Samsung 2013 Annual Report Download - page 29
Download and view the complete annual report
Please find page 29 of the 2013 Samsung annual report below. You can navigate through the pages in the report by either clicking on the pages listed below, or by using the keyword search tool below to find specific information within the annual report.
54 55
2013 SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS ANNUAL REPORT
(C) Changes in scope for consolidation
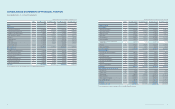
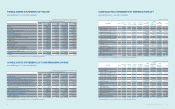
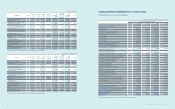
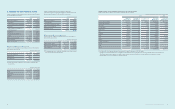
(1) Subsidiaries newly included in the consolidation for the year ended December 31, 2013:
Area Subsidiaries Description
America
NeuroLogica Acquisition of shares
Intellectual Keystone Technology (IKT) Incorporation
Europe Samsung Electronics Switzerland GmbH (SESG) Incorporation
Asia
Samsung Electronics Vietnam THAINGUYEN (SEVT) Incorporation
Samsung Electronics New Zealand (SENZ) Incorporation
China
Samsung Network R&D Center China-Shenzhen (SRC-Shenzhen) Incorporation
Samsung R&D Institute China-Xian (SRC-Xian) Incorporation
SEMES (Xian) Incorporation
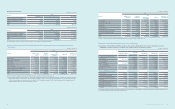
(2) Subsidiaries excluded from the consolidation for the year ended December 31, 2013:
Area Subsidiaries Description
Domestic
SECRON Merger
GES Merger
America
Newton Sub Merger
Samsung Medison America (SMUS) Liquidation
Deltapoint Cardiac Diagnostics (Deltapoint) Liquidation
Intellectual Keystone Technology (IKT) Disposal of shares
mSpot Merger
Samsung Electronics Corporativo (SEC) Merger
Samsung Medison Brasil (SMBR) Merger
Europe
Samsung Telecoms (UK) (STUK) Liquidation
Samsung LCD Netherlands R&D Center (SNRC) Disposal
Samsung LCD Netherlands R&D Center UK (SNRC (UK)) Disposal
General RF Modules Liquidation
Samsung Medison France (SMFR) Liquidation
Samsung Opto-Electronics GmbH (SOG) Liquidation
Samsung Medison Italia (SMIT) Liquidation
Asia
Samsung Electronics Philippines Manufacturing (SEPHIL) Disposal
Batino Realty Corporation (BRC) Disposal
TNP Small/Medium Size & Venture Enterprise Growth Promotion Investment
Limited Partnership (TSUNAMI) Reclassied into an associate from a subsidiary
China
Samsung LCD Netherlands R&D Center HK (SNRC (HK)) Disposal
Medison (Shanghai) (SMS2) Liquidation
The principal accounting policies applied in the preparation of these
consolidated nancial statements are set out below. These policies have
been consistently applied to all the years presented, unless otherwise
stated.
2.1 Basis of Presentation
The Company has prepared the consolidated nancial statements in
accordance with Korean International Financial Reporting Standards
(“K-IFRS”). International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS) have been
adopted by the Korean Accounting Standards Board as K-IFRS based on
standards and interpretations published by the International Accounting
Standards Board.
K-IFRS permits the use of critical accounting estimates in the preparation
of the nancial statements and requires management judgments in applying
accounting policies. Footnote 3 explains where more complex and higher
standards of judgment or critical assumptions and estimates are required.
2.2 Changes in Accounting Policy and Disclosures
(A) New and amended standards adopted by the Company
The Company applied the following amended and enacted standards for
the annual period beginning on January 1, 2013:
K-IFRS 1110, ‘Consolidated Financial Statements’
The standard introduces a single control concept and provides a specic
guidance for the control. The adoption of this standard does not have an
impact on consolidation scope in the consolidated nancial statements.
K-IFRS 1111, ‘Joint Arrangements’
The standard reects the substance of joint arrangements and focuses on
the rights and obligations of the parties to the joint arrangements rather than
on the legal forms of the arrangements. Joint arrangements are classied
into joint operations or joint ventures. The adoption of this standard does
not have a material impact on the consolidated nancial statements.
K-IFRS 1112, ‘Disclosure of Interests in Other Entities’
The standard provides disclosure requirements for all types of equity
investments in other entities including subsidiaries, joint arrangements,
associates and unconsolidated structured entities.
K-IFRS 1113, ‘Fair Value Measurement’
The standard provides a precise denition of fair value, and a single source
of fair value measurement and disclosure requirements for use across
K-IFRS. The adoption of this standard does not have a material impact on
the consolidated nancial statements.
K-IFRS 1027, ‘Separate Financial Statements’
The standard contains accounting treatments and requirements for
investments in subsidiaries, associates, and joint ventures relating only to
separate nancial statements of the Company.
(B) New and amended standards early adopted by the Company
Amendment to K-IFRS 1036, ‘Impairment of Assets’
The amendment reects the change in disclosure requirement of
the recoverable amount for each cash-generating unit including goodwill
or intangible assets with indenite useful lives. The amendment requires
disclosure of the recoverable amount only if the entity has recognized
impairment losses or reversals of impairment losses. For consistency,
the amendment also requires additional disclosures when the recoverable
amount of impaired assets is based on fair value less costs of disposal.
The amendment to this standard does not have a material impact on
the consolidated nancial statements.
Amendments to K-IFRS 1110, ‘Consolidated Financial Statements’, K-IFRS
1112, ‘Disclosure of Interests in Other Entities’, and K-IFRS 1027, ‘Separate
Financial Statements’
The amendments dene an investment entity and require a parent that is
an investment entity to measure its investments in particular subsidiaries at
fair value through prot or loss instead of presenting consolidated nancial
statements. These amendments do not apply to a parent of an investment
entity if the parent itself is not an investment entity. The amendments to
K-IFRS 1110 and K-IFRS 1027 do not have a material impact on
the consolidated nancial statements.
(C) New and amended standards not adopted by the Company
New standards, amendments and interpretations issued but not effective for
the nancial year beginning January 1, 2013 and not early adopted are as
follows:
Amendment to K-IFRS 1032, ‘Financial Instruments: Presentation’
The standard provides that the right to offset must not be contingent on
a future event and must be legally enforceable in all of circumstances;
and if an entity can settle amounts in a manner such that outcome is,
in effect, equivalent to net settlement, the entity will meet the net settlement
criterion. This amendment is effective for annual periods beginning on
or after January 1, 2014, and the Company is assessing the impact of
application of this amendment on its consolidated nancial statements.
Enactment of K-IFRIC Interpretations 2121, ‘Levies’
The interpretation requires that the liability to pay a levy is recognized when
the activity that triggers the payment of the levy occurs, as identied by
the legislation (the obligating event). This interpretation is effective for
annual periods beginning on or after January 1, 2014, with early adoption
permitted. The Company is assessing the impact of application of
this interpretation on its consolidated nancial statements.
2.3 Consolidation
The Company prepares annual consolidated nancial statements in
accordance with K-IFRS 1110, ‘Consolidated Financial Statements’
(A) Subsidiaries
Subsidiaries are all entities (including special purpose entities) over which
the Company has control. The Company controls the corresponding
investee when it is exposed, or has rights, to variable returns from its
involvement with the investee and has the ability to affect those returns
through its power over the investee. Consolidation of a subsidiary begins
from the date the Company obtains control of a subsidiary and ceases
when the Company loses control of the subsidiary.
2. Summary of Signicant
Accounting Policies