Samsung 2013 Annual Report Download - page 50
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 50 of the 2013 Samsung annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.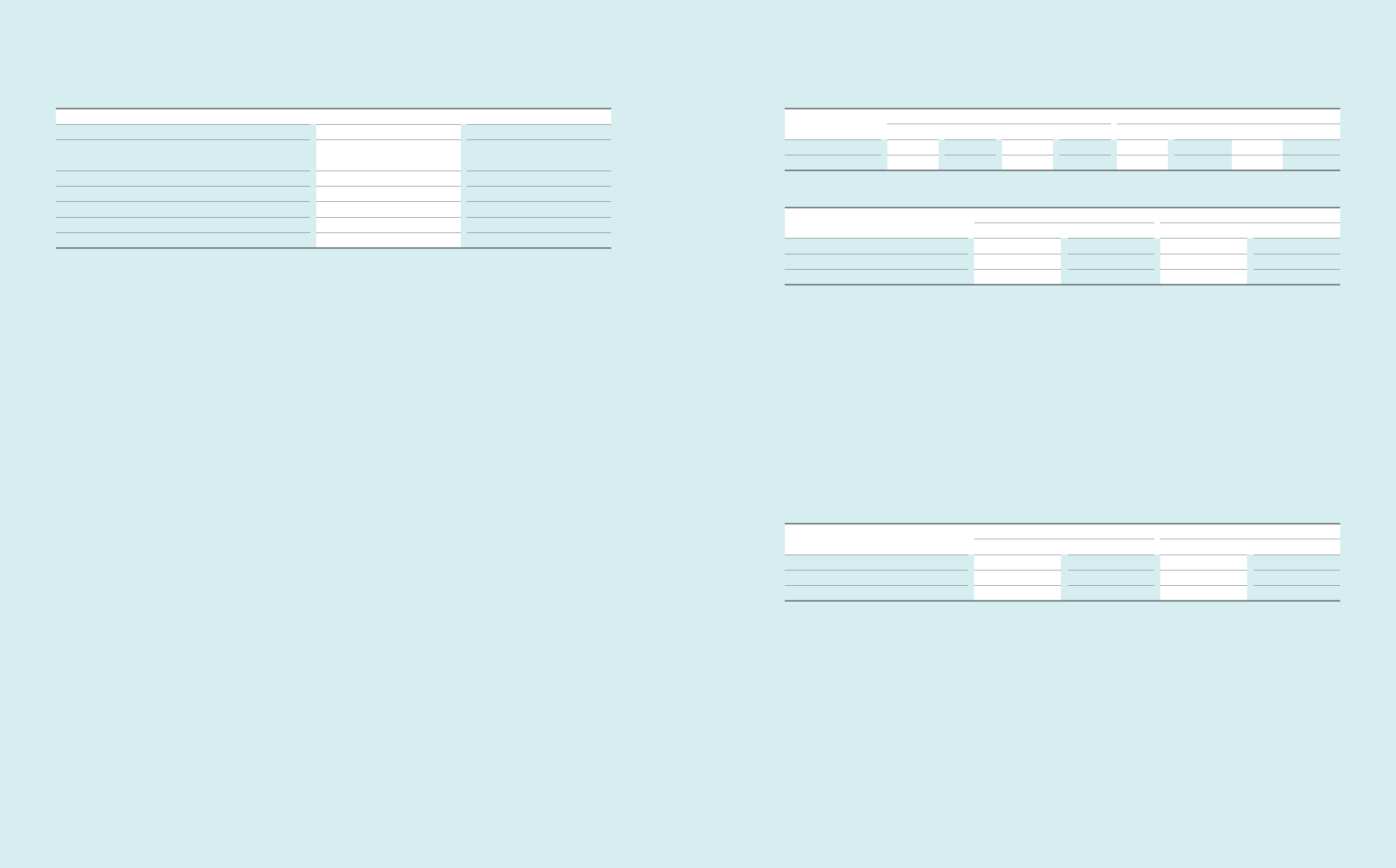
96 97
2013 SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS ANNUAL REPORT
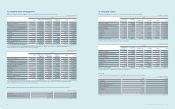
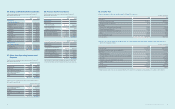
A summary of foreign assets and liabilities of the Company, presented in Korean won, as of December 31, 2013 and 2012 is as follows:
(In millions of Korean won)
2013 2012
USD EUR JPY Others USD EUR JPY Others
Financial assets ₩9,834,247 ₩1,253,898 ₩269,600 ₩1,581,019 ₩12,709,235 ₩1,085,390 ₩178,373 ₩1,577,076
Financial liabilities 9,664,814 1,071,174 1,172,213 191,674 9,550,081 978,953 1,142,081 214,639
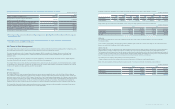
Foreign currency exposure to nancial assets and liabilities of a 5% currency rate change against the Korean won are presented below.
(In millions of Korean won)
2013 2012
Increase Decrease Increase Decrease
Financial assets ₩646,938 ₩(646,938) ₩777,504 ₩(777,504)
Financial liabilities (604,994) 604,994 (594,288) 594,288
Net effect 41,944 (41,944) 183,216 (183,216)
(2) Price risk
The Company’s investment portfolio consists of direct and indirect investments in equity securities classied as available-for-sale, which is in line with
the Company’s strategy.
As of December 31, 2013 and 2012, a price uctuation in relation to marketable equity securities by 1% would result in changes in other comprehensive income
(before income tax) of ₩43,933 million and ₩44,359 million, respectively.
(3) Interest rate risk
Risk of changes in interest rate for a oating interest rate nancial instrument is dened as the risk that the fair value of future cash ows of a nancial instrument
will uctuate because of changes in market interest rates. The Company is exposed to interest rate risk mainly through interest bearing liabilities and assets.
The Company’s position with regard to interest rate risk exposure is mainly driven by its debt obligations such as bonds, interest-bearing deposits and issuance of
receivables. In order to avoid interest rate risk, the Company maintains minimum external borrowings by facilitating cash pooling systems on a regional and global
basis. The Company manages exposed interest rate risk via periodic monitoring and handles risk factors on a timely basis.
The sensitivity risk of the Company is determined based on the following assumptions:
- Changes in market interest rates that could impact the interest income and expenses of oating interest rate nancial instruments
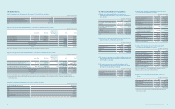
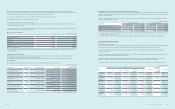
Based on the above assumption, changes to prot and net equity as a result of 1% increases in interest rate on borrowings are presented below:
(In millions of Korean won)
2013 2012
Increase Decrease Increase Decrease
Financial assets ₩46,025 ₩(46,025) ₩78,164 ₩(78,164)
Financial liabilities (22,942) 22,942 (21,864) 21,864
₩23,083 ₩(23,083) ₩56,300 ₩(56,300)
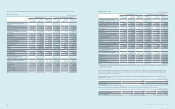
(B) Signicant transactions not affecting cash ows for the years ended December 31, 2013 and 2012, are as follows:
(In millions of Korean won)
2013 2012
Valuation of available-for-sale nancial assets ₩1,271,817 ₩1,185,256
Reclassication of construction in progress and machinery
in transit to property, plant and equipment 16,578,339 19,567,010
Reclassication of investment in associates to assets held for sale 2,716,733 -
Valuation of investments in associates and joint ventures 20,756 (350,491)
Non-cash consideration transferred for business combinations - (633,708)
Reclassication of current maturities of long-term borrowings 1,920,748 493,860
Reclassication of current maturities of bonds 505,277 505,356
(C) The Company reported cash receipts and payments arising from transactions occurring frequently and short-term nancial instruments, loans, and
borrowings on a net basis.
(D) Among the net cash used in investing activities for the year ended December 31, 2013, cash outows from business combination include
the acquisition of assets and liabilities of NeuroLogica.
32. Financial Risk Management
The Company’s nancial risk management focuses on minimizing market risk, credit risk, and liquidity risk arising from operating activities. To mitigate these risks,
the Company implements and operates a nancial risk policy and program that closely monitors and manages such risks.
The nance team mainly carries out the Company’s nancial risk management. With the cooperation of the Company’s divisions, domestic and foreign
subsidiaries, the nance team periodically measures, evaluates and hedges nancial risk and also establishes and implements the global nancial risk
management policy.
Also, nancial risk management ofcers are dispatched to the regional headquarters of each area including the United States of America, England, Singapore,
China, Japan, Brazil and Russia to operate the local nance center for global nancial risk management.
The Company’s nancial assets that are under nancial risk management are composed of cash and cash equivalents, short-term nancial instruments, available-
for-sale nancial assets, trade and other receivables and other nancial assets. The Company’s nancial liabilities under nancial risk management are composed
of trade and other payables, borrowings, debentures, and other nancial liabilities.
(A) Market risk
(1) Foreign exchange risk
The Company is exposed to foreign exchange risk arising from various currency exposures, primarily with respect to the United States of America, European
Union, South America, Japan and other Asian countries. Revenues and expenses arise from foreign currency transactions and exchange positions, and the most
widely used currencies are the US Dollar, EU’s EURO, Japanese Yen and Chinese Yuan. Foreign exchange risk management of the Company is carried out by both
SEC and its subsidiaries. To minimize foreign exchange risk arising from operating activities, the Company’s foreign exchange management policy requires normal
business transactions to be in local currency or for the cash-in currency to be matched up with the cash-out currency. The Company’s foreign exchange risk
management policy also denes foreign exchange risk, measuring period, controlling responsibilities, management procedures, hedging period and hedge ratio.
The Company limits all speculative foreign exchange transactions and operates a system to manage receivables and payables denominated in foreign currency.
It evaluates, manages and reports foreign currency exposures to receivables and payables.