Hasbro 2006 Annual Report Download - page 58
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 58 of the 2006 Hasbro annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
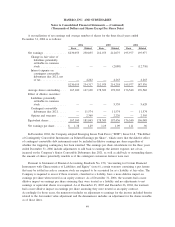
Risk Management Contracts
Hasbro uses foreign currency forward and option contracts, generally purchased for terms of not more
than eighteen months, to mitigate the impact of adverse currency rate fluctuations on firmly committed and
projected future foreign currency transactions. These over-the-counter contracts, which hedge future purchases
of inventory and other cross-border currency requirements not denominated in the functional currency of the
unit, are primarily denominated in United States and Hong Kong dollars, Euros and United Kingdom pound
sterling and are entered into with counterparties who are major financial institutions. The Company believes
any risk related to default by a counterparty to be remote. Hasbro does not enter into derivative financial
instruments for speculative purposes.
At the inception of the contracts, Hasbro designates its derivatives as either cash flow or fair value
hedges. The Company formally documents all relationships between hedging instruments and hedged items as
well as its risk management objectives and strategies for undertaking various hedge transactions. All hedges
designated as cash flow hedges are linked to forecasted transactions and the Company assesses, both at the
inception of the hedge and on an on-going basis, the effectiveness of the derivatives used in hedging
transactions in offsetting changes in the cash flows of the forecasted transaction. The ineffective portion of a
hedging derivative, if any, is immediately recognized in the consolidated statements of operations.
The Company records all derivatives, such as foreign currency exchange contracts, on the balance sheet
at fair value. Changes in the derivative fair values that are designated effective and qualify as cash flow hedges
are deferred and recorded as a component of accumulated other comprehensive earnings (“AOCE”) until the
hedged transactions occur and are then recognized in the consolidated statements of operations. The
Company’s foreign currency contracts hedging anticipated cash flows are designated as cash flow hedges.
When it is determined that a derivative is not highly effective as a hedge, the Company discontinues hedge
accounting prospectively. Any gain or loss deferred through that date remains in AOCE until the forecasted
transaction occurs, at which time it is reclassified to the consolidated statements of operations. To the extent
the transaction is no longer deemed probable of occurring, hedge accounting treatment is discontinued
prospectively and amounts deferred would be reclassified to the consolidated statements of operations. In the
event hedge accounting requirements are not met, gains and losses on such instruments are included currently
in the consolidated statements of operations. The Company uses derivatives to hedge intercompany loans
denominated in foreign currencies. Due to the short-term nature of the contracts involved, the Company does
not use hedge accounting for these contracts.
The Company also uses interest rate swap agreements to adjust the amount of long-term debt subject to
fixed interest rates. The interest rate swaps are matched with specific long-term debt obligations and are
designated and effective as fair value hedges of the change in fair value of those debt obligations. These
agreements are recorded at their fair value as an asset or liability. Gains and losses on these contracts are
included currently in the consolidated statements of operations and are wholly offset by changes in the fair
value of the related long-term debt. These hedges are considered to be perfectly effective under Statement of
Financial Accounting Standards No. 133, “Accounting for Derivative Instruments and Hedging Activities,” as
amended by Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No. 138 (collectively “SFAS 133”). The interest
rate swap contracts are with a number of major financial institutions in order to minimize counterparty credit
risk. The Company believes that it is unlikely that any of its counterparties will be unable to perform under
the terms of the contracts.
Accounting for Stock-Based Compensation
At December 31, 2006, the Company had stock-based employee compensation plans and plans for non-
employee members of the Company’s Board of Directors, which are described more fully in note 10. Effective
December 26, 2005, the first day of fiscal 2006, the Company adopted Statement of Financial Accounting
47
HASBRO, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements — (Continued)
(Thousands of Dollars and Shares Except Per Share Data)