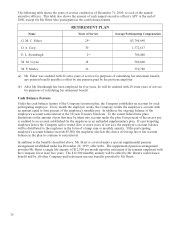
Kodak 2000 Annual Report Download - page 101
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 101 of the 2000 Kodak annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.29
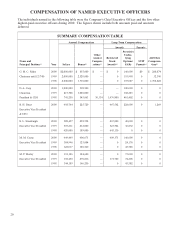
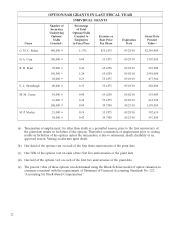
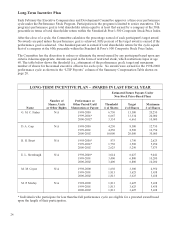
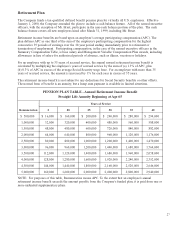
REPORT OF THE EXECUTIVE COMPENSATION
AND DEVELOPMENT COMMITTEE
Role of the Committee
The Executive Compensation and Development Committee is made up of four independent members of the
Board. The Committee members are neither employees nor former employees of the Company. The functions
of the Committee include:
• reviewing the executive compensation strategy,
• reviewing the design of the executive compensation program,
• overseeing the administration of the executive compensation plans,
• monitoring and overseeing the career development of executives,
• annually establishing performance commitments for the CEO, executive officers and key management,
• reviewing performance annually and determining the individual elements of total compensation for the
CEO and other designated executives, and
• reviewing at least annually diversity representation at the senior and mid-management levels.
Principles of Executive Compensation
The Company’s executive compensation program is designed to:
• tie compensation to performance that is consistent with the Company’s values and increases
shareholder value,
• attract and retain employees needed to meet the Company’s growth and performance objectives,
• set the total compensation of executives at market competitive levels,
• link compensation to both short and long-term performance,
• place a significant portion of each executive’s compensation at risk; the more senior an executive’s
position, the more compensation should be at risk, and
• link the interests of executives with our owners through stock ownership.
Executive Compensation Practices
Each year, the Company participates in surveys prepared by outside consultants. The companies included in
these surveys are those the Company competes with for executive talent. Most, but not all, of these companies
are included in the Dow Jones Industrial Index shown in the Performance Graph on page 33. Based largely on
the median compensation of these surveyed companies, the Committee sets the target compensation of senior
executives.
Components of Executive Compensation Program
The components of the executive compensation program are:
• base salary,
• short-term bonus, and
• long-term incentives.
Base Salary: Base salary is the only fixed portion of an executive’s compensation. Each executive’s base
salary is reviewed annually based on (1) a compensation range which corresponds to the executive’s job
responsibilities; and (2) the executive’s individual performance.
The Company measures individual performance in large part through the management appraisal process. This
process evaluates performance against a combination of financial and non-financial goals established in the
following three areas:
• shareholder satisfaction,
• customer satisfaction, and
• employee satisfaction.