Starwood 2006 Annual Report Download - page 72
Download and view the complete annual report
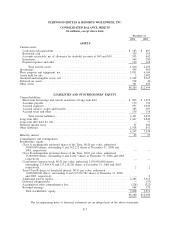
Please find page 72 of the 2006 Starwood annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.The liability for the SPG program is included in other long-term liabilities and accrued expenses in the
accompanying consolidated balance sheets. The total actuarially determined liability as of December 31, 2006 and
2005 is $409 million and $314 million, respectively, of which $132 million and $99 million, respectively, is
included in accrued expenses.
Legal Contingencies. The Company is subject to various legal proceedings and claims, the outcomes of
which are subject to significant uncertainty. SFAS No. 5, “Accounting for Contingencies,” requires that an estimated
loss from a loss contingency be accrued by a charge to income if it is probable that an asset has been impaired or a
liability has been incurred and the amount of the loss can be reasonably estimated. Disclosure of a contingency is
required if there is at least a reasonable possibility that a loss has been incurred. The Company evaluates, among
other factors, the degree of probability of an unfavorable outcome and the ability to make a reasonable estimate of
the amount of loss. Changes in these factors could materially impact the Company’s financial position or its results
of operations.
Derivative Financial Instruments. The Company enters into interest rate swap agreements to manage
interest rate exposure. The net settlements paid or received under these agreements are accrued consistent with the
terms of the agreements and are recognized in interest expense over the term of the related debt. The related fair
value of the swaps is included in other liabilities or assets.
From time to time, the Company enters into foreign currency hedging contracts to manage exposure to foreign
currency fluctuations. All foreign currency hedging instruments have an inverse correlation to the hedged assets or
liabilities. Changes in the fair value of the derivative instruments are classified in the same manner as the
classification of the changes in the underlying assets or liabilities due to fluctuations in foreign currency exchange
rates.
The Company does not enter into derivative financial instruments for trading or speculative purposes and
monitors the financial stability and credit standing of its counterparties.
Foreign Currency Translation. Balance sheet accounts are translated at the exchange rates in effect at each
period end and income and expense accounts are translated at the average rates of exchange prevailing during the
year. The national currencies of foreign operations are generally the functional currencies. Gains and losses from
foreign exchange and the effect of exchange rate changes on intercompany transactions of a long-term investment
nature are generally included in other comprehensive income. Gains and losses from foreign exchange rate changes
related to intercompany receivables and payables that are not of a long-term investment nature are reported
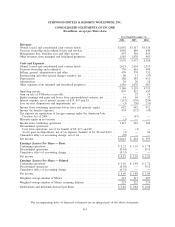
currently in costs and expenses and amounted to a net gain of $8 million, $2 million and $9 million in 2006, 2005
and 2004, respectively. Gains and losses from foreign currency transactions are reported currently in costs and
expenses and amounted to a net loss of $4 million in 2005. Gains and losses from foreign currency transactions were
insignificant in 2006 and 2004.
Income Taxes. The Company provides for income taxes in accordance with SFAS No. 109, “Accounting for
Income Taxes.” The objectives of accounting for income taxes are to recognize the amount of taxes payable or
refundable for the current year and deferred tax liabilities and assets for the future tax consequences of events that
have been recognized in an entity’s financial statements or tax returns.
Deferred tax assets and liabilities are measured using enacted tax rates in effect for the year in which those
temporary differences are expected to be recovered or settled. The effect on deferred tax assets and liabilities of a
change in tax rates is recognized in earnings in the period when the new rate is enacted.
F-11
STARWOOD HOTELS & RESORTS WORLDWIDE, INC.
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)