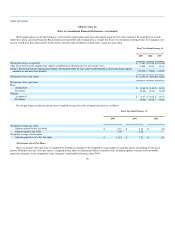
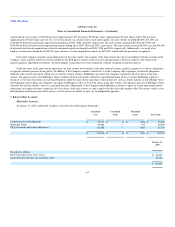
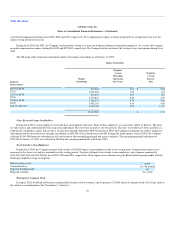
At January 31, 2005, marketable securities consisted of the following (in thousands):
Amortized
Cost
Unrealized
Gains
Unrealized
Losses
Fair Value
Corporate notes and obligations $ 78,773 $ 13 $ (418) $ 78,368
Municipal bonds 26,085 — (35) 26,050
US government and agency obligations 66,098 — (309) 65,789
$ 170,956 $ 13 $ (762) $ 170,207
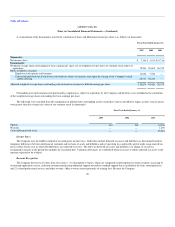
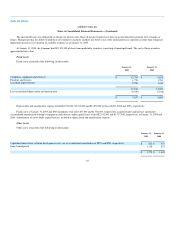
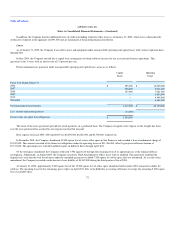
January 31,
2005
Recorded as follows:
Short-term (due in one year or less) $ 83,087
Long-term (due between one and three years) 87,120
$ 170,207
64